URETRITIS RADANG SALURAN KENCING DAN SOLUSINYA - DOKTER SADDAM ISMAIL
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker explains urethritis, an inflammation of the urethra, which can cause pain, discomfort, and complications like urinary issues, infections, and infertility. Urethritis is more common in women due to their shorter urethra and can be caused by bacterial or viral infections, including gonorrhea and chlamydia. Symptoms vary for men and women, ranging from painful urination to pelvic discomfort. The speaker emphasizes the importance of prevention, such as safe sexual practices and hygiene. Treatment typically involves antibiotics or antivirals depending on the cause, and early intervention is crucial to avoid severe complications.
Takeaways
- 😀 Urethritis is inflammation or swelling of the urethra, the tube connecting the bladder to the outside of the body.
- 😀 The condition can cause discomfort, especially when urinating, such as pain or a burning sensation.
- 😀 Women are more likely to experience urethritis due to the shorter length of their urethra compared to men.
- 😀 The most common cause of urethritis is bacterial infection, often from bacteria around the genital area entering the urethra.
- 😀 There are two main types of urethritis: gonococcal (caused by gonorrhea) and non-gonococcal (caused by various other bacteria, viruses, or irritants).
- 😀 Non-gonococcal causes include chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, and even viruses like cytomegalovirus and human papillomavirus.
- 😀 Risk factors for urethritis include unsafe sexual practices, frequent partner changes, and a history of sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- 😀 Common symptoms in men include painful urination, penile discharge, swollen lymph nodes, and pain during ejaculation or sexual intercourse.
- 😀 For women, symptoms often include pelvic pain, discomfort during urination, vaginal discharge, and fever or chills.
- 😀 Treatment typically involves antibiotics for bacterial causes, or antiviral medication for viral infections, with the goal of eliminating the infection.
- 😀 Untreated urethritis can lead to complications such as infections of the testes, kidneys, or bladder, as well as infertility and prostatitis in men, and pelvic inflammatory disease or vaginitis in women.
- 😀 Preventive measures include practicing safe sex, maintaining genital hygiene, and urinating after sexual activity to reduce the risk of infection.
Q & A
What is urethritis?
-Urethritis is the inflammation or swelling of the urethra, which is the tube that connects the bladder to the outside of the body. It is responsible for the excretion of urine, and when inflamed, it can cause discomfort, especially during urination.
What causes urethritis?
-Urethritis is primarily caused by bacterial infections, most commonly from sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Other causes include viral infections, parasites, and irritation from chemicals. Common bacteria include Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonorrhea), Chlamydia, Mycoplasma genitalium, and Ureaplasma urealyticum.
Who is most at risk for developing urethritis?
-Women are more likely to develop urethritis due to the shorter length of their urethra compared to men. Other risk factors include unprotected sex, multiple sexual partners, and a history of sexually transmitted infections.
What are the main symptoms of urethritis in men?
-The common symptoms of urethritis in men include painful urination, a burning sensation when urinating, a yellow or green discharge from the penis, swelling and redness in the genital area, and pain during ejaculation or sexual intercourse.
What symptoms of urethritis might women experience?
-Women with urethritis may experience painful urination, pelvic or lower abdominal pain, fever, abnormal vaginal discharge, and discomfort during or after sexual intercourse.
How is urethritis diagnosed?
-Urethritis is typically diagnosed through a physical examination and laboratory tests, such as urine tests or a swab from the genital area to detect the presence of bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens.
What treatments are available for urethritis?
-Treatment depends on the underlying cause. If the infection is bacterial, antibiotics are prescribed to eliminate the bacteria. For viral infections, antiviral medications may be used. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage discomfort.
What complications can arise from untreated urethritis?
-If left untreated, urethritis can lead to serious complications such as kidney infections, bladder infections, prostatitis in men, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women, and even infertility.
Can urethritis be prevented?
-Preventing urethritis involves practicing safe sex (using condoms), maintaining proper genital hygiene, and avoiding multiple sexual partners or unprotected sexual contact. Staying hydrated and urinating after sexual activity can also help reduce the risk of infection.
What are the different types of urethritis?
-There are two main types of urethritis: gonococcal urethritis, caused by the gonorrhea bacteria, and non-gonococcal urethritis, which can be caused by other bacteria, viruses, or parasites such as Chlamydia, Mycoplasma, and Trichomonas.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
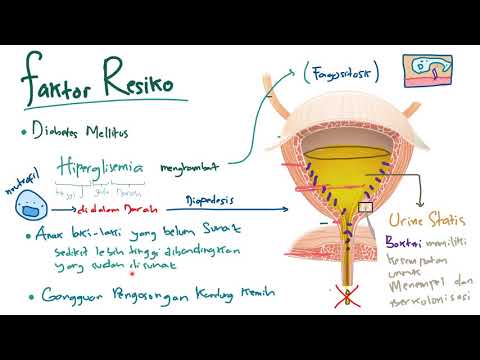
Patofisiologi - Infeksi saluran kemih bagian bawah (ISK) / Lower urinary tract infection (UTI)

Ureaplasma Infection *what you need to consider*

Ectopic Pregnancy: Causes & Symptoms | Vijay Karnataka | Dr. Sunil Eshwar | Aster RV Hospital
MAPA MENTAL SIMPLIFICADO DO SISTEMA URINÁRIO

How Oxalates Can Cause Chronic UTI, Interstitial Cystitis & Bladder Irritation

Hemodialysis
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)