2025 ATI TEAS 7 Science Chemistry with Nurse Cheung | Properties of Solutions, Osmosis, Diffusion
Summary
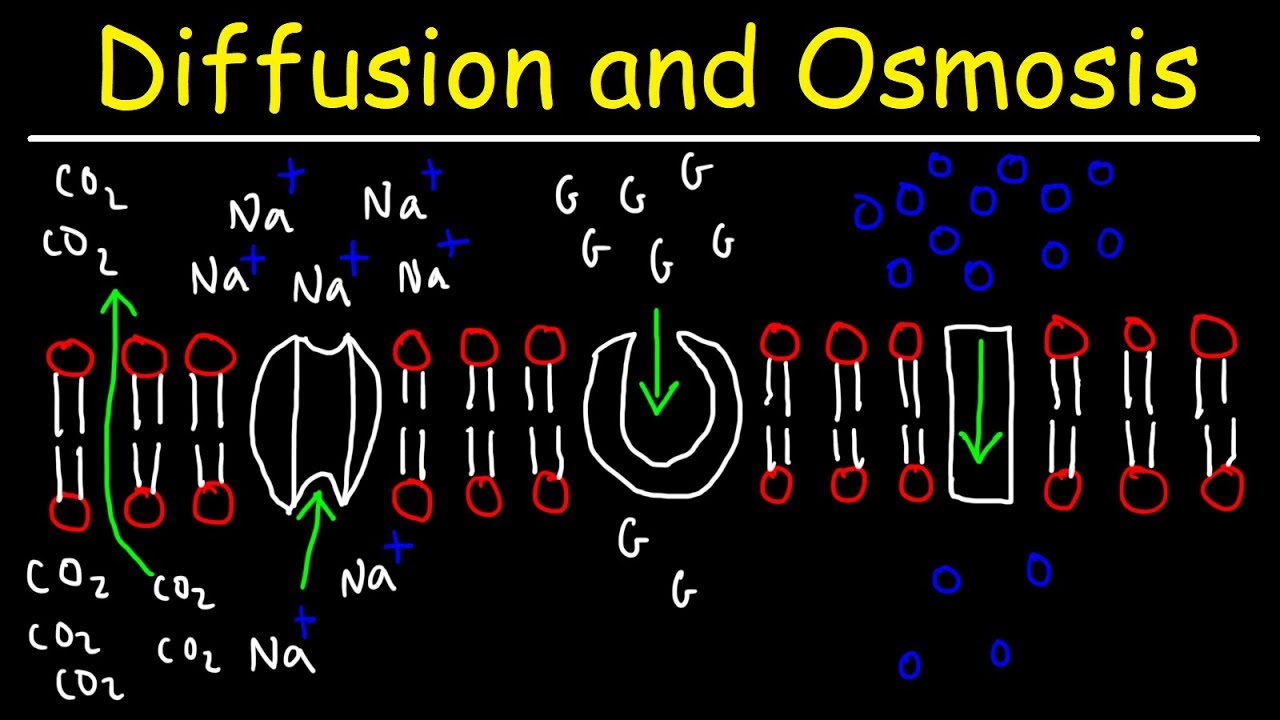
TLDRThis video breaks down the key principles of diffusion, osmosis, and active transport in biological systems. It explains how molecules move down concentration gradients in processes like diffusion, including facilitated diffusion that involves protein channels. The video also contrasts passive transport with active transport, which requires energy from ATP to move substances against their gradient. Key factors influencing diffusion, such as distance, temperature, and barrier characteristics, are also covered. The video emphasizes how these transport mechanisms are crucial for cellular functions and physiological processes across organisms.
Takeaways
- 😀 Osmosis refers to the movement of water through a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to high solute concentration.
- 😀 Tonicity describes how solutions compare based on their solute concentration relative to a cell, which influences water movement.
- 😀 Isotonic solutions have the same concentration of solutes as the inside of the cell, causing no net movement of water.
- 😀 Hypotonic solutions have lower solute concentration than the cell, causing water to move into the cell, potentially leading to cell swelling.
- 😀 Hypertonic solutions have higher solute concentration than the cell, causing water to move out of the cell, leading to cell shrinkage.
- 😀 Diffusion is the passive movement of particles from high to low concentration and does not require energy input.
- 😀 Facilitated diffusion is a type of diffusion that requires a protein channel to assist larger or more complex molecules across a cell membrane.
- 😀 Active transport requires ATP energy to move molecules against their concentration gradient, from low to high concentration.
- 😀 The rate of diffusion is influenced by factors such as distance, temperature, solvent characteristics, mass of the substance, and the nature of the membrane.
- 😀 Active transport is vital for processes such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and ion balance, which are crucial for cellular and organismal function.
Q & A
What is the key difference between osmosis and diffusion?
-Osmosis refers to the movement of water (the solvent) across a membrane, while diffusion is the movement of particles (solutes) from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Osmosis specifically deals with water molecules, whereas diffusion deals with the movement of solutes.
How does diffusion relate to air fresheners?
-Diffusion allows air fresheners to spread their scent. When sprayed, the molecules of the air freshener move from a high concentration (where the spray was applied) to a low concentration, allowing the scent to be detected at a distance.
What is meant by 'net movement' in diffusion?
-'Net movement' refers to the overall direction in which molecules move during diffusion. While molecules may still move in the opposite direction, the net movement is towards the area of lower concentration, resulting in equilibrium over time.
What factors influence the rate of diffusion?
-Several factors affect the rate of diffusion, including the distance molecules need to travel, temperature (higher temperatures speed up diffusion), solvent characteristics (density of solvent), the mass of the diffusing substance (lighter substances diffuse faster), and the characteristics of any barriers (e.g., cell membranes).
How does temperature impact the rate of diffusion?
-Higher temperatures increase the diffusion rate because molecules move more rapidly, enhancing their energy and making them spread out more quickly.
What is facilitated diffusion, and how does it differ from regular diffusion?
-Facilitated diffusion is a type of diffusion where molecules that are too large or have other characteristics preventing them from crossing the cell membrane pass through a protein channel. Unlike regular diffusion, which occurs directly through the membrane, facilitated diffusion requires a channel but still does not require energy.
What is active transport, and how does it differ from passive transport?
-Active transport is the process by which molecules are moved against their concentration gradient (from low to high concentration), which requires energy in the form of ATP. Unlike passive transport (which doesn't require energy and moves molecules along their concentration gradient), active transport requires cellular energy.
Why is active transport crucial for cellular functions?
-Active transport is vital for maintaining essential cellular functions, such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and ion balance. It is also key in processes like nutrient absorption in the intestines and ion reabsorption in the kidneys.
How does the mass of a substance affect diffusion?
-The mass of a substance plays a critical role in its diffusion rate. Heavier substances typically diffuse slower than lighter substances due to their greater inertia.
What role do protein channels play in facilitated diffusion?
-Protein channels in the cell membrane assist molecules that are too large or polar to pass through the membrane by themselves. These channels allow molecules to move along their concentration gradient without requiring energy.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Mekanisme Transpor Pada Membran Sel || BIOLOGI SMA
Diffusion and Osmosis - Passive and Active Transport With Facilitated Diffusion

Cellular Transport Project

Transport in Cells: Diffusion and Osmosis | Cells | Biology | FuseSchool

BIOLOGI Kelas 11 - Bioproses Sel (Transpor Membran) | GIA Academy

Transportasi pada membran sel - Biologi kelas 11 SMA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
