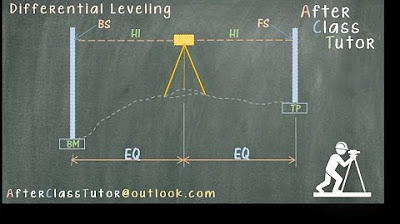
Differential Leveling Part 2 of 2
Summary
TLDRThis instructional video demonstrates how to calculate elevation at various points using differential leveling. It begins by determining the elevation at station 0+00 using the given benchmark elevation, back sight, and fore sight. The process is repeated for subsequent stations, with the video also showcasing a shortcut for finding the elevation at station 2+00 by using the height of the instrument and subtracting the fore sight. The video concludes with a reminder to subscribe and engage with the content.
Takeaways
- 📏 The video demonstrates how to determine elevation at various points using differential leveling.
- 🔢 The process starts by calculating the elevation at station 0+000 using the formula: Elevation at Benchmark + Back Sight at Benchmark - Fore Sight at station.
- ➡️ The elevation at subsequent stations is found by adding or subtracting the back and fore sights from the previous station's elevation.
- 📍 A turning point is introduced, and its elevation is calculated similarly by considering the instrument height and fore sight.
- 🔄 The method involves iterative steps of adding back sights and subtracting fore sights to find elevations at different stations.
- 📉 The script provides a shortcut for calculating the elevation at station 2+000 without recalculating from the beginning.
- 📊 The shortcut involves sketching a diagram and using the known elevation at the Benchmark and back sight to determine instrument height.
- 📐 The height of the instrument is used to find the elevation at turning points and subsequent stations.
- 🔢 The final elevation at station 2+000 is calculated to be 102.8 using the shortcut method.
- 🎓 The video concludes by encouraging viewers to subscribe and leave comments or questions for further engagement.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of the video script?
-The main purpose of the video script is to explain how to determine the elevation at different points using differential leveling techniques.
What is the first step in determining the elevation at station 0+000?
-The first step is to use the equation that involves the elevation at the Benchmark, the back side at the Benchmark, and the foresight at station 0+000.
What is the equation used to find the elevation at station 0+000?
-The equation used is Elevation at 0+000 = Elevation at Benchmark + Back side at Benchmark - Foresight at station 0+000.
What is the elevation at station 0+000 according to the script?
-The elevation at station 0+000 is calculated to be 106.6.
How is the elevation at station 0+50 determined?
-The elevation at station 0+50 is determined by taking the elevation at the Benchmark and adjusting for the back side at the Benchmark and the foresight at station 0+50.
What is the process to find the elevation at the Turning Point 1?
-The elevation at the Turning Point 1 is found by adding the back side at the Benchmark to the elevation at the Benchmark and then subtracting the foresight at the Turning Point.
What is the significance of the height of the instrument in the leveling process?
-The height of the instrument is significant as it helps determine the elevation at different points by being added to the elevation at one point and then subtracting the foresight at the next point.
How is the elevation at Station 2+000 calculated using the height of the instrument?
-The elevation at Station 2+000 is calculated by taking the height of the instrument at the Turning Point and subtracting the foresight at Station 2+000.
What is the final elevation at Station 2+000 as per the script?
-The final elevation at Station 2+000 is 102.8.
Why is sketching a diagram helpful in solving the leveling problem?
-Sketching a diagram is helpful as it visually represents the known elevations and backsight and foresight measurements, aiding in understanding the relationships between different points and simplifying the calculation process.
What is the benefit of using the first equation for calculating the elevation at Station 2+000 directly?
-Using the first equation directly for Station 2+000 simplifies the process by allowing the calculation to be done in one step without needing to calculate intermediate elevations.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)