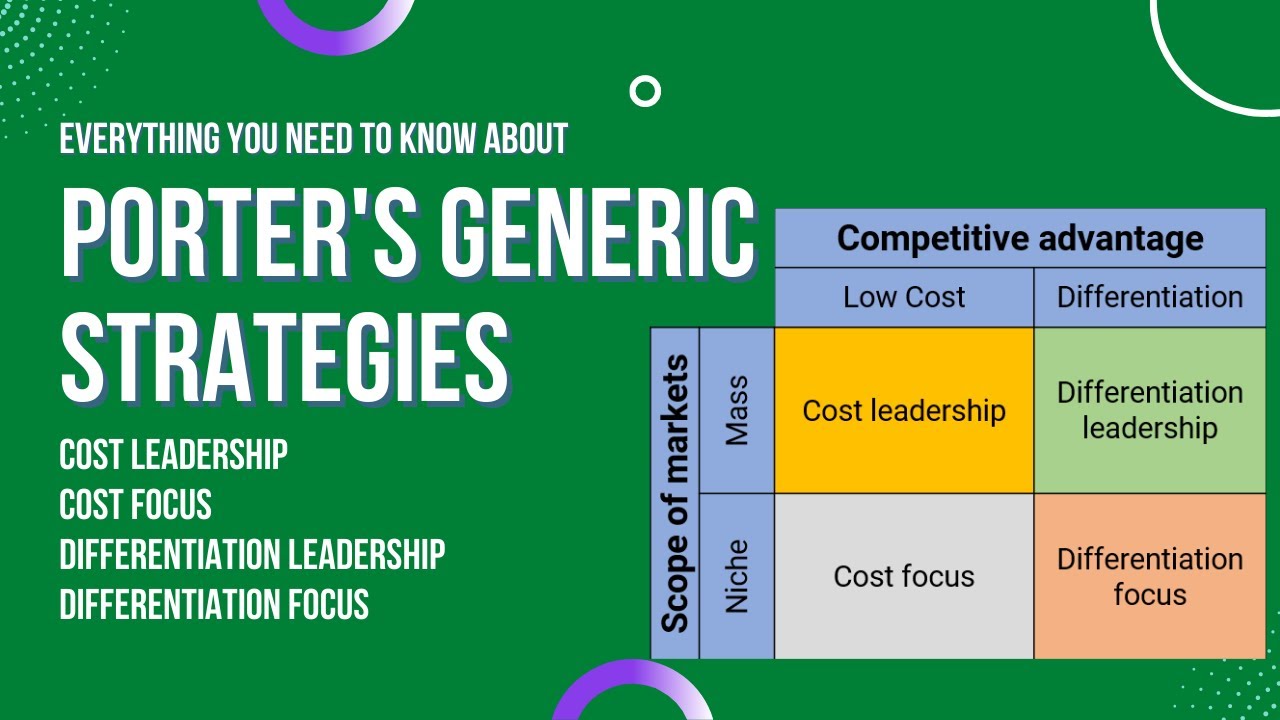
Porter's Generic Strategies Explained with Examples
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson, we explore Michael Porter's Generic Strategies, a framework for achieving a sustainable competitive advantage. The three key strategies are Cost Leadership (being the lowest cost producer), Differentiation (offering unique products), and Focus (targeting a niche market). Focus is further divided into Cost Focus and Differentiation Focus. Porter also warns against mixing strategies, as it can result in being 'stuck in the middle' with no clear competitive edge. Successful companies like Walmart, Apple, and Ikea exemplify these strategies. Ultimately, businesses must select a clear strategy based on their market position and goals.
Takeaways
- 😀 Porter's Generic Strategies help businesses gain a sustainable competitive advantage by offering greater value than competitors.
- 😀 There are three core generic strategies: cost leadership, differentiation, and focus.
- 😀 Cost leadership means becoming the lowest cost producer in the industry, using strategies like economies of scale and tight cost control.
- 😀 Differentiation strategy focuses on creating unique products or services, often at a higher price, leading to customer loyalty.
- 😀 Focus strategy targets a niche market, either by offering the lowest cost or by providing the most unique products in that niche.
- 😀 A firm must avoid being 'stuck in the middle,' where it fails to excel in either cost leadership or differentiation, leading to below-average profitability.
- 😀 Cost leadership does not just mean being cheap but being the lowest cost provider with sustainable practices.
- 😀 Examples of cost leadership firms include Walmart, Southwest Airlines, and Ryanair.
- 😀 Differentiation strategy involves making products unique, with examples including Louis Vuitton, Apple, and Harley-Davidson.
- 😀 Companies that successfully combine strategies, like IKEA, can avoid being stuck in the middle, offering both low cost and differentiation.
- 😀 To apply Porter's strategies, firms should conduct a SWOT analysis for each strategy and choose the one that best suits their position in the market.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of Porter's Generic Strategies?
-The main purpose of Porter's Generic Strategies is to help businesses choose a clear and sustainable strategy to achieve a competitive advantage in the market, which in turn influences their profitability.
How does a clear strategy affect a firm's profitability?
-A clear strategy allows a firm to gain a sustainable competitive advantage over its competitors, leading to better decision-making, more efficient operations, and higher profitability.
What are the three primary mechanisms of Porter's Generic Strategies?
-The three primary mechanisms of Porter's Generic Strategies are cost leadership, differentiation, and focus. Cost leadership aims to be the cheapest, differentiation focuses on creating unique products, and focus targets a niche market.
What does Porter's concept of 'cost leadership' entail?
-Cost leadership refers to a strategy where a firm aims to become the lowest-cost producer within its industry. This can be achieved through economies of scale, tight cost control, and offering simplified products or services.
Why is simply being 'low cost' not enough in a cost leadership strategy?
-Simply being low cost is not enough because competitors can undercut your prices. A true cost leader must ensure it can maintain the lowest costs consistently while offering products that meet customer needs.
Can you give examples of companies that use a cost leadership strategy?
-Examples of companies that use a cost leadership strategy include Walmart, Southwest Airlines, Amazon, and Ryanair. These companies focus on offering lower-cost products or services while still being profitable.
What is the differentiation strategy about?
-The differentiation strategy focuses on making a firm's products or services unique and desirable. Companies using this strategy typically price their offerings higher due to their uniqueness, which fosters customer loyalty.
How does a company using a differentiation strategy benefit from customer loyalty?
-Customer loyalty is a key benefit because it reduces direct competition. Loyal customers are willing to pay a premium for products they perceive as unique, which helps the company maintain its market position.
What are examples of companies using a differentiation strategy?
-Companies using a differentiation strategy include Louis Vuitton, Apple, Lego, and Harley-Davidson. These companies offer unique products or services that stand out from their competitors.
What is the difference between cost focus and differentiation focus?
-Cost focus targets a specific niche and aims to be the lowest-cost provider within that niche, while differentiation focus aims to offer the most unique and desirable products within a niche market.
What does Porter mean by being 'stuck in the middle'?
-Being 'stuck in the middle' refers to firms that attempt to combine multiple strategies, such as cost leadership and differentiation, but fail to execute either effectively. These companies usually suffer from below-average profitability because they don’t excel at any one strategy.
Can a company successfully combine strategies, as Porter's model suggests otherwise?
-Yes, in some cases, companies can successfully combine strategies. For example, Ikea combines cost leadership (through flat-packed furniture) with differentiation (offering unique designs), proving that it is possible to blend strategies and still succeed.
How can a firm decide which of Porter's strategies to adopt?
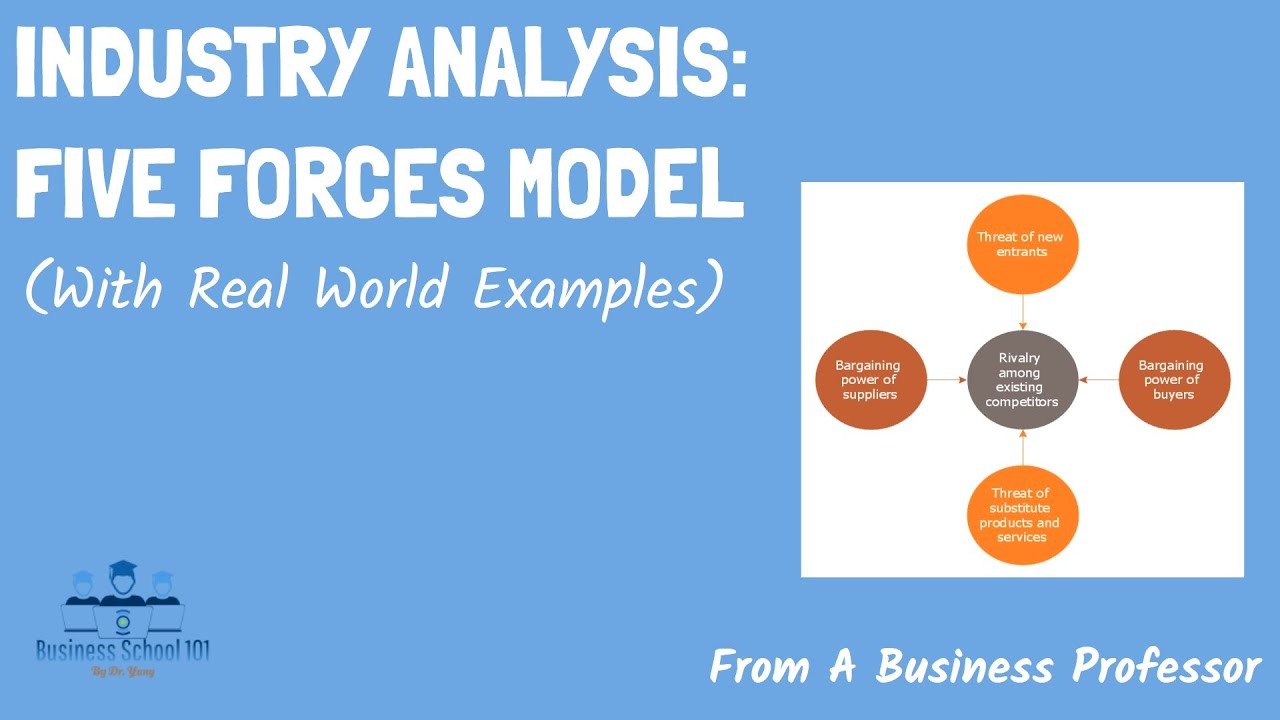
-A firm can use the five forces model to assess market attractiveness, conduct a SWOT analysis for each strategy to understand the pros and cons, and then select the most appropriate strategy that best aligns with its market position and goals.
Why might a firm fail to choose the best strategy according to Porter’s model?
-A firm might fail to choose the best strategy if it does not conduct thorough market analysis, is unclear about its competitive position, or attempts to combine strategies that cannot be executed effectively, leading to 'strategic mediocrity.'
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)