REPRODUKSI SEKSUAL BAKTERI : KONJUGASI, TRANSDUKSI DAN TRANSFORMASI
Summary
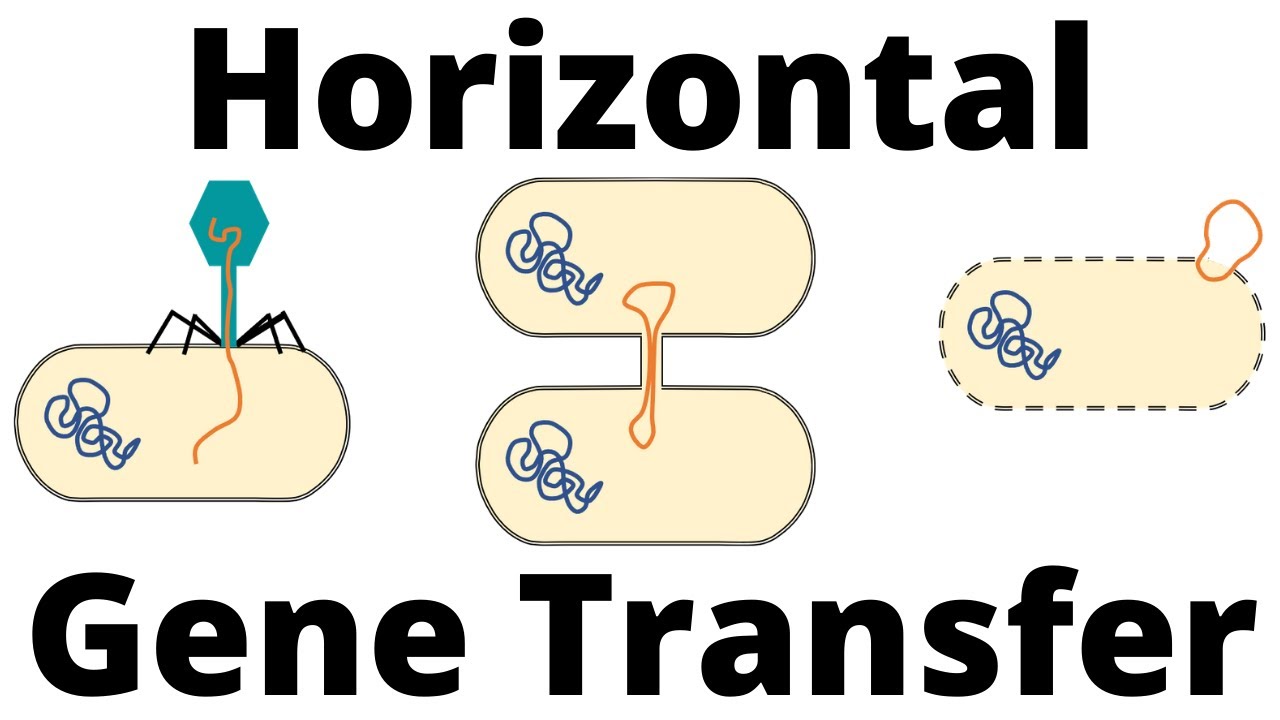
TLDRThis video explains three key methods of genetic material transfer in bacteria: conjugation, transduction, and transformation. In conjugation, DNA is transferred directly between two bacteria via a pilus, leading to genetic recombination. Transduction involves a bacteriophage (virus) transferring DNA from one bacterium to another, enabling genetic exchange. Transformation occurs when bacteria absorb DNA from their environment, often from closely related species, leading to genetic alteration. These processes are essential for bacterial evolution and can impact their behavior, such as when harmless bacteria acquire harmful traits, as in the case of Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Takeaways
- 😀 Conjugation is a process where DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another through direct contact.
- 😀 A pilus (bridge-like structure) is produced by the donor bacterium to establish contact with the recipient bacterium.
- 😀 The recipient bacterium takes in the genetic material from the donor bacterium during conjugation, leading to recombination.
- 😀 In transduction, bacteria acquire DNA via a virus (bacteriophage) that carries the donor bacterium's DNA into the recipient bacterium.
- 😀 The virus acts as an intermediary in transduction, facilitating DNA transfer between bacteria.
- 😀 Transformation occurs when bacteria absorb DNA from their surrounding environment, often from related bacteria.
- 😀 Transformation can cause non-pathogenic bacteria to become pathogenic if they acquire harmful genes, such as in the case of *Streptococcus*.
- 😀 Conjugation, transduction, and transformation are all mechanisms that enable bacteria to exchange genetic material and evolve.
- 😀 Bacteria can quickly evolve by acquiring new traits, such as antibiotic resistance, through these genetic transfer mechanisms.
- 😀 The genetic changes resulting from conjugation, transduction, and transformation can significantly alter a bacterium's behavior or virulence.
Q & A
What is conjugation in bacteria?
-Conjugation is a process where DNA is transferred from one bacterium (the donor) to another (the recipient) through a bridge-like structure called a pilus. This allows for genetic material to be shared between bacteria.
What role does the pilus play in bacterial conjugation?
-The pilus acts as a bridge that connects the donor bacterium to the recipient, facilitating the transfer of genetic material from the donor to the recipient bacterium.
What happens after the recipient bacterium receives DNA during conjugation?
-After receiving the DNA, the recipient bacterium integrates the new genetic material into its own DNA, resulting in genetic recombination, and the creation of a new bacterial strain.
What is the difference between the donor and recipient bacteria in the conjugation process?
-The donor bacterium is the one that provides the DNA, while the recipient bacterium is the one that receives the genetic material during the conjugation process.
What is transduction in bacteria?
-Transduction is the process where bacteria acquire DNA from a bacteriophage (a virus that infects bacteria). The bacteriophage carries the donor bacterium’s DNA and transfers it to the recipient bacterium.
How does a bacteriophage contribute to transduction?
-The bacteriophage infects the donor bacterium, capturing its DNA. When the virus then infects a recipient bacterium, it introduces the donor bacterium’s DNA into the recipient bacterium.
What occurs after the recipient bacterium receives DNA through transduction?
-Once the recipient bacterium receives the DNA, recombination happens, and the recipient bacterium may exhibit new characteristics as a result of the transferred genetic material.
What is transformation in bacteria?
-Transformation is the process where bacteria take up DNA from their surrounding environment, particularly from dead or lysed bacterial cells, and incorporate it into their own genetic material.
How do bacteria recognize DNA for transformation?
-Bacteria have surface proteins that can recognize and bind to DNA that is related or similar to their own genetic material. Once identified, the DNA is transported into the bacterial cell.
What is an example of transformation in bacteria, and what is the result?
-An example of transformation is when Streptococcus bacteria, initially non-pathogenic, take up DNA from Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium, and become harmful, causing pneumonia.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
Transformation, Transduction and Conjugation (Horizontal Gene Transfer in Bacteria)

REPRODUKSI BAKTERI LENGKAP (REPRODUKSI SEKSUAL DAN ASEKSUAL)

Reproduksi Bakteri

Reproduksi Bakteri | Biologi Kelas X

CONJUGATION, TRANSFORMATION, TRANSDUCTION (HORIZONTAL GENE TRANSFER)

BIOLOGI Kelas 10 - Bakteri (PART 2) | GIA Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
