Psoriasis: Types, Symptoms, Causes, Pathology, and Treatment, Animation
Summary
TLDRPsoriasis is a common chronic skin condition that causes recurrent flare-ups and periods of remission. It manifests through red, itchy, scaly patches, most commonly on the scalp, elbows, and knees. There are various types of psoriasis, including plaque, guttate, inverse, pustular, and erythrodermic psoriasis. Genetic factors play a major role in its development, and triggers like infections, stress, and medications can lead to flare-ups. Psoriasis can lead to complications such as ocular psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Treatment varies from topical agents to systemic therapies, with phototherapy being an option for severe cases.
Takeaways
- 😀 Psoriasis is a chronic, inflammatory skin condition affecting about 3% of the global population.
- 😀 It evolves in recurrent flare-ups followed by periods of remission.
- 😀 Psoriasis often begins in young adulthood but can start at any age.
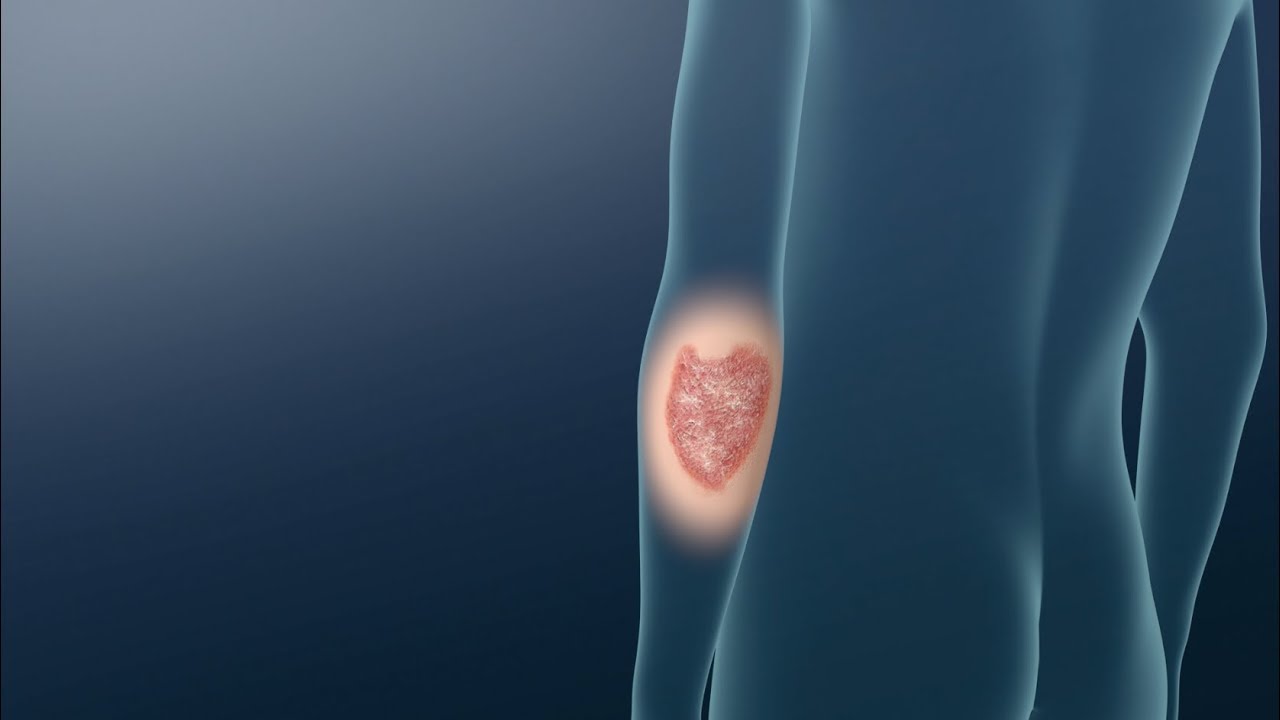
- 😀 The most common form is plaque psoriasis, characterized by red, raised, itchy, and scaly patches on the skin.
- 😀 Other types of psoriasis include guttate, inverse, pustular, and erythrodermic, each with distinct symptoms and severity.
- 😀 Psoriasis has a strong genetic component, with several genes linked to its susceptibility, often involving immune system pathways.
- 😀 Triggers for flare-ups include infections, injuries, stress, smoking, alcohol use, and certain medications.
- 😀 The condition involves an overactive inflammatory response, which leads to rapid skin cell production and scaly patches.
- 😀 Psoriasis can lead to complications such as ocular psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular diseases, obesity, and depression.
- 😀 Mild to moderate psoriasis can be effectively managed with topical agents, while severe cases may require phototherapy or systemic treatments.
Q & A
What is psoriasis?
-Psoriasis is a common inflammatory skin condition affecting about 3% of the global population. It is a chronic disease that presents as recurrent flare-ups of inflammation followed by periods of partial or complete remission.
At what age does psoriasis typically develop?
-Psoriasis can develop at any age but often begins in young adulthood.
Is psoriasis contagious?
-No, psoriasis is not contagious, even though it may appear as if it is due to its visible symptoms.
What are the main characteristics of plaque psoriasis?
-Plaque psoriasis is the most common type and is characterized by red, raised, itchy, and scaly patches of skin. These plaques often appear on the scalp, in front of the knees, and behind the elbows.
What are the different types of psoriasis?
-The different types of psoriasis include plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, and erythrodermic psoriasis. Each type has distinct features and may affect different areas of the body.
What is guttate psoriasis?
-Guttate psoriasis involves small, numerous spots that appear over a large area of the body. It primarily affects children and young adults.
What is inverse psoriasis?
-Inverse psoriasis presents as smooth patches of inflamed skin that worsen with friction and sweating, typically found in skin folds such as under the arms, in the groin, or under the breasts.
What is the role of genetics in psoriasis?
-Psoriasis has a strong genetic component, with multiple genes linked to susceptibility. These genes are mainly involved in immune system functions, particularly inflammatory pathways, and psoriasis can be inherited as an autosomal dominant trait in some families.
What factors can trigger psoriasis flare-ups?
-Psoriasis flare-ups can be triggered by factors such as infections, traumatic injuries, stress, smoking, alcohol use, and certain medications.
What are the common complications associated with psoriasis?
-Common complications of psoriasis include ocular psoriasis (eye diseases) and psoriatic arthritis (chronic inflammation in the joints, particularly in the fingers and toes). Psoriasis is also associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, obesity, diabetes, and mental health issues like depression and low self-esteem.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

How to CLEAR SEBORRHEIC DERMATITIS on the face| Dr Dray
Understanding Psoriasis

Psoriasis Explained Clearly - Including Types and Treatment

1 TSP CURES Your Skin Problems in Just 7 Days! | Barbara O'Neill
What is chronic bronchitis? | Respiratory system diseases | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy

Finding Relief from Psoriasis | Anthony Fernandez, MD
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
