Integrasi Numerik | Metode Trapezium | Simpson 1/3 | Simpson 3/8
Summary
TLDRIn this tutorial, Setiawan explains numerical integration methods for calculating definite integrals. He covers three key methods: the Trapezoidal Rule, Simpson's 1/3 Rule, and Simpson's 3/8 Rule, illustrating their formulas and step-by-step calculations. The video demonstrates the application of these methods using a specific integral example, and discusses how to compute the error (or 'galat') for each method by comparing the numerical results with the analytical solution. Setiawan emphasizes the importance of understanding these methods for solving integrals when an analytical approach is not feasible.
Takeaways
- 😀 Numerical integration refers to calculating integrals numerically rather than analytically, using specific methods.
- 😀 Common numerical integration methods include Trapezoidal Method, Simpson's 1/3 Rule, and Simpson's 3/8 Rule.
- 😀 The key formula used in numerical integration is 'h = (b - a) / n', where h is the step size, and n is the number of intervals.
- 😀 The Trapezoidal Rule involves approximating the area under a curve using trapezoids and applying a specific formula with coefficients.
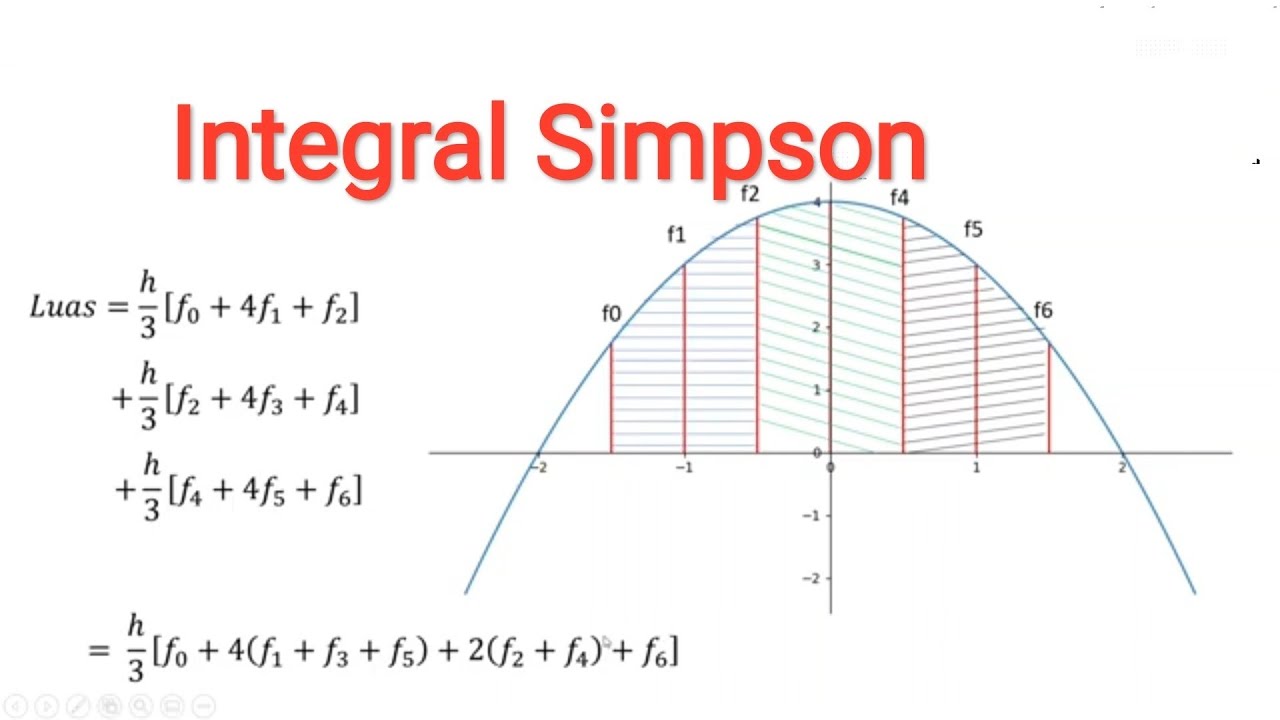
- 😀 Simpson's 1/3 Rule uses a formula with step size 'h/3' and includes coefficients for odd and even terms for better accuracy.
- 😀 Simpson's 3/8 Rule uses a formula with step size '3h/8' and involves a specific pattern of coefficients for odd and even terms.
- 😀 A sample example involving the integral of a function, such as '2x^4 + 4x^2', demonstrates how to apply these methods numerically.
- 😀 Numerical integration can be made easier by creating tables that display the function values at each step.
- 😀 The number of intervals 'n' is crucial for calculating numerical integration accurately, and it is calculated using the formula 'n = (b - a) / h'.
- 😀 After calculating numerical integrals, the actual value can be compared with analytical solutions to find the error or 'galat'.
- 😀 The lowest error or galat is typically found using Simpson's 1/3 Rule, which provides the most accurate results among the three methods.
Q & A
What is numerical integration?
-Numerical integration is the process of calculating the integral of a function using numerical methods, rather than performing the integration analytically.
What are the methods used for numerical integration as mentioned in the script?
-The methods discussed in the script for numerical integration are the Trapezoidal method, Simpson's 1/3 method, and Simpson's 3/8 method.
What is the formula for the Trapezoidal method?
-The formula for the Trapezoidal method is: I = h/2 * (f(x0) + 2 * (sum of f(xi) for odd indices) + f(xn)) where h is the interval width.
What is the main rule for numerical integration that is common across all methods?
-The main rule is that h = (b - a) / n, where h is the interval length, b and a are the upper and lower limits of integration, and n is the number of intervals.
What is Simpson's 1/3 method, and how does it differ from the Trapezoidal method?
-Simpson's 1/3 method is a numerical integration method that uses a specific weighted combination of function values at equally spaced points. The key difference from the Trapezoidal method is that Simpson's 1/3 uses a weighting of 4 for the odd indexed points and 2 for the even indexed points.
How does Simpson's 3/8 method work?
-Simpson's 3/8 method works by applying a combination of weights 3 and 2 for successive terms. It involves calculating the sum of function values at intervals that are a multiple of 3 and 8, hence the name.
How is the error (or galat) in numerical integration calculated?
-The error is calculated by comparing the numerically computed integral value with the analytically calculated exact integral. The absolute error is then divided by the exact integral value and multiplied by 100 to get the percentage error.
In the example given, what function is being integrated?
-The function being integrated is 2x^4 + 4x^2, with the limits of integration from 1 to 3.
What is the exact value of the integral of 2x^4 + 4x^2 from 1 to 3?
-The exact value of the integral is 13.147.
Which numerical integration method showed the smallest error in the example?
-The Simpson's 1/3 method showed the smallest error, with a calculated error of 0.22%.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
Integral Numerik dengan metode Simpson serta kode Pythonnya.

LENGKAP Integral tak tentu, integral tertentu, integral subtitusi dan integral parsial

Konsep Dasar Integral Fungsi Aljabar (Integral Part 1) M4THLAB

Numerical Integration With Trapezoidal and Simpson's Rule

INTEGRAL LIPAT 2 #KALKULUS 2

Integration | Finite | Infinite | شرح قواعد التكامل المحدود وغير المحدود Part (1)FCES
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
