CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY | SCIENCE 10 - Week 8 Part I
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the concept of continental drift, highlighting Alfred Wegener's theory that all continents were once part of a supercontinent, Pangaea. Evidence supporting this includes the fitting shapes of continents like South America and Africa, unique fossil distributions across now-separated landmasses, matching rock formations, glacial striations in tropical regions, and coal deposits suggesting past tropical climates. The video aims to enhance understanding of Earth's geological history and the dynamic nature of its landmasses.
Takeaways
- 🌐 The concept of continental drift suggests that the Earth's continents were once part of a single landmass.
- 🧩 Alfred Wegener's theory of continental drift was initially based on the observation that the continents' shapes fit together like a puzzle.
- 📚 Wegener's book, 'The Origin of Continents and Oceans', laid out the foundational ideas for the continental drift theory.
- 🌍 Pangea, meaning 'all earth', was the proposed supercontinent that existed around 200 million years ago, surrounded by the mega ocean, Panthalassa.
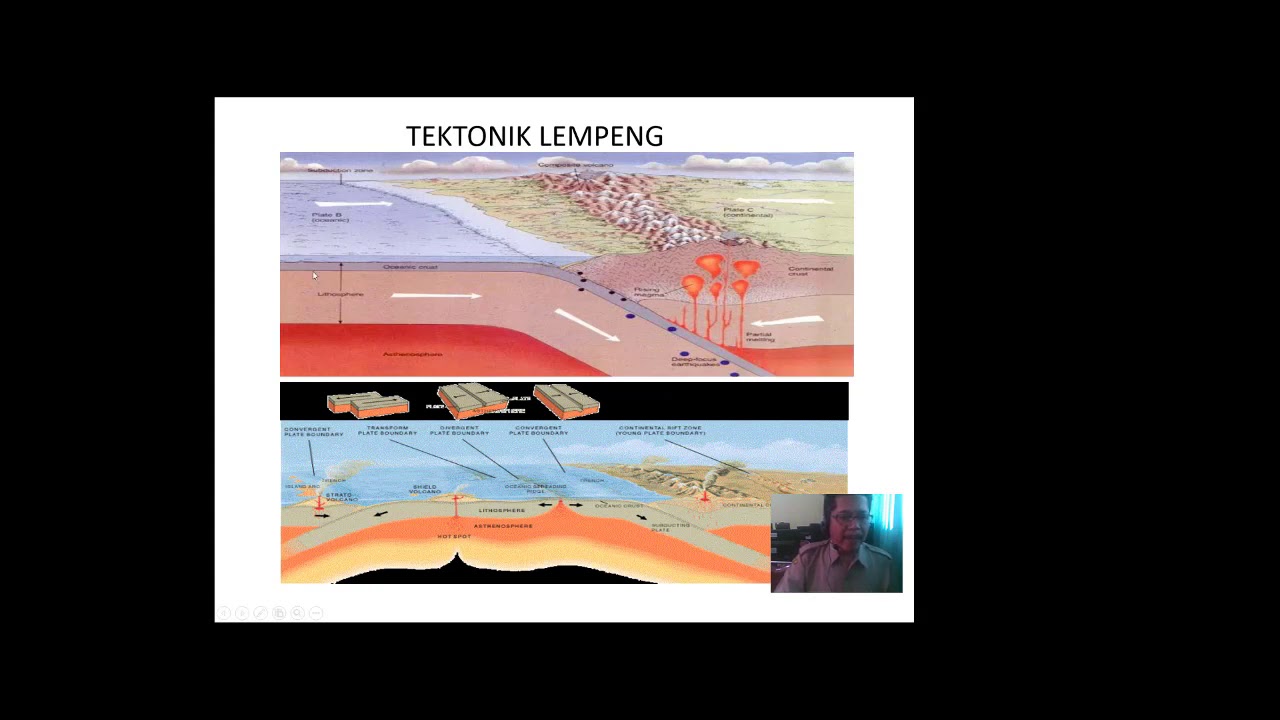
- 🔍 The theory of plate tectonics, published in 1965, provided the mechanism that explained how continents moved, thus supporting Wegener's theory.
- 🌿 Fossil evidence, such as the distribution of Glossopteris plants and Mesosaurus reptiles, supports the idea that continents were once connected.
- 🏔 Rock formations, like the Cape Mountains in South America and Africa, show alignment that suggests these continents were once a single landmass.
- ❄️ Glacial striations found in regions like South America and Africa, which are now tropical, indicate they were once in colder climates near the South Pole.
- 🌿 Coal deposits in Antarctica and other continents suggest that these areas once had a much warmer climate and were located closer to the equator.
- 🔬 The lesson concludes that the evidence from fossils, rock formations, glacial striations, and coal deposits collectively supports the continental drift theory.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the discussion in the provided transcript?
-The main focus of the discussion is the learning competency related to plate movement, specifically the continental drift theory and the evidences that support it.
What are the three key takeaways from the lesson on continental drift theory?
-The three key takeaways are: 1) Describing the continental drift theory, 2) Tracing the geologic formation of continents within the continental drift theory, and 3) Explaining the evidences that support the continental drift theory.
What observation about the world map led to the development of the continental drift theory?
-The observation that the shapes of landmasses seem to fit together like a puzzle, particularly the continents of South America and Africa, led to the development of the continental drift theory.
Who proposed the continental drift theory and in which book did he lay out his case?
-Alfred Wegener proposed the continental drift theory and he laid out his case in his book 'The Origin of Continents and Oceans'.
What was the name of the supercontinent that Alfred Wegener proposed existed 200 million years ago?
-The supercontinent that Alfred Wegener proposed existed 200 million years ago was named Pangea, which means 'all earth'.
What were the two smaller supercontinents that Pangea broke into according to Wegener's theory?
-According to Wegener's theory, Pangea broke into two smaller supercontinents: Laurasia in the north and Gondwanaland in the south.
What are the four main lines of evidence that support the continental drift theory mentioned in the transcript?
-The four main lines of evidence supporting the continental drift theory mentioned are: 1) Continental jigsaw puzzle, 2) Fossil evidence, 3) Rock formations, and 4) Glacial striations.
How do the fossil evidences, such as Mesosaurus and Glossopteris, support the continental drift theory?
-Fossil evidences like Mesosaurus and Glossopteris, which are found in continents now separated by oceans, support the continental drift theory by indicating that these continents were once connected.
What do glacial striations indicate about the past geographical positions of South America and Africa?
-Glacial striations in the present-day tropical rainforests of South America and Africa indicate that these regions were once located in colder areas, such as near the South Pole, supporting the idea that they were part of a connected landmass.
How do coal deposits in Antarctica suggest past climatic and geographical changes?
-The presence of coal deposits in Antarctica, which currently cannot sustain substantial life, suggests that it once experienced a tropical climate and was positioned closer to the equator, indicating past climatic and geographical changes.
What does the alignment of rock formations in Africa and South America suggest about the past?
-The alignment of rock formations in Africa and South America suggests that these continents were once part of a single, continuous landmass, supporting the continental drift theory.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Plate Tectonics

Continental Drift Theory - Alfred Wegener | Pangea | Gondwanaland

Evidences Of Plate Tectonics,Continental Drift,Seafloor Spreading,Magnetic Reversal,Grade 10 Science
IPS KELAS 9 MATERI TEORI TERBENTUKNYA BENUA

Araling Panlipunan 8 MATATAG Q1 Week 1-2 Mga Teorya sa Pagkakabuo ng mga Kontinente with PPT and DLL

Module 5 Part 1 - Evidence of Plate Movement: Continental Drift Theory
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
