What is a Servo Motor and How it Works?
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept and operation of servo motors, highlighting their use in closed-loop systems for precise motion control in various industrial and commercial applications. It covers the types of servo motors—AC and DC—along with their components such as encoders, controllers, and amplifiers. The video also distinguishes between brushed and brushless motors, explaining the differences in efficiency and performance. Additionally, it explores the working principles of DC and AC servo motors and provides insights into their applications in robotics, camera autofocus systems, and antenna positioning. The video concludes with an invitation to explore more educational content on motion control.
Takeaways
- 😀 Servo motors are crucial in closed-loop systems, providing precise position control for industrial and commercial applications.
- 😀 A servo motor is a self-contained device that rotates parts of a machine with high efficiency and precision.
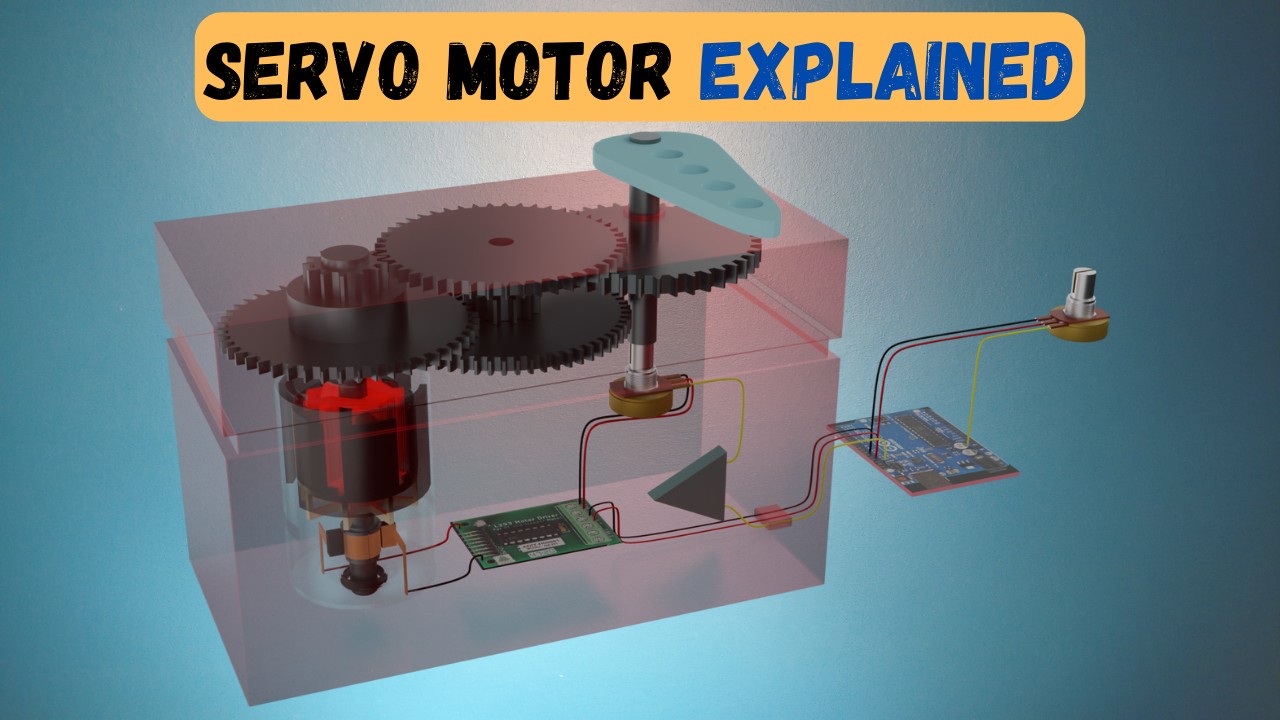
- 😀 Servo motors consist of several parts: a control circuit, motor, shaft, amplifier, and encoder/resolver for positional feedback.
- 😀 Servo motors utilize positional feedback from sensors (encoders or resolvers) to control speed and position, making them more precise than regular motors.
- 😀 Servo motors are classified based on their power source: AC (alternating current) or DC (direct current), and also based on commutation type (brushed or brushless).
- 😀 AC servo motors are commonly used in high-precision applications like robotics and industrial manufacturing, as they withstand higher currents.
- 😀 DC servo motors can be either brushed or brushless. Brushed motors are simpler and cheaper, while brushless motors offer higher efficiency and reliability.
- 😀 The speed of a DC motor is proportional to the voltage applied, while the speed of an AC motor is determined by the frequency of the voltage and the number of magnetic poles.
- 😀 AC servo motors are divided into synchronous and asynchronous (induction) types based on how their rotor interacts with the stator's magnetic field.
- 😀 In synchronous AC motors, the rotor rotates at the same speed as the stator's rotating magnetic field, providing higher efficiency.
- 😀 Servo motors have a wide range of applications, including in robotics for joint movement, camera autofocus systems, and antenna positioning systems.
Q & A
What are servo motors commonly used for?
-Servo motors are most commonly used in closed-loop systems where precise position control is required. They are commonly found in applications such as robotics, metal fabrication machines, antenna positioning systems, and military vehicles with bomb detection.
What is the basic function of a servo motor?
-A servo motor is a self-contained electrical device designed to rotate parts of a machine with high efficiency and precision. It can move an output shaft to a specific angle, position, and velocity, which regular motors cannot achieve.
How do servo motors differ from regular motors?
-Unlike regular motors, servo motors use a feedback loop that incorporates sensors like encoders or resolvers to provide positional feedback. This feedback allows the motor to control the rotational or linear speed and position with high accuracy.
What are the key components of a servo motor system?
-A servo motor system typically consists of a control circuit, the servo motor itself, a shaft, an amplifier, and either an encoder or resolver for feedback on speed and position.
What are the main types of servo motors based on current type?
-Servo motors can be classified based on the type of current they use: AC (alternating current) or DC (direct current).
What is the main difference between AC and DC servo motors in terms of performance?
-The primary difference between AC and DC servo motors is in how speed is controlled. In a DC motor, speed is directly proportional to the supply voltage, while in an AC motor, speed depends on the frequency of the applied voltage and the number of magnetic poles.
What is the difference between brushed and brushless DC motors in servo systems?
-Brushed DC motors are simpler, less expensive, and use a mechanical commutator, while brushless DC motors are more reliable, efficient, and less noisy. Brushless designs also use electronic commutation through devices like Hall effect sensors or encoders.
What is a synchronous versus an asynchronous servo motor?
-In a synchronous servo motor, the rotor rotates at the same speed as the stator’s rotating magnetic field. In contrast, in an asynchronous (induction) motor, the rotor rotates slower than the stator’s rotating magnetic field.
How does feedback work in a DC servo motor?
-In a DC servo motor, a potentiometer produces a voltage corresponding to the motor’s position. The motor’s actual position is compared with the desired position, and any error in position is amplified and used to correct the motor's movement until it reaches the desired position.
What are some applications of servo motors in industry?
-Servo motors are used in robotics for precise movement of each joint, in camera autofocus systems to adjust lens positioning, and in antenna positioning systems for controlling azimuth and elevation, such as in telescopes or radio observatories.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Difference between Stepper and Servo Motor | Servo और Stepper Motor कैसे काम करता है ?
Servo Motor Explained - 3D Animation

Elements of Motion Control - Open and Closed-loop Control

Stepper Motors vs Servo Motors: A Quick Comparison

Explaining Open and Closed loop Systems in Robotics - Control System Engineering

Sistem Kontrol || Open Loop dan Close Loop
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
