pH DETERMINATION
Summary
TLDRThe video explores the principles of pH determination and its significance in biological processes. It explains the properties of acids and bases, referencing the Bronsted-Lowry definition, and details how substances interact with pH indicators like litmus paper and chemicals such as phenolphthalein. The role of acids and bases in reactions is highlighted, along with examples like hydrochloric acid and ammonia. Additionally, the video covers how the body's regulation of pH involves the lungs and kidneys, emphasizing their impact on maintaining blood pH through carbon dioxide and bicarbonate management.
Takeaways
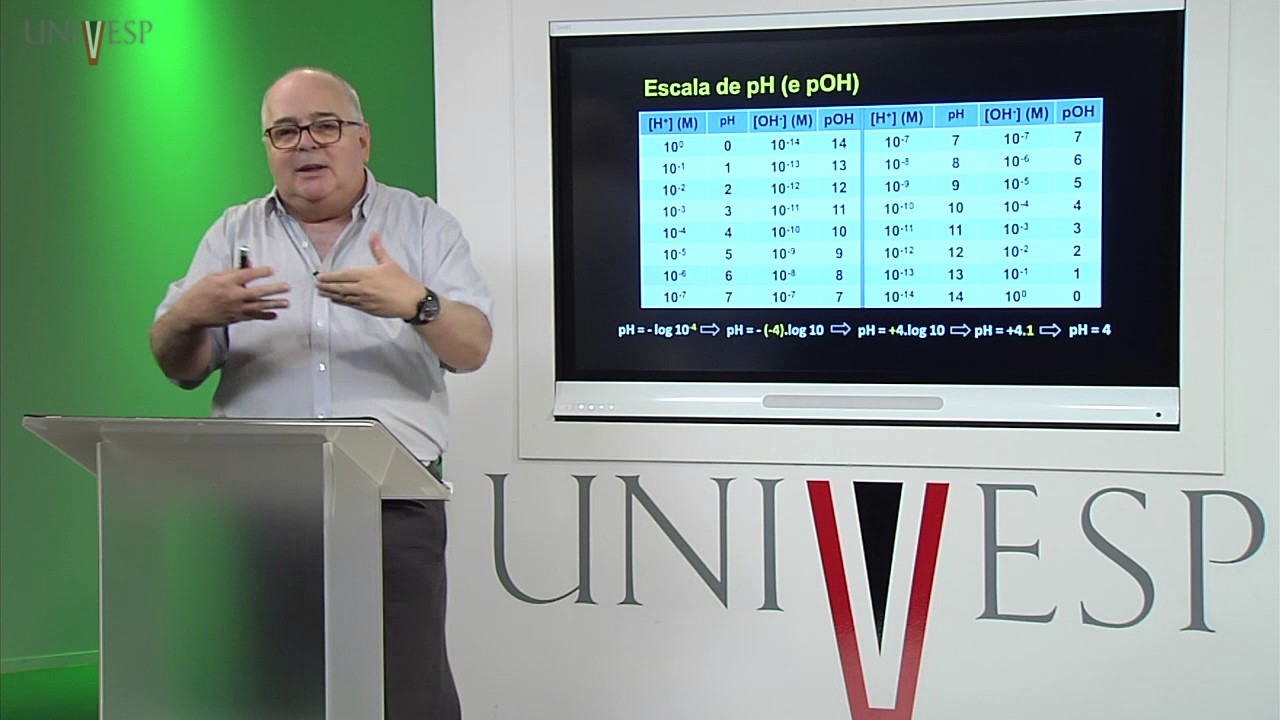
- 🔍 The pH scale is crucial for determining the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, with values ranging from 0 (strongly acidic) to 14 (strongly alkaline), and a neutral pH of 7.
- 🌟 Hydronium ion concentration is a key factor affecting biological processes and is represented by pH levels.
- 🍋 Acids are substances that donate hydrogen ions (protons) to other substances, exemplified by hydrochloric acid forming hydronium ions when dissolved in water.
- 🧼 Bases, according to Bronsted-Lowry, are substances that accept hydrogen ions from acids, like ammonia which forms ammonium ions.
- 🌈 Litmus paper is a simple indicator used to test for acids and bases; blue litmus paper turns red in the presence of acids, and red litmus paper turns blue with bases.
- 🌡 The pH scale is a logarithmic scale that indicates the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution, with each whole pH change representing a tenfold change in acidity or alkalinity.
- 🌿 Chemical indicators like phenol red, methyl red, and bromothymol blue are used in laboratories to identify the acidity or alkalinity of substances.
- 🩺 Normal blood pH is maintained between 7.35 and 7.45, with deviations indicating acidemia or alkalemia, and more severe conditions known as acidosis or alkalosis.
- 🫁 The lungs play a critical role in regulating acid-base balance by controlling the amount of carbon dioxide, an acidic gas, through the rate and depth of breathing.
- 💧 Kidneys help maintain blood pH by regulating bicarbonate levels, which are slightly alkaline, and can reabsorb bicarbonate to buffer excess hydrogen ions and normalize blood pH.
Q & A
What is the significance of hydronium ion concentration in biological processes?
-Hydronium ion concentration, represented by pH, greatly affects all biological processes as it indicates the acidity or alkalinity of the environment.
How is pH used to determine if a substance is acidic or basic?
-pH is a scale from 0 to 14 where a pH less than 7 indicates an acidic substance, a pH greater than 7 indicates a basic substance, and a pH of 7 is neutral.
What is the role of hydrochloric acid in the context of pH?
-Hydrochloric acid donates a proton to water when dissolved, forming hydronium ions, and has a pH level less than seven, indicating it is an acid.
What is the definition of a base according to the Bronsted-Lowry definition?
-A base is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions (protons) from acids.
How does ammonia demonstrate its basic nature?
-Ammonia accepts a proton to form the ammonium ion, showing its basic nature.
What are the characteristics of acids that are commonly associated with them?
-Acids have a sour taste, can change the color of blue litmus paper to red, react with metals to produce hydrogen gas, and can react with bases to form water and ionic compounds.
What is the role of bases in a water solution?
-Bases are capable of liberating hydroxide ions in a water solution.
How do chemical indicators like phenol red, methyl red, and bromothymol blue help in identifying substances as acids or bases?
-These indicators change color in the presence of acids or bases, with methyl red turning red or pink in acids, bromothymol blue turning blue in bases, and phenol red showing different colors for acidic, neutral, or basic solutions.
What is the normal pH range for human blood?
-The normal pH range for human blood is 7.35 to 7.45.
How do the lungs and kidneys play a role in regulating acid-base balance?
-The lungs regulate by adjusting the rate and depth of breathing to control carbon dioxide levels, while the kidneys regulate by absorbing or generating bicarbonate ions to maintain blood pH.
What happens if the blood pH is less than 7.35 or greater than 7.45?
-If the blood pH is less than 7.35, it is acidic and called acidemia; if greater than 7.45, it is alkaline and called alkalosis.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)