Transformers - working & applications (step up and step down) | A.C. | Physics | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis script explains the functioning of a transformer, a device that can step up or step down AC voltage. It operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where an alternating current in the primary coil generates a fluctuating magnetic field, inducing an electromotive force (EMF) in the secondary coil. The transformer's ability to adjust voltage is achieved by varying the number of turns in the coils. The script also touches on the transformer's role in wireless charging and electric power transmission, and clarifies that transformers do not work with DC power due to the lack of changing current.
Takeaways
- 🔌 Transformers are essential for converting voltage levels, allowing devices like microwaves and cell phones to operate from a common power supply.
- ⚡ The primary function of a transformer is to either step up (increase) or step down (decrease) the AC voltage, depending on the device's requirements.
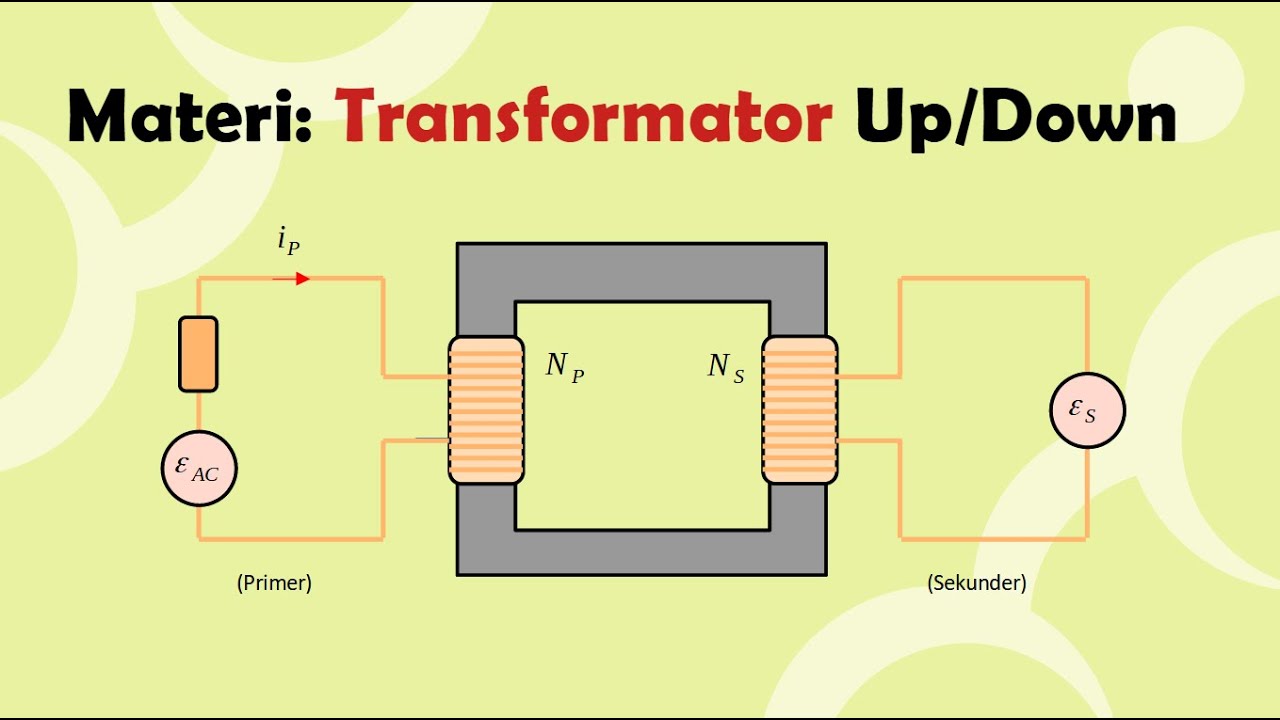
- 🧲 At the heart of a transformer are two coils, the primary coil connected to the power supply and the secondary coil connected to the device.
- 🌀 The alternating current in the primary coil generates a fluctuating magnetic field, which induces an electromotive force (EMF) in both the primary and secondary coils.
- ⚖️ The voltage transformation ratio between the primary and secondary coils is directly proportional to the number of turns in each coil.
- 🔝 A step-up transformer increases the voltage by having more turns in the secondary coil than in the primary, which is used in devices like microwave ovens.
- 🔽 A step-down transformer reduces the voltage by having fewer turns in the secondary coil, suitable for devices like cell phones.
- 🔄 Transformers only work with AC (alternating current) because they rely on the changing magnetic field induced by the fluctuating current.
- 🔗 The principle of electromagnetic induction, discovered by Michael Faraday, is the foundation of how transformers operate.
- 🤔 Transformers enable wireless charging by utilizing the same principle of electromagnetic induction, where the phone acts as the secondary coil.
- 🌐 Transformers are crucial for efficient power transmission, ensuring that electricity can be sent over long distances with minimal loss.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a transformer?
-A transformer's primary function is to either step up (increase) or step down (decrease) the AC voltage, allowing it to be suitable for different devices.
How does a transformer work?
-A transformer works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It uses two coils, the primary and secondary, to transfer energy through a changing magnetic field without direct electrical connection.
What causes the voltage to change in a transformer?
-The voltage change in a transformer is caused by the varying magnetic field created by the alternating current in the primary coil, which induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the secondary coil.
Why can't a transformer be used with a DC supply?
-Transformers cannot be used with DC because they rely on the changing magnetic field created by alternating current; DC does not produce the necessary changing magnetic field for induction to occur.
What is the relationship between the number of turns in the primary and secondary coils and the voltage transformation?
-The voltage transformation in a transformer is directly proportional to the ratio of the number of turns in the primary to the secondary coils. If the secondary has more turns, it steps up the voltage, and if it has fewer turns, it steps down the voltage.
How does a step-up transformer differ from a step-down transformer?
-A step-up transformer has a secondary coil with more turns than the primary coil, increasing the voltage, while a step-down transformer has a secondary coil with fewer turns, decreasing the voltage.
Why don't cell phones blow up when connected to a 230V supply?
-Cell phones don't blow up because they use a step-down transformer to convert the high voltage from the mains supply to a much lower voltage suitable for charging the phone.
What is the role of a ferromagnetic core in a transformer?
-A ferromagnetic core in a transformer helps to concentrate the magnetic field lines from the primary coil to the secondary coil, ensuring that the flux through each coil is the same, which is crucial for maintaining the relationship between voltage and the number of turns.
How does the transformer principle apply to wireless charging?
-Wireless charging uses the transformer principle by having a primary coil in the charging pad and a secondary coil in the phone. The primary coil induces a current in the secondary coil, which then charges the phone without a direct electrical connection.
Why are transformers essential for electric power transmission?
-Transformers are essential for electric power transmission because they allow the voltage to be stepped up for efficient long-distance transmission and stepped down for safe use by consumers, making the power grid feasible and practical.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)