FISIKA VEKTOR KELAS XI [FASE F] PART 2 - KURIKULUM MERDEKA
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses vector components, focusing on identifying vector components along the x and y axes and determining the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector. It explains how to decompose a vector into its components based on the angle with respect to the axes and provides examples to calculate the resultant force and its direction.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video discusses the second part of vector material, focusing on vector components and their identification along the x and y axes.
- 🔍 The objective is to identify the vector components in the x and y directions and to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector.
- 📐 A vector can be decomposed into components based on its magnitude and direction, which are then analyzed in relation to the x and y axes.
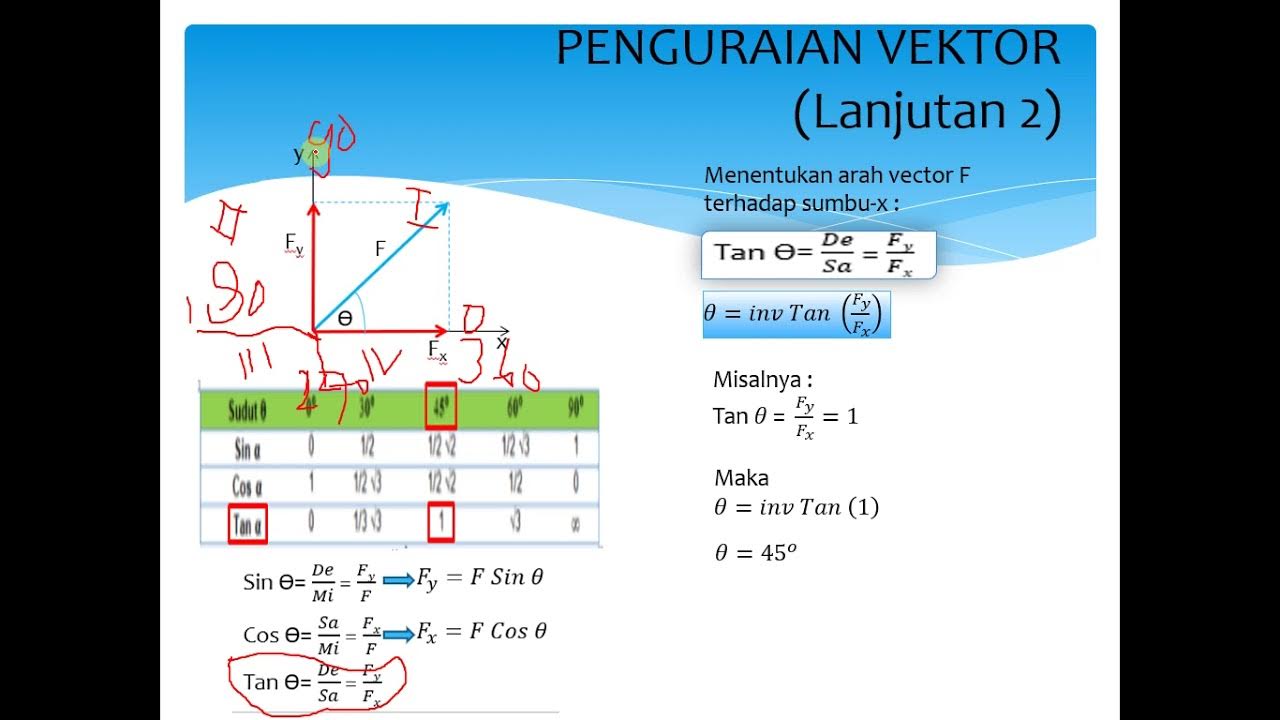
- 🧭 The script explains that the force vector F has components acting along the x-axis (FX) and y-axis (FY), determined by the angle (Teta) it makes with the axes.
- 📈 The magnitude of FX is given by F multiplied by the cosine of the angle (F * cos(Teta)), while FY is given by F multiplied by the sine of the angle (F * sin(Teta)).
- 📉 The importance of understanding the angle's proximity to the axes is emphasized, as it determines whether the component is calculated using cosine or sine.
- 🔄 The script provides examples to illustrate how to calculate the components of a vector when the angle is different from the standard positions.
- 📝 The process of finding the resultant vector involves adding the components along the x and y axes, considering their directions (positive or negative).
- 🔢 The magnitude of the resultant vector is calculated using the formula R = √(FX² + FY²), and its direction is found using the tangent of the angle (tan(Teta) = FY/FX).
- 📚 The video script includes a step-by-step guide on how to calculate the resultant vector's magnitude and direction using given vector components.
- 👨🏫 The explanation is designed to help viewers understand the fundamental concepts of vector components and their application in determining the resultant vector.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video?
-The main topic discussed in the video is the components of vectors, specifically how to identify vector components along the x and y axes and how to determine the magnitude and direction of vector components.
What are the objectives of the learning material presented in the video?
-The objectives are to identify vector components along the x and y axes and to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector.
How can a vector be decomposed into components?
-A vector can be decomposed into components by projecting it onto the x and y axes. Each component represents the force or effect acting along that specific axis.
What is the relationship between the angle of a vector and its components?
-The components of a vector are determined by the angle it makes with the axes. If the angle is close to the x-axis, the component along the x-axis (Fx) is given by the cosine of the angle, and the component along the y-axis (Fy) is given by the sine of the angle.
How is the magnitude of the resultant vector calculated?
-The magnitude of the resultant vector is calculated using the formula R = √(Fx² + Fy²), where Fx and Fy are the components of the vector along the x and y axes, respectively.
What is the formula used to determine the direction of the resultant vector?
-The direction of the resultant vector is determined using the formula tan(θ) = Fy/Fx, where θ is the angle of the resultant vector with respect to the x-axis.
What is the significance of the angle in determining the components of a vector?
-The angle is crucial in determining the components of a vector because it dictates the distribution of the vector's magnitude along the x and y axes. The closer the angle is to an axis, the greater the component along that axis.
How does the video explain the process of finding the resultant force along the x-axis?
-The video explains that to find the resultant force along the x-axis, you sum the components of the individual vectors along the x-axis, taking into account their signs (positive or negative) based on their direction.
What is an example given in the video to illustrate the calculation of the resultant vector?
-The video provides an example with three vectors (F1, F2, F3) acting along the x and y axes. It demonstrates how to calculate the components of each vector along the axes and then sum these components to find the resultant vector.
How does the video simplify the process of determining the direction of the resultant vector?
-The video simplifies the process by suggesting that if the resultant force along the x-axis (Fx) is positive and the resultant force along the y-axis (Fy) is negative, the direction of the resultant vector will be from the positive x-axis towards the negative y-axis.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)