Kurikulum Merdeka Rangkuman Materi IPA Kelas 10 Bab 1 Pengukuran dalam Kegiatan Kerja Ilmiah
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the essentials of scientific measurement, covering various measuring tools, primary and derived dimensions, and the international system of units. It explains the importance of significant figures and scientific notation in data processing, introduces the use of rulers and micrometers with their inherent uncertainties, and emphasizes the necessity of repeated measurements to reduce errors. The script concludes with a reminder to engage with the content through likes, comments, and subscriptions.
Takeaways
- 📏 The video discusses various measuring instruments used in daily life, depending on the object being measured and the desired accuracy.
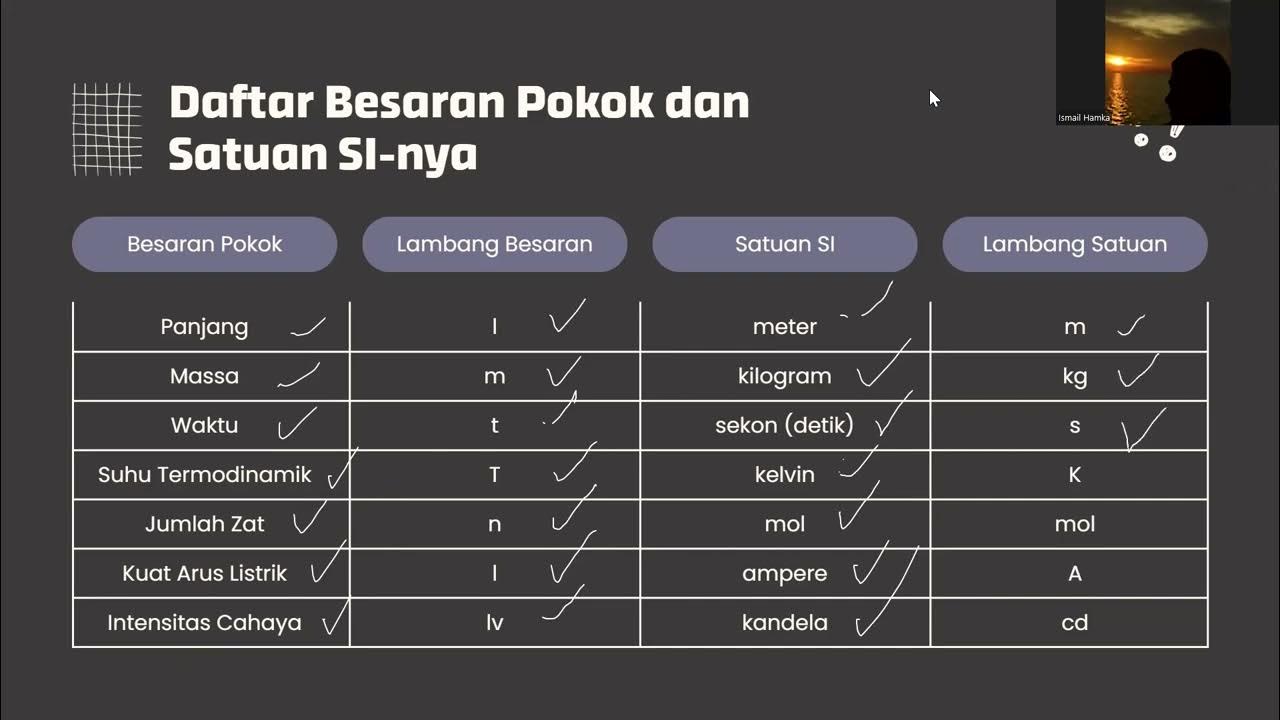
- 🔍 It differentiates between 'basic quantities' and 'derived quantities', with basic quantities having established units and derived quantities being composed of multiple basic units.
- 📐 The script introduces the concept of a 'system of units', which is an internationally agreed standard used universally, also known as international units.
- 📏 An example of an international unit is given, where 'length' is represented by the symbol 'l' and its international unit is 'm' (meter).
- 📏 The concept of 'dimensions' is explained, which is the way derived quantities are organized based on basic quantities, using specific symbols in parentheses.
- 📏 The script provides a detailed explanation of a 'vernier caliper', including its parts and the potential measurement errors associated with its use.
- 🔢 The importance of 'significant figures' and 'scientific notation' in calculations is highlighted, emphasizing the need for rounding and proper data presentation.
- ⚖️ The formula for 'uncertainty in measurement' is introduced, which is half the smallest scale value, and its inclusion in final results to account for potential errors.
- 🔬 The video emphasizes the importance of repeating measurements to reduce uncertainty, suggesting at least five measurements to calculate the standard deviation.
- 🔧 The script explains the parts of a 'micrometer screw gauge' and its use in precise measurements, similar to the vernier caliper with inherent uncertainties.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video script?
-The main topic discussed in the video script is the summary of the IPA (Physics) material for 10th-grade class 1, focusing on measurement in scientific activities.
What are some examples of measuring instruments mentioned in the script?
-Examples of measuring instruments mentioned include scales, rulers, stopwatches, thermometers, beakers, and graduated cylinders.
What are the two categories of measurements according to the script?
-The two categories of measurements are 'basic measurements' and 'derived measurements'.
What is meant by 'basic measurements' in the context of the script?
-'Basic measurements' refer to measurements whose units have been established, serving as the foundation for other measurements.
What is the role of derived measurements in the script's discussion?
-Derived measurements are those whose units are composed of several basic measurement units.
What is a 'system of units' as discussed in the script?
-A 'system of units' is an agreed-upon standard used universally by the scientific community, also known as international units.
Can you provide an example of an international unit mentioned in the script?
-An example of an international unit mentioned in the script is the meter (m), which is the international unit for length.
What is a 'dimension' in the context of the script?
-A 'dimension' is a way of organizing derived measurements based on their basic measurements, represented by symbols in parentheses.
What are the parts of a vernier caliper mentioned in the script?
-The parts of a vernier caliper mentioned include the thimble, frame, lock nut, sleeve, and ratchet.
What is the concept of 'uncertainty' in measurements as discussed in the script?
-The 'uncertainty' in measurements refers to the potential error in the measurement process due to inaccuracy or carelessness, and it is quantified by the formula Δx = (1/2) * smallest scale value.
How should the final result of a measurement be presented according to the script?
-The final result of a measurement should be presented as the value plus or minus the uncertainty, for example, X ± Δx.
What is the significance of the 'significant figures' rule in measurement?
-The 'significant figures' rule is a guideline for rounding and writing results of data processing to ensure accuracy and consistency with the precision of the measuring instrument used.
How should repeated measurements be approached to account for human error?
-To account for human error, measurements should not be done just once but at least five times, and the standard deviation formula can be used to calculate the uncertainty of repeated measurements.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)