Construction and Working of a Single phase Induction Motor | Skill-Lync
Summary
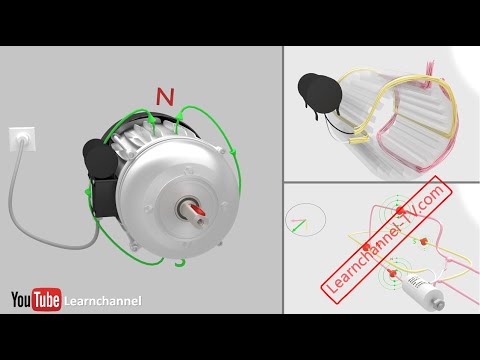
TLDRIn this video, the working and construction of a single-phase induction motor are explained. The motor, which is commonly used in home appliances, converts electrical energy into mechanical energy and consists of two main parts: the stator and the rotor. The stator produces an alternating magnetic field that induces a magnetic field in the rotor. However, due to the nature of the magnetic fields, the rotor doesn’t initially rotate. The problem is solved by introducing an auxiliary winding that generates a starting torque, allowing the rotor to begin rotating. A capacitor is used to maintain the phase difference needed for optimal performance.
Takeaways
- 😀 Single phase induction motors are commonly used in household appliances like fans, dishwashers, and washing machines due to their efficiency and ease of use.
- 😀 These motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy and consist of two main parts: the stator and the rotor.
- 😀 The stator is the stationary part of the motor and is made of laminated sheets with holes to hold the windings, reducing eddy current losses.
- 😀 The stator is powered by a single-phase AC supply, which creates an alternating magnetic field in the motor.
- 😀 The alternating magnetic field induces a magnetic field in the rotor, following the principles of electromagnetic induction.
- 😀 According to Lorentz's law, the interaction between the electrical and magnetic fields generates force, causing the rotor to rotate.
- 😀 A key issue is that the rotor tends to vibrate in place due to the opposing nature of the alternating magnetic fields in the stator, a phenomenon explained by the double revolving field theory.
- 😀 The problem of insufficient torque for rotation is overcome by introducing a starting torque, which is provided by an auxiliary winding.
- 😀 The auxiliary winding is placed perpendicular to the main winding and connected to an AC source, helping create two magnetic fields that produce the necessary starting torque.
- 😀 After the rotor starts rotating, the auxiliary winding is disconnected by a switch, and a capacitor is added to maintain a 90-degree phase difference, ensuring continued rotor motion.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a single-phase induction motor?
-The primary function of a single-phase induction motor is to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, typically to power household appliances like fans, dishwashers, and washing machines.
What are the two main parts of a single-phase induction motor?
-A single-phase induction motor consists of two main parts: the stator and the rotor.
What is the role of the stator in a single-phase induction motor?
-The stator is the stationary part of the motor and consists of laminated sheets that hold the windings. These windings are supplied with a single-phase AC supply, producing an alternating magnetic field.
Why are laminated sheets used in the stator?
-Laminated sheets are used in the stator to reduce eddy current losses, improving the efficiency of the motor.
How does the alternating magnetic field affect the rotor?
-The alternating magnetic field in the stator induces a magnetic field in the rotor through electromagnetic induction, but it does not immediately cause the rotor to rotate.
What is the double revolving field theory, and how does it affect rotor movement?
-The double revolving field theory states that the alternating magnetic field consists of two equal and opposite rotating magnetic fields, which do not provide effective torque for the rotor's movement, leading to no rotation.
How is the problem of the rotor not rotating addressed in a single-phase induction motor?
-The problem is overcome by providing starting torque to the motor, which is achieved by adding an auxiliary winding that creates a secondary magnetic field to help initiate rotation.
What is the purpose of the auxiliary winding in a single-phase induction motor?
-The auxiliary winding is placed perpendicular to the main winding and produces two magnetic fields, one of which adds up to the magnetic field of the main winding, providing the necessary starting torque for the rotor.
How is the auxiliary winding disconnected once the motor starts rotating?
-The auxiliary winding is disconnected through a switch, and its current is cut off after the motor has received the initial torque, allowing the rotor to continue rotating.
Why is a capacitor connected in series with the auxiliary winding?
-A capacitor is connected in series with the auxiliary winding to maintain a 90-degree phase difference between the auxiliary winding and the main winding, which is crucial for producing the starting torque required for rotor movement.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Single Phase Induction Motor, How it works ?

How Three-Phase Induction Motors Work in Telugu | Understanding Three-Phase Induction Motors.

How does a fan work ? | Single phase induction motor

Synchronous Motor vs Asynchronous Motor | Synchronous vs Induction Motor | Come4Concepts
Single Phase Induction Motor (Capacitor Induction Motor or AC Motor) explained

Practical Marine Electrical Knowledge: Program 4. Motors and Starters
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
