Rotating Magnetic Field (How it produce) Unit 4 Electrical Machines (1st year Engineering) EEE (BEE)
Summary
TLDRThe video focuses on understanding the concept of rotating magnetic fields in electrical motors, particularly induction motors. It explains how magnetic fields are generated and how they rotate at a constant speed, demonstrating the working mechanism inside a motor. The video also explores the role of current and magnetic fields in generating rotational movement, using principles like the right-hand thumb rule to determine the direction of the magnetic field. Various electrical concepts such as transformers, windings, and phase differences are also touched upon, providing a comprehensive understanding of motor operation and magnetic field dynamics.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video explains the concept of rotating magnetic fields and how they are generated in electrical machines like induction motors.
- 😀 Induction motors produce a rotating magnetic field at a constant speed, which is a fundamental principle in their operation.
- 😀 The speed of the rotating magnetic field is equal to 120 times the frequency of the supply divided by the number of poles in the motor.
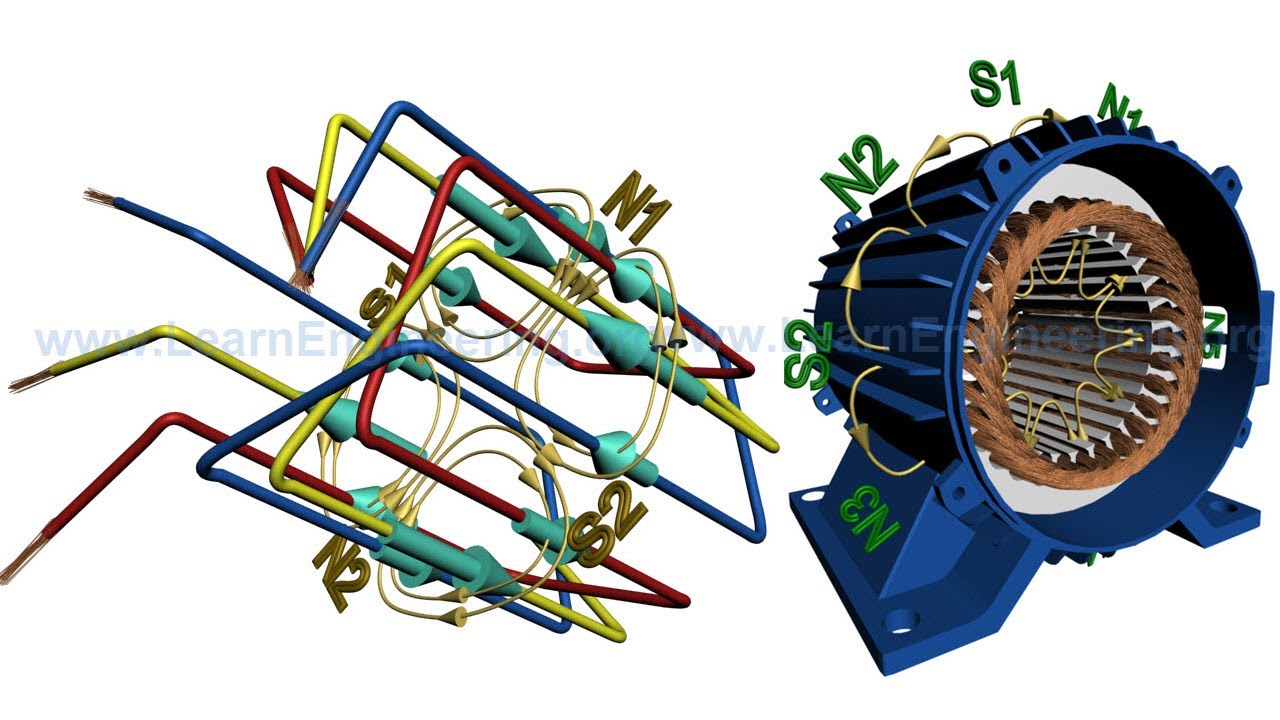
- 😀 The stator of an induction motor is stationary, and it receives a three-phase supply, creating a rotating magnetic field.
- 😀 The rotor inside the motor generates an electrical current due to electromagnetic induction when exposed to the rotating magnetic field.
- 😀 The current generated in the rotor produces its own magnetic field, which interacts with the stator field, causing the rotor to rotate.
- 😀 The Right-Hand Rule is used to determine the direction of the magnetic field produced by the current flowing through the wires of the stator.
- 😀 The three-phase current supply to the motor results in a 120-degree phase difference between the currents in the windings.
- 😀 The concept of magnetic flux is crucial in understanding how motors work and how the induced current produces a rotating magnetic field.
- 😀 The video also touches on the mathematical calculations behind the system, including the use of sine and cosine functions to determine magnetic flux and other electrical parameters.
- 😀 The rotating magnetic field plays a key role in converting electrical energy into mechanical energy in induction motors.
Q & A
What is the meaning of a rotating magnetic field in an induction motor?
-A rotating magnetic field in an induction motor is produced when a magnetic field rotates at a constant speed, which is equal to 120 times the frequency of the supply voltage divided by the number of poles.
How is the rotating magnetic field generated in an induction motor?
-The rotating magnetic field is generated by the interaction of the stator's three-phase AC supply, which creates a time-varying magnetic field that rotates inside the motor. This rotating field induces current in the rotor, causing it to rotate.
What is the role of the stator and rotor in an induction motor?
-In an induction motor, the stator is the stationary part that receives the AC supply and creates a rotating magnetic field. The rotor is the rotating part that interacts with the magnetic field induced by the stator, leading to its motion.
What is the significance of the 120 degrees phase difference in the windings of an induction motor?
-The 120 degrees phase difference between the windings ensures that the magnetic field produced by the stator is continuous and rotating. This phase difference is critical for the consistent operation of the motor.
How is the direction of the magnetic field determined in an induction motor?
-The direction of the magnetic field can be determined using the right-hand thumb rule. When you align your fingers in the direction of the current flow, your thumb points in the direction of the magnetic field.
What happens when three-phase AC supply is given to the stator windings?
-When a three-phase AC supply is given to the stator windings, it generates a rotating magnetic field inside the motor, which induces current in the rotor, causing it to rotate and produce mechanical motion.
How does the current in the rotor generate a magnetic field?
-The current induced in the rotor by the rotating magnetic field generates its own magnetic field. This rotor field interacts with the stator's magnetic field, producing torque that causes the rotor to rotate.
Why is the frequency of the supply voltage important for the speed of the rotating magnetic field?
-The frequency of the supply voltage directly affects the speed of the rotating magnetic field. The speed is determined by the formula: Speed = 120 × (Frequency / Number of poles), where a higher supply frequency results in a faster rotating magnetic field.
What is the relationship between the induced current and the magnetic field in an induction motor?
-The induced current in the rotor creates its own magnetic field, which interacts with the stator's magnetic field. This interaction produces a force that causes the rotor to rotate, generating mechanical output.
What mathematical rule helps in determining the direction of the induced magnetic field?
-The right-hand thumb rule is used to determine the direction of the induced magnetic field. By pointing the fingers in the direction of current flow, the thumb will point in the direction of the magnetic field.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)