How a Car Engine Works
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Jake O'Neal of Animagraffs explains the inner workings of a car engine through the four-stroke cycle: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. He details the role of pistons, crankshaft, valves, and camshafts, and discusses auxiliary systems like air intake, fuel delivery, cooling, electrical ignition, and oil lubrication. The video also touches on the importance of the exhaust system and its components, offering a comprehensive look at the engine's operation.
Takeaways
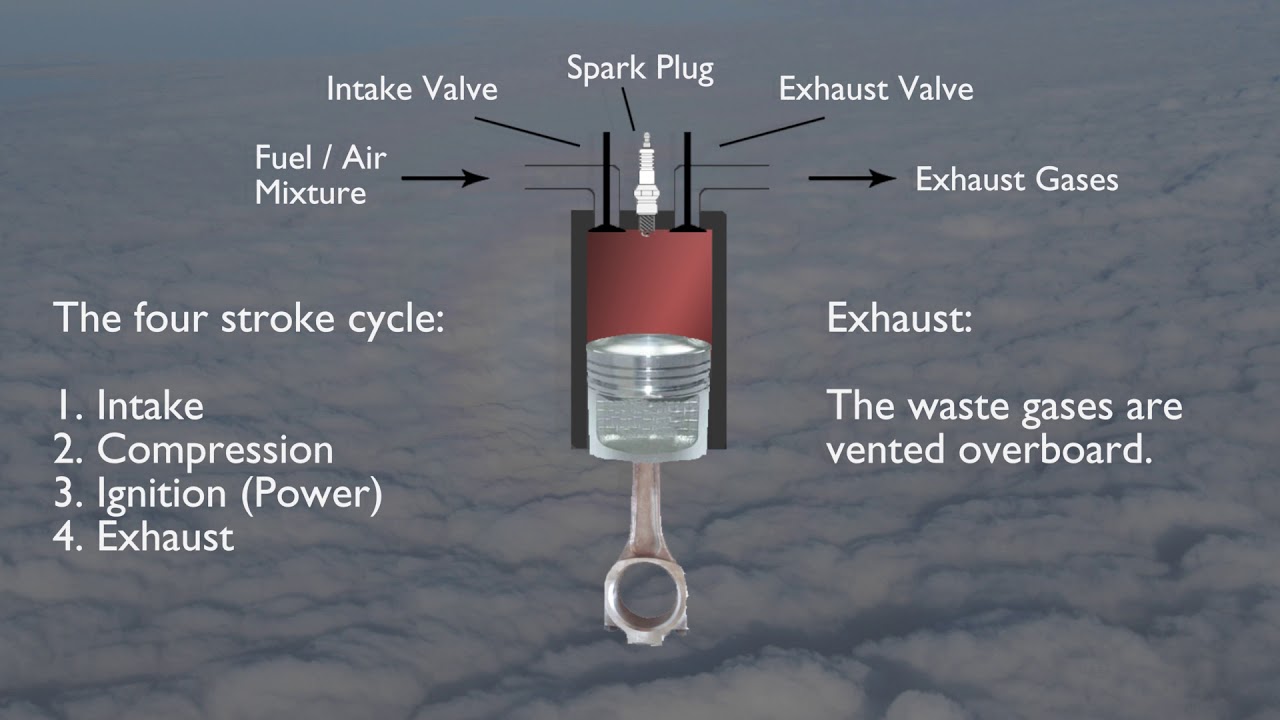
- 🔧 A car engine operates on a four-stroke cycle: intake, compression, power, and exhaust.
- 🌀 The piston is the powerhouse of the engine, moving through strokes to facilitate the combustion process.
- 🔄 The intake stroke draws an air-fuel mixture into the cylinder, while the compression stroke squeezes it for more power.
- 🔥 The power stroke is where the spark ignites the mixture, forcing the piston down and transferring energy to the crankshaft.
- ⏳ The exhaust stroke expels the spent gases, completing the cycle and making way for a fresh intake.
- 🔄 Multiple pistons fire in a specific order for smooth power delivery, coordinated by the camshaft and timing belt or chain.
- 💡 The crankshaft is pivotal in translating piston power into rotational energy for the vehicle.
- 🏗️ The engine block houses the crankshaft and cylinders, while the cylinder head contains valves, ports, and cams.
- 🔗 The flywheel connects the engine to the transmission and is where the starter engages the system.
- 🔄 Different cylinder configurations exist, such as inline-four, V6, or V8, but they all follow the basic engine operation principles.
- 🌡️ Cooling systems are essential to maintain engine temperature within safe limits, using coolant and a radiator.
- 🔌 The electrical system includes spark plugs for ignition, the ECM for controlling engine functions, and the alternator for power generation.
- 🛢️ Motor oil plays a crucial role in lubrication, cleaning, and cooling, with the oil pump and filter ensuring its proper circulation.
- 🌪️ The exhaust system collects and treats engine gases, reducing noise and harmful emissions through the muffler and catalytic converter.
Q & A
What is the fundamental unit of power in a car engine?
-The fundamental unit of power in a car engine is a single piston, which is the powerhouse of the engine.
What is the four-stroke cycle in a car engine?
-The four-stroke cycle in a car engine includes intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes. It's the process of drawing in the air-fuel mixture, compressing it, igniting it to generate power, and then expelling the exhaust gases.
How does the intake stroke work in a car engine?
-During the intake stroke, the piston descends, drawing an air-fuel mixture into the cylinder through the intake port with both intake valves open.
What is the purpose of the compression stroke in a car engine?
-The compression stroke is when the piston moves up with all valves closed, compressing the fuel and air mixture to increase the power of combustion.
What happens during the power stroke of the engine cycle?
-During the power stroke, an electrical spark ignites the compressed fuel and air mixture, forcing the piston down and transferring this power to the crankshaft via a connecting rod.
What is the role of the exhaust stroke in a car engine?
-The exhaust stroke pushes the spent air-fuel mixture out of the cylinder through open exhaust valves and the exhaust port as the piston moves up.
Why is a firing order important in a multi-piston engine?
-A firing order is important for smooth power delivery, ensuring that pistons take turns firing and that the engine operates efficiently and evenly.
What is the function of the camshaft in an engine?
-The camshaft has specially shaped cams that push spring-loaded valves open in turn, controlling the timing of the intake and exhaust valves.
What does RPM stand for in the context of engines?
-RPM stands for revolutions per minute, which is a measure of how many times the crankshaft completes a full rotation in one minute.
How does the cooling system of an engine work?
-The cooling system circulates a special liquid called 'anti-freeze' around the cylinders and through the cylinder heads to maintain safe operating temperatures. The heated coolant then passes through the radiator, where it is cooled by air before being recirculated.
What is the role of the spark plug in the combustion process?
-The spark plug delivers the electrical spark needed to ignite the fuel-air mixture for combustion, with the spark jumping between the conductive surfaces of the metal core and the outer casing.
How does the oil system contribute to engine operation?
-The oil system lubricates engine parts, cleans them, prevents corrosion, improves sealing, and cools the engine by carrying heat away from moving parts. It involves oil galleries, an oil pump, and an oil filter to ensure clean and pressurized oil flow.
What is the purpose of the catalytic converter in the exhaust system?
-The catalytic converter captures toxic chemicals in the engine exhaust, helping to reduce harmful emissions before the exhaust gases are released through the muffler.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

How Car Engine Works Animation | Car Engine Explained | Engine Animation 4 stroke

How Does A Small Engine Work? 2 & 4 Cycle

Bagaimana Mesin Sepeda Motor 4 Tak Bekerja? - Cara Kerja Motor 4 Tak

How car engine works? / 4 stroke internal combustion engine (3D animation)

El ciclo diésel (cuatro tiempos)
How a Reciprocating Engine Works
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
