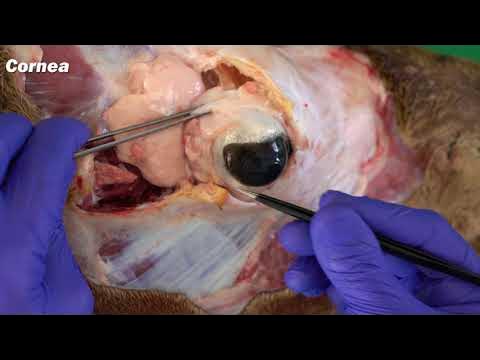
Anatomy - Eye Overview
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an insightful overview of the anatomy of the eye, covering key structures such as the cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, and optic nerve. It explains how light is focused on the retina by bending through the cornea and lens. The video also delves into the function of the iris and pupil in regulating light intake, the role of aqueous humor in the anterior cavity, and the importance of accommodation in adjusting vision. Additionally, it discusses eye conditions like glaucoma and presbyopia, along with the process of pupilary constriction and dilation, enhancing viewers' understanding of the eye's complex functions.
Takeaways
- 😀 The eye is made up of three main layers: the outer sclera and cornea, the middle choroid, iris, and ciliary body, and the inner retina which contains photoreceptors.
- 😀 The cornea and lens are responsible for bending incoming light to focus on the retina, enabling vision.
- 😀 The iris controls the size of the pupil and regulates the amount of light entering the eye.
- 😀 The fovea, located in the retina, contains cone cells that provide sharp central vision.
- 😀 The retina's photoreceptors (rods and cones) capture images and send them via the optic nerve to the brain for processing.
- 😀 The eye's fluid-filled cavities, the vitreous humor in the posterior and aqueous humor in the anterior, play important roles in maintaining eye shape and nourishing eye structures.
- 😀 The ciliary body controls the shape of the lens to accommodate for focusing on objects at different distances.
- 😀 Parasympathetic stimulation causes pupil constriction, while sympathetic stimulation causes pupil dilation (fight-or-flight response).
- 😀 Glaucoma is caused by the blockage of aqueous humor drainage, leading to high eye pressure and potential damage to the optic nerve.
- 😀 Presbyopia, an age-related condition, reduces the eye's ability to focus on near objects due to the lens losing its ability to accommodate.
- 😀 Cataracts occur when the lens becomes opaque, preventing light from entering the eye, resulting in blurry vision.
Q & A
What are the main structures responsible for bending light to focus on the retina?
-The cornea and the lens are the primary structures responsible for bending light and focusing it on the retina.
What role does the iris play in vision?
-The iris controls the size of the pupil, adjusting the amount of light entering the eye, and it also determines the color of the eye.
How does the lens change shape for accommodation?
-The ciliary muscles control the shape of the lens. When they contract, the lens becomes rounder and stronger to focus on near objects, while relaxing causes the lens to flatten for distant objects.
What is the fovea and why is it important?
-The fovea is a small central pit in the retina that contains a high concentration of cone cells, making it essential for sharp, central vision.
What is the vitreous humor and where is it found?
-The vitreous humor is a clear fluid found in the posterior cavity of the eye, and it helps maintain the shape of the eyeball.
What is the function of the aqueous humor?
-The aqueous humor is produced by the ciliary body and nourishes the anterior structures of the eye. It also helps maintain intraocular pressure.
What happens when there is an obstruction of the aqueous humor drainage?
-Obstruction of the aqueous humor drainage can lead to glaucoma, a condition where pressure builds up in the eye and can damage the optic nerve, leading to vision loss.
What is presbyopia and how does it affect vision?
-Presbyopia is the age-related loss of the ability to accommodate, meaning the lens becomes less flexible and struggles to focus on near objects, leading to blurry vision.
How do sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves affect the iris and pupil?
-Sympathetic stimulation causes pupil dilation by acting on the dilator muscles, while parasympathetic stimulation leads to pupil constriction by acting on the sphincter muscles.
What is the function of the suspensory ligaments in the eye?
-The suspensory ligaments connect the ciliary body to the lens, helping to control the shape of the lens during accommodation.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)