MATEMATIKA KELAS 9 - PELUANG - KONSEP PELUANG
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the concept of probability is explained through various examples such as tossing coins, rolling dice, and drawing balls from a bag. The presenter covers the fundamental formula for calculating probabilities, emphasizes the importance of determining sample spaces, and provides step-by-step solutions to different problems. Viewers are shown how to calculate the likelihood of events like getting heads or tails, rolling specific numbers, and drawing certain colored balls. The video encourages engagement and continued learning through interactive explanations and problem-solving.
Takeaways
- 😀 The concept of probability involves comparing the observed event to all possible events or the sample space.
- 😀 The probability of an event A is calculated as the ratio of the number of occurrences of event A to the total number of possible outcomes in the sample space.
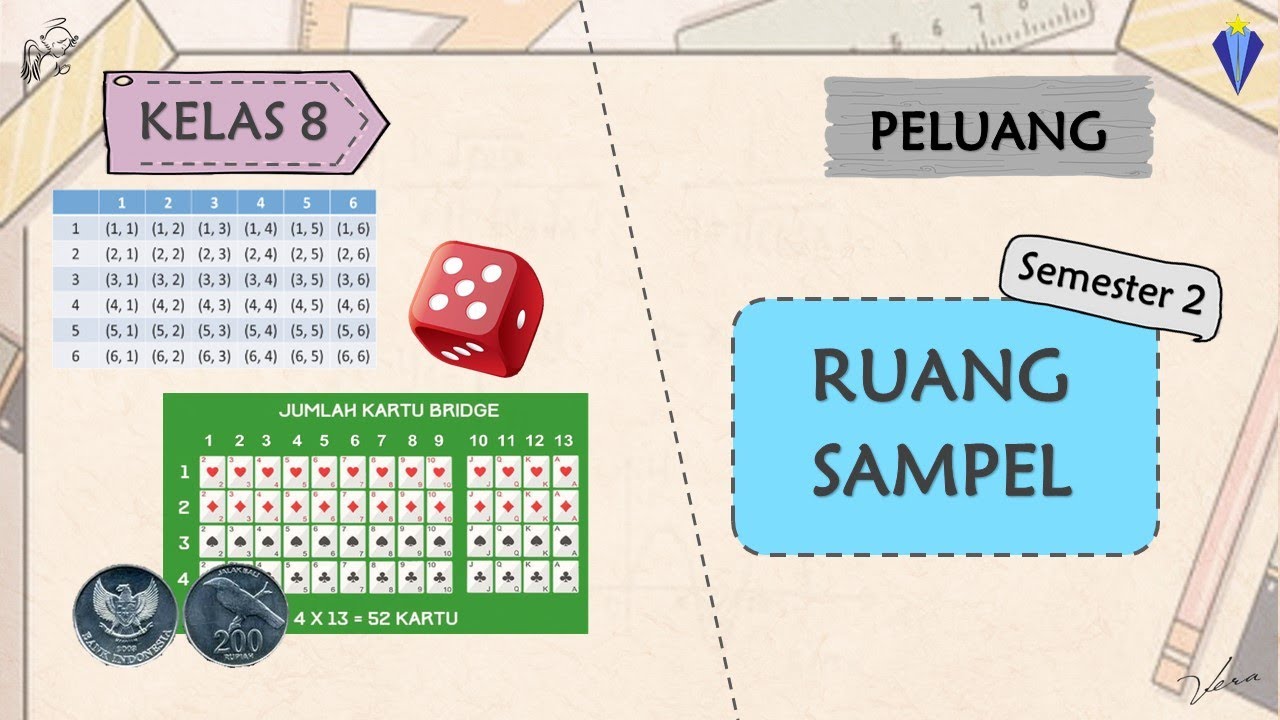
- 😀 For two coins being tossed, the sample space consists of four possible outcomes: (Heads, Heads), (Heads, Tails), (Tails, Heads), and (Tails, Tails).
- 😀 The probability of both coins landing on heads is 1/4, while the probability of getting at least one tails (Head-Tail or Tail-Head) is 1/2.
- 😀 When tossing three coins, the sample space has 8 outcomes, and the probability of all heads is 1/8, while the probability of having at least one heads is 7/8.
- 😀 In the case of a die, the sample space consists of 6 outcomes (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6). The probability of rolling an odd number (1, 3, or 5) is 3/6 or 1/2.
- 😀 For a prime number on a die, the possible outcomes are 2, 3, and 5, giving a probability of 3/6 or 1/2.
- 😀 When two dice are thrown, the probability of the black die showing 5 is 1/6, and the probability of their sum being 6 is 5/36.
- 😀 The probability of the difference between the dice being 4 (either 5-1 or 6-2) is 4/36 or 1/9.
- 😀 The probability of rolling doubles (the same number on both dice) is 6/36, while the probability of the red die showing at least 3 is 24/36 or 2/3.
- 😀 The probability of drawing a blue ball from a bag containing 4 blue balls and 6 red balls is 4/10 or 2/5.
- 😀 The probability of drawing a card numbered 3 from a deck of 52 cards is 4/52 or 1/13.
Q & A
What is probability and how is it calculated?
-Probability is the comparison between observed events and all possible events. It is calculated using the formula: P(A) = (Number of favorable outcomes) / (Total number of possible outcomes), where 'A' represents the event being observed and the denominator represents the sample space.
What is the sample space when tossing two coins?
-The sample space for tossing two coins consists of four possible outcomes: {HH, HT, TH, TT}. These represent the possible results for each coin toss, with 'H' standing for heads and 'T' for tails.
What is the probability of getting two heads when tossing two coins?
-The probability of getting two heads (HH) when tossing two coins is 1/4. This is because there is one favorable outcome (HH) out of four possible outcomes in the sample space.
How do you calculate the probability of getting at least one head when tossing three coins?
-To calculate the probability of getting at least one head when tossing three coins, first exclude the outcome where all coins show tails (TTT). The sample space has 8 outcomes in total, and 7 of those include at least one head. Therefore, the probability is 7/8.
What is the probability of rolling an odd number on a six-sided die?
-The odd numbers on a six-sided die are 1, 3, and 5, so there are 3 favorable outcomes. Since there are 6 possible outcomes in total, the probability of rolling an odd number is 3/6 = 1/2.
What is the probability of getting a sum of 6 when rolling two dice?
-The probability of getting a sum of 6 when rolling two dice is 5/36. The five possible outcomes that sum to 6 are (1,5), (2,4), (3,3), (4,2), and (5,1).
How do you calculate the probability of rolling a difference of 4 between two dice?
-The probability of rolling a difference of 4 between two dice is 4/36 = 1/9. The possible outcomes with a difference of 4 are (5,1), (6,2), (1,5), and (2,6).
What is the probability of rolling doubles (same number on both dice) with two dice?
-The probability of rolling doubles with two dice is 6/36 = 1/6. The six possible outcomes where both dice show the same number are (1,1), (2,2), (3,3), (4,4), (5,5), and (6,6).
What is the probability of drawing a blue ball from a bag containing 4 blue balls and 6 red balls?
-The probability of drawing a blue ball from a bag containing 4 blue balls and 6 red balls is 4/10 = 2/5. There are 4 favorable outcomes (blue balls) out of 10 total balls.
What is the probability of drawing a card numbered 3 from a deck of 52 cards?
-The probability of drawing a card numbered 3 from a deck of 52 cards is 4/52 = 1/13. There are 4 cards with the number 3, one from each suit (hearts, diamonds, spades, and clubs).
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

MENENTUKAN RUANG SAMPEL DAN TITIK SAMPEL PELUANG PART 1

Pembahasan materi PELUANG dasar! Sampai semua paham, ngerti, understand! #MatematikAsik
1. RUANG SAMPEL - PELUANG - KELAS 8 SMP

Peluang Teoritik

Menentukan Peluang Empirik Frekuensi Relatif dari Suatu Kejadian

Media Pembelajaran Matematika Materi Peluang
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
