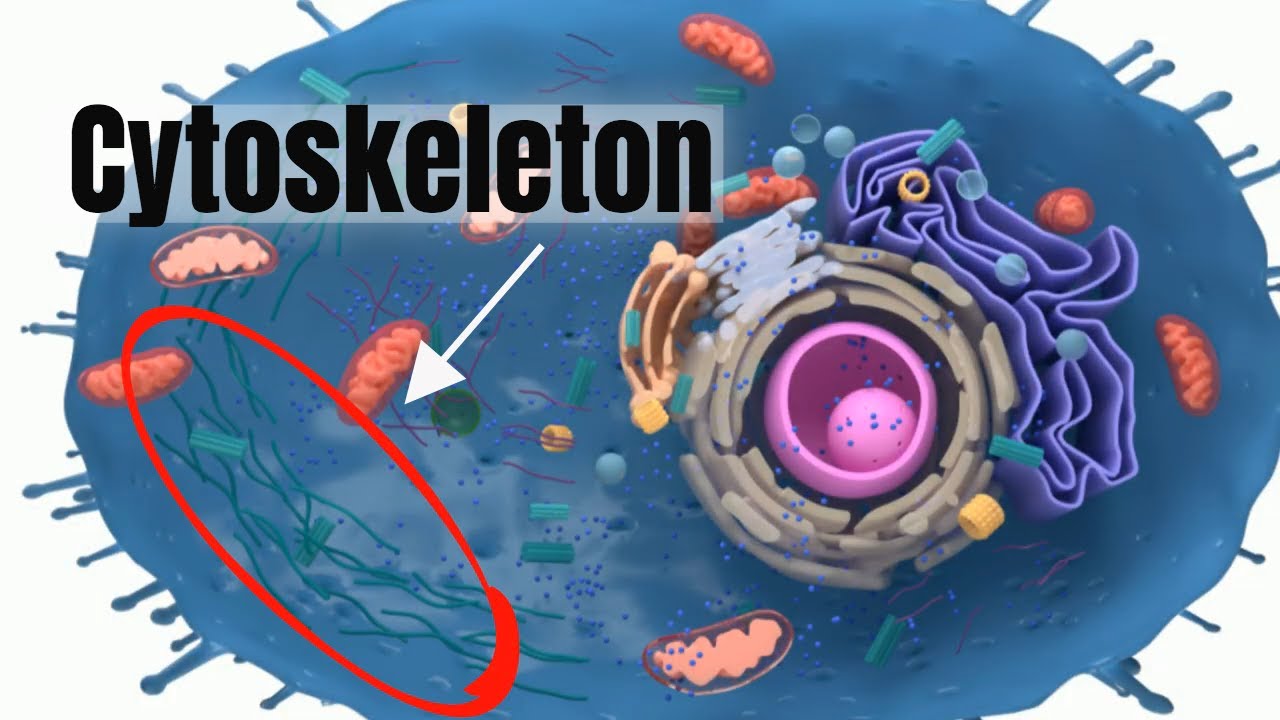
CITOESQUELETO - CITOLOGIA | Biologia com Samuel Cunha
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses essential concepts in cell biology, focusing on the cytoskeleton and its components, including microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. It explains the specific roles of different filaments in various tissues, such as neurofilaments in neurons, cytokeratin in the skin, and vimentin in connective tissue. The teacher offers insights into the structure and function of cells and motivates students to persist in their studies. The lesson also hints at deeper exploration of actin microfilaments in future sessions, highlighting the dynamic nature of biology education.
Takeaways
- 😀 The cytoskeleton consists of different types of intermediate filaments, each specific to certain cell types.
- 😀 Neurons contain neurofilaments, which are key components of their cytoskeleton.
- 😀 Epidermal cells contain cytokeratin, an intermediate filament that helps maintain skin structure and resilience.
- 😀 Cytokeratin plays a crucial role in skin lesions and is involved in embryonic attachment development.
- 😀 Connective tissue cells use vimentin as their intermediate filament, which helps maintain cell structure and integrity.
- 😀 Muscle cells have desmin, an intermediate filament that supports muscle cell structure and function.
- 😀 The speaker briefly discusses the three major components of the cytoskeleton: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules.
- 😀 Cilia are an important cytoskeletal structure, likely covered in a separate detailed lesson.
- 😀 Mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and peroxisomes play vital roles in cellular function, especially in the cytoplasm.
- 😀 The speaker emphasizes the importance of understanding the differentiation of cytoskeletal components in various tissues.
- 😀 Encouragement is given for perseverance in studies, with a reminder that the journey may be difficult but is ultimately rewarding.
Q & A
What are neurofilaments and what role do they play in cells?
-Neurofilaments are intermediate filaments found in neurons. They provide structural support to the cell and help maintain the shape of the neuron. These filaments are important for the mechanical strength of the neuron and assist in the organization of the cytoskeleton within nerve cells.
What is the significance of keratin in the epidermis?
-Keratin is a type of intermediate filament found in the epidermis. It plays a crucial role in the structural integrity of the skin, providing resilience and protection against physical stress, water loss, and pathogens. Keratin is responsible for the tough, waterproof nature of the outer layer of the skin.
What is the function of vimentin in connective tissue?
-Vimentin is an intermediate filament found in connective tissue cells. It is important for maintaining the shape and stability of the cell, as well as providing mechanical support to the tissues. Vimentin also plays a role in various cellular processes, including signal transduction and cell movement.
How does actin contribute to the cytoskeleton?
-Actin is a major component of microfilaments, which are part of the cytoskeleton. It plays a critical role in cell movement, division, and shape. Actin filaments form a network beneath the cell membrane, supporting cellular processes such as muscle contraction, cell migration, and the formation of cell protrusions like filopodia.
What are the key differences between the three types of cytoskeletal filaments?
-The three types of cytoskeletal filaments are microfilaments (made of actin), intermediate filaments (such as vimentin and keratin), and microtubules (made of tubulin). Microfilaments are involved in cell movement and structure, intermediate filaments provide mechanical strength, and microtubules help with cell division and intracellular transport.
What is the role of mitochondria in cells as mentioned in the script?
-Mitochondria are the energy-producing organelles of the cell. They generate ATP, which is essential for various cellular processes. The script suggests that understanding the function of mitochondria is crucial when studying cell structures in advanced biology.
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) as highlighted in the transcript?
-The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) plays a vital role in protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. It can be rough (with ribosomes attached) or smooth (without ribosomes). The rough ER is involved in protein production and folding, while the smooth ER is involved in lipid production and detoxification processes.
Why are intermediate filaments important in muscle cells?
-In muscle cells, intermediate filaments such as desmin help maintain cell integrity and facilitate the mechanical strength needed for muscle contraction. These filaments anchor the contractile elements within the cell and maintain the organization of muscle fibers.
What does the script suggest about the study of cytoskeleton in higher education?
-The script implies that the study of the cytoskeleton becomes more specialized and detailed in higher education, often going beyond the general topics covered in high school. Advanced studies may require a deeper understanding of the various components of the cytoskeleton and their specific functions in different cell types.
What advice does the speaker give regarding the study process?
-The speaker encourages persistence in studies, reminding the audience that the journey may be challenging at first but becomes easier over time. The speaker emphasizes that the first step is often the hardest, and with time, the process becomes more manageable and rewarding.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)