Ureaplasma Infection *what you need to consider*
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the host discusses Ureaplasma and Mycoplasma, two bacteria that can cause infections in the vaginal canal and urethra. While these infections are often transmitted sexually, they are not classified as typical STDs. Common symptoms include vaginal burning, painful urination, and watery discharge. Ureaplasma and Mycoplasma can lead to complications like infertility, miscarriage, and abnormal pap smears. Testing is simple and involves a swab, and treatment typically consists of antibiotics. The video emphasizes the importance of testing and treating both partners, especially for those with recurring symptoms or fertility concerns.
Takeaways
- 😀 Ureaplasma and Mycoplasma are tiny bacteria that can colonize the vaginal canal and urethra, transmitted through sexual contact.
- 😀 These infections are not classified as typical STDs like chlamydia, gonorrhea, or herpes, but can cause symptoms such as vaginal burning, urinary burning, watery vaginal discharge, and a fishy odor.
- 😀 Men can often be asymptomatic carriers, while women tend to show more noticeable symptoms.
- 😀 Ureaplasma and Mycoplasma can lead to cervicitis, endometritis, infertility, and complications with pregnancy such as miscarriage, fetal demise, and premature rupture of membranes (PROM).
- 😀 These infections can also cause respiratory issues in infants if transmitted during childbirth.
- 😀 Abnormal pap smears can sometimes occur in the absence of HPV, often due to infections like Ureaplasma and Mycoplasma.
- 😀 If you've had recurrent abnormal pap smears without HPV, it's recommended to test for Ureaplasma and Mycoplasma infections.
- 😀 Testing for these infections is simple, typically done via vaginal or cervical swab, though urine tests may be inaccurate and prone to false negatives.
- 😀 Treatment usually involves antibiotics like doxycycline or azithromycin, but resistant infections may require additional rounds of antibiotics such as Levaquin or Cipro.
- 😀 Follow-up testing is important to confirm the infection is cleared, and both partners should be treated, especially if infertility or pregnancy complications are a concern.
Q & A
What are urea plasma and mycoplasma, and how are they transmitted?
-Urea plasma and mycoplasma are tiny bacteria that can colonize the vaginal canal and the urethra. They are typically transmitted through direct or sexual contact, though they are not classified under the standard sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) like chlamydia, gonorrhea, or herpes.
What are some common symptoms of urea plasma and mycoplasma infections?
-Common symptoms include vaginal burning, burning during urination, watery vaginal discharge, and sometimes a fishy odor. In men, penile discharge can occur, but many people, especially men, may remain asymptomatic carriers.
Can urea plasma and mycoplasma infections lead to serious complications?
-Yes, these infections can cause serious complications, such as cervicitis, endometritis, infertility, early pregnancy loss (miscarriage), late-term pregnancy complications, and premature rupture of membranes (PROM). Infants born to mothers with these infections may also experience respiratory issues.
How do urea plasma and mycoplasma infections affect pregnancy?
-These infections can increase the risk of complications such as early miscarriage, late-term pregnancy loss, premature rupture of membranes, and infections of the amniotic fluid. In some cases, transmission to the baby during pregnancy can lead to respiratory problems in the infant.
What is the relationship between abnormal pap smears and urea plasma/mycoplasma infections?
-Urea plasma and mycoplasma infections can cause abnormal pap smears, even in the absence of HPV (Human Papillomavirus). While HPV is a known cause of abnormal cervical cell changes, infections like urea plasma and mycoplasma can also lead to similar abnormalities due to inflammation or infection.
How is urea plasma tested for?
-Testing for urea plasma is typically done via a vaginal or cervical swab, similar to a regular STD culture or pap smear. Testing through urine is less accurate and tends to result in false negatives, so a vaginal culture is preferred.
What is the first-line treatment for urea plasma and mycoplasma infections?
-The first-line treatment for these infections typically involves antibiotics such as doxycycline or azithromycin. If the infection is resistant or recurring, stronger antibiotics like Levaquin or Cipro (in the fluoroquinolone family) may be prescribed.
How is treatment monitored for urea plasma and mycoplasma infections?
-After completing a round of antibiotics, patients are typically brought back for a follow-up culture four weeks later to check if the infection has cleared. If still positive, a second round of antibiotics may be needed, and partners should be treated as well, especially if pregnancy or infertility is a concern.
What should patients do if they experience symptoms like vaginal burning or watery discharge?
-If you're experiencing symptoms such as vaginal burning, watery discharge with an odor, or pain during intercourse, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider for testing. Urea plasma and mycoplasma may be the cause, especially if standard tests for yeast infections, BV, or UTIs return negative.
Why are urea plasma and mycoplasma infections becoming more common?
-Urea plasma and mycoplasma infections are increasingly being identified in clinical settings, especially among women with recurrent vaginal symptoms or unexplained infertility. They can often be mistaken for other conditions, leading to underdiagnosis until proper testing is done.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Normal vagina flora; Lactobacillus species dominate healthy vaginal microbiome
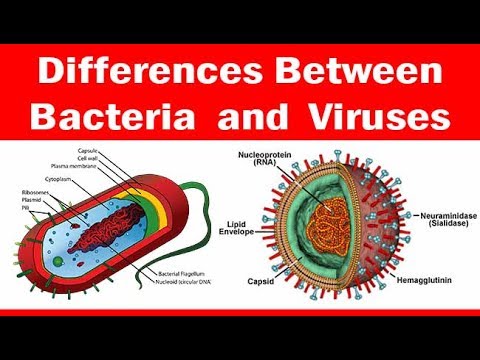
Viruses vs. Bacteria | What's The Difference?

URETRITIS RADANG SALURAN KENCING DAN SOLUSINYA - DOKTER SADDAM ISMAIL
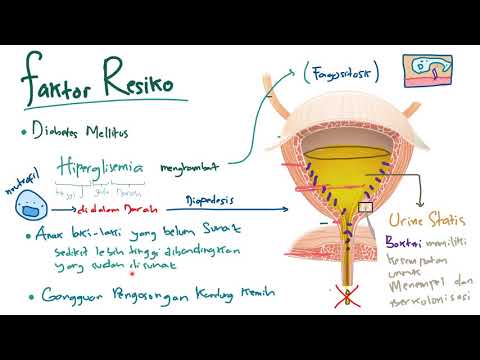
Patofisiologi - Infeksi saluran kemih bagian bawah (ISK) / Lower urinary tract infection (UTI)

Bacterial Pathogenesis: How Bacteria Cause Damage

Bacterial Infections - Causes, Symptoms and Treatments and More
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
