What is ATP?
Summary
TLDRThis video from the Amoeba Sisters explains the significance of ATP, often seen in science materials as an 'energy currency.' ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is a nucleotide derivative crucial for various cellular processes, including active transport, muscle contraction, and cell signaling. The video delves into ATP's structure, consisting of adenine, ribose, and three phosphates, and how it's generated through processes like aerobic and anaerobic respiration. It highlights the ATP cycle, where ATP is hydrolyzed to release energy, which can then be used for essential cellular functions, emphasizing the importance of this molecule in biology.
Takeaways
- 🔬 ATP is a nucleotide derivative and a crucial molecule in cellular processes, often depicted as an energy source in scientific illustrations.
- 🌟 ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate, which includes a nitrogenous base (adenine), a sugar (ribose), and three phosphate groups.
- 💡 Students often consider ATP as an 'energy currency' due to its role in facilitating various cellular activities.
- 🚀 ATP is essential for processes such as active transport against concentration gradients and muscle contraction involving actin and myosin.
- 📢 ATP plays a critical role in cell signaling, enabling communication between cells.
- 🌱 ATP generation varies among organisms, with processes like aerobic and anaerobic respiration, and fermentation being common methods.
- 🔄 The ATP cycle involves ATP being hydrolyzed to ADP, releasing energy, and then being regenerated through cellular respiration or similar processes.
- 🔄 The hydrolysis of ATP is an exergonic reaction, meaning it releases free energy that can be harnessed for cellular work.
- 🔄 The energy release from ATP hydrolysis is often coupled with endergonic processes, such as active transport of molecules against concentration gradients.
- 🔄 Phosphorylation, the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to another molecule, is a key mechanism in activating proteins for specific cellular functions.
- 🌐 ATP's significance extends to a wide range of biological phenomena, from cell division to protein synthesis, emphasizing its fundamental role in life.
Q & A
What is ATP and why is it significant in cellular processes?
-ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is a nucleotide derivative that is crucial for cellular processes because it serves as a direct source of energy for many cell functions. It is often referred to as the 'energy currency' of the cell.
How is ATP represented in textbooks and what misconception might students have about it?
-In textbooks, ATP is often depicted as a starburst or thunderbolt, which might lead students to think of it as a large burst of energy. However, ATP is more accurately described as a molecule that stores and releases energy through its chemical reactions.
What are some examples of cellular processes that require ATP?
-Examples of cellular processes that require ATP include active transport against concentration gradients, muscle contraction through the actin and myosin cross-bridge mechanism, and various types of cell signaling for communication.
What are the three components of ATP?
-ATP consists of three components: a nitrogenous base called adenine, a sugar molecule known as ribose, and three phosphate groups.
How does ATP differ from other nucleotides found in DNA or RNA?
-While ATP shares the sugar and base components with DNA and RNA nucleotides, the key difference is that ATP has three phosphate groups instead of just one, which is why it is called 'triphosphate.'
What are the different processes by which cells generate ATP?
-Cells generate ATP through processes such as aerobic cellular respiration, which involves oxygen, and anaerobic respiration or fermentation, which do not require oxygen. These processes can vary among different organisms, including plants, animals, bacteria, fungi, protists, and archaea.
What is the ATP cycle and why is it important?
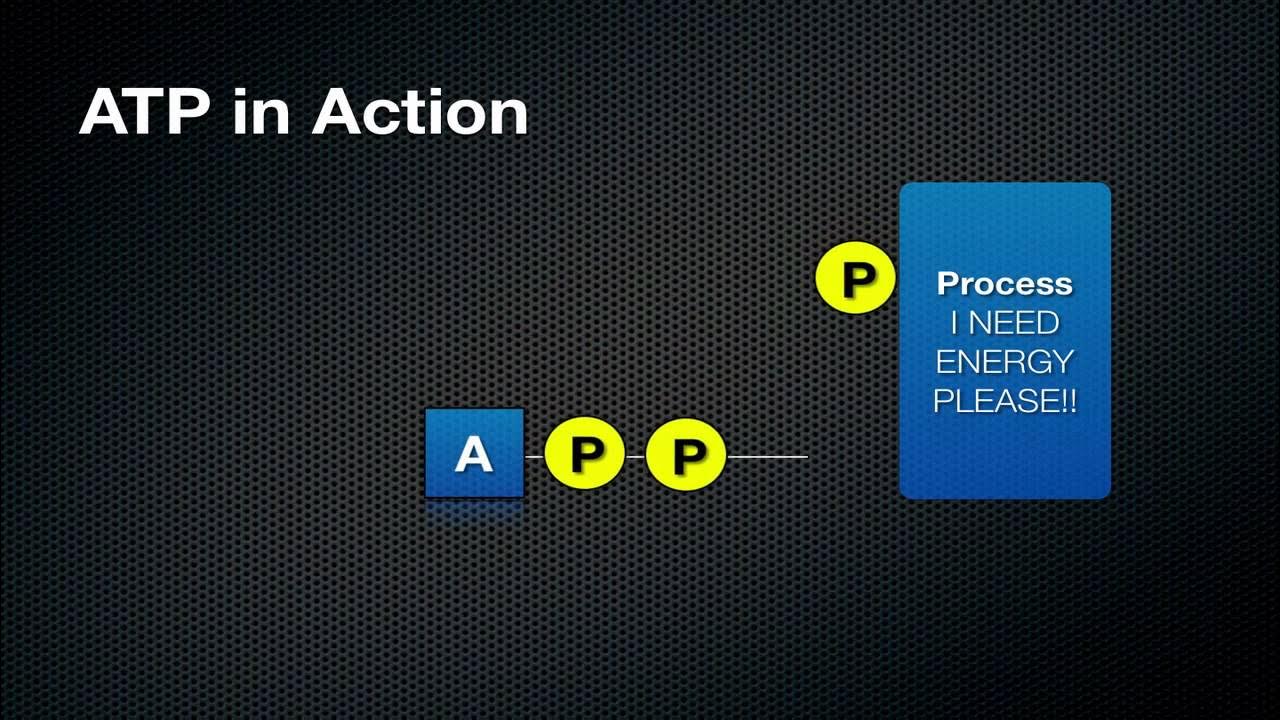
-The ATP cycle refers to the process where ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP, releasing energy and a phosphate group, and then regenerated from ADP by adding a phosphate, often through cellular respiration. This cycle is important because it allows for the rapid and continuous use of ATP in the cell.
How is the energy from ATP hydrolysis utilized by the cell?
-The energy released from ATP hydrolysis is coupled to endergonic processes, which are processes that require energy. This coupling ensures that the energy is used efficiently and directed towards necessary cellular activities.
What is the spring illustration used to understand ATP and how does it work?
-The spring illustration compares ATP to a compressed spring, which represents the stored energy in ATP. When the spring is released, it returns to a relaxed state, analogous to ATP becoming ADP upon hydrolysis and releasing energy.
What happens when a protein is phosphorylated during ATP hydrolysis?
-Protein phosphorylation occurs when a phosphate group from ATP is transferred to the protein. This modification can change the protein's reactivity and stability, often activating it to perform a specific function, such as moving molecules against a concentration gradient.
How does ATP play a role in processes like muscle movement or cell division?
-ATP provides the energy required for various cellular movements and processes, such as the beating of cilia, the separation of chromosomes during cell division, and the binding of the correct amino acid to a tRNA molecule.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)