DPI-681 Class 1 - Introduction to Large Language Models
Summary
TLDRIn this course introduction, Char Goyle, alongside Dan and Teddy, introduces the science behind generative AI, focusing on large language models like ChatGPT. The process involves three key steps: gathering a massive dataset, predicting the next word in a sequence, and fine-tuning the model to align with desired behavior. Char explains how these models generate coherent text through word prediction and highlights the challenges involved in training and aligning these models. The session touches on the philosophical aspects of prediction in AI, emphasizing its role in encoding knowledge and grammar, blurring the lines between human and machine creativity.
Takeaways
- 😀 Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT are built in three main steps: collecting a large corpus of data, predicting the next word, and fine-tuning the model to align with desired behavior.
- 😀 The first step of building LLMs is collecting a vast amount of text data from web pages, forums, books, and proprietary content, often comprising trillions of words.
- 😀 The second step is learning to predict the next word in a given sequence based on the corpus, which is a crucial part of generative AI.
- 😀 Generative AI is fundamentally about prediction, and although it's complex, at its core, it is still a prediction problem.
- 😀 Fine-tuning is the third step, where the model is adjusted to align with specific desired behaviors, which can be a challenging task due to the complexity of human behavior.
- 😀 The process of predicting the next word in a sequence is done one word at a time, with the model continually building on the previous word.
- 😀 Predicting words based on previous context gives the impression of mimicking human language, even though the model is purely driven by statistical probabilities.
- 😀 The example of completing a sentence one word at a time demonstrates how predictions in language models are based on probabilities, not exact matches from the training data.
- 😀 The model doesn't rely on searching for exact phrases from its training corpus but instead uses a statistical model to predict the most likely next word based on context.
- 😀 Prediction in generative AI can encode a lot of knowledge, such as facts (like the capital of Australia), grammar, and context, which the model learns during training.
Q & A
What are the three main steps involved in building large language models (LLMs)?
-The three main steps are: 1) Collecting a large corpus of data, typically written by humans. 2) Learning to predict the next word in a sequence based on the collected data. 3) Fine-tuning the model to align with desired behavior.
How does generative AI differ from traditional AI models?
-Generative AI looks different in its output because it generates text, but at its core, it is still fundamentally based on prediction, which is a core feature of traditional AI as well.
What role does predicting the next word play in language generation by AI models?
-Predicting the next word is the key step in generating coherent text. The AI looks at the previously generated words and uses that information to predict the next word, continuing the process until a full response is generated.
What challenges are involved in fine-tuning a language model to align with desired behavior?
-Fine-tuning is challenging because it's difficult to make a model behave exactly as we want, and it is also complex to define whose behavior the model should align with.
How does the AI model handle text generation when it is given a prompt or question?
-When a prompt or question is given, the AI model starts by predicting the first word in the answer, then continues to predict each subsequent word, forming a coherent response over time.
What is the difference between using autocomplete and how language models like LLMs generate text?
-Autocomplete simply tries to match a phrase to exact phrases in a database, while language models generate text by predicting the most likely next word based on the context of all previous words, not relying on exact matches in the data.
Why is it difficult to find exact phrase matches in large datasets for language models?
-In English, with a vocabulary of around 30,000 words, the number of ways to arrange these words into meaningful phrases is vast. Even with a large corpus, it's unlikely that an exact match for any brief phrase will be found in the data.
What philosophical concept is introduced when discussing language model predictions?
-The concept that relatively brief utterances are unique and ephemeral, suggesting that predicting exact matches is nearly impossible and why statistical models like LLMs are necessary to generate reasonable text.
How can prediction itself encode knowledge in a language model?
-Prediction in language models can encode facts and grammar rules. For example, predicting that 'the capital of Australia is' is more likely to be followed by 'Canberra' than 'banana' shows that the model has encoded geographical knowledge.
What is the central question about the difference between human and machine intelligence as discussed in the script?
-The script raises the philosophical question of whether there is a clear distinction between human knowledge, creativity, and reasoning, and whether these traits are fundamentally different from the capabilities of machines when framed in terms of prediction.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Roadmap to Learn Generative AI(LLM's) In 2024 With Free Videos And Materials- Krish Naik

Introduction to large language models
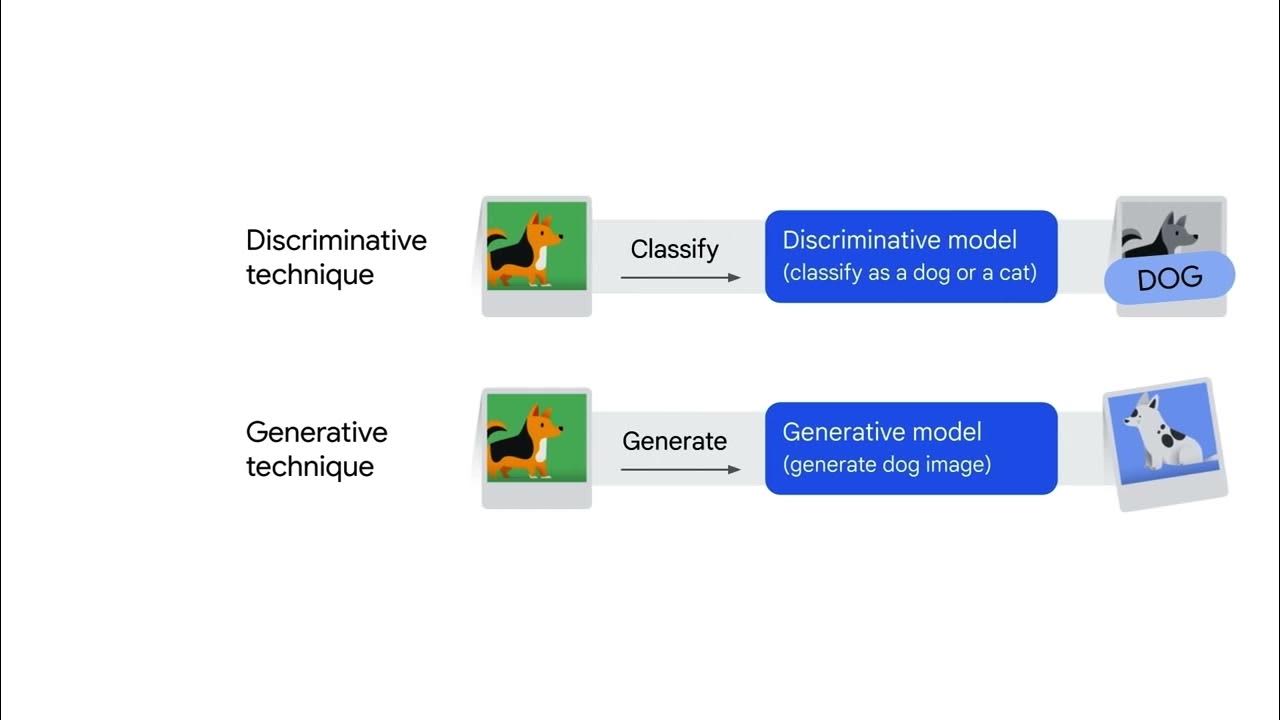
Introduction to Generative AI

Generative AI Vs NLP Vs LLM - Explained in less than 2 min !!!

Introduction to Generative AI and LLMs [Pt 1] | Generative AI for Beginners

Introduction to Generative AI
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
