Citoesqueleto - Aula 21 - Módulo 1: Biologia celular
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the concept of the cytoskeleton in cells, a crucial yet often overlooked structure that provides support, shape, and movement. The cytoskeleton is made up of three main types of protein fibers: microtubules, intermediate filaments, and microfilaments. It plays vital roles in cellular organization, division, and internal transport of substances. The video delves into the functions of these components, such as the movement of vesicles, cellular shape maintenance, and cell division processes like mitosis and meiosis. With engaging visuals and explanations, the video aims to simplify this essential topic for students and biology enthusiasts.
Takeaways
- 😀 Microscopy advancements in 1931 allowed a better understanding of cellular structures, leading to the discovery of the cytoskeleton in the 1950s.
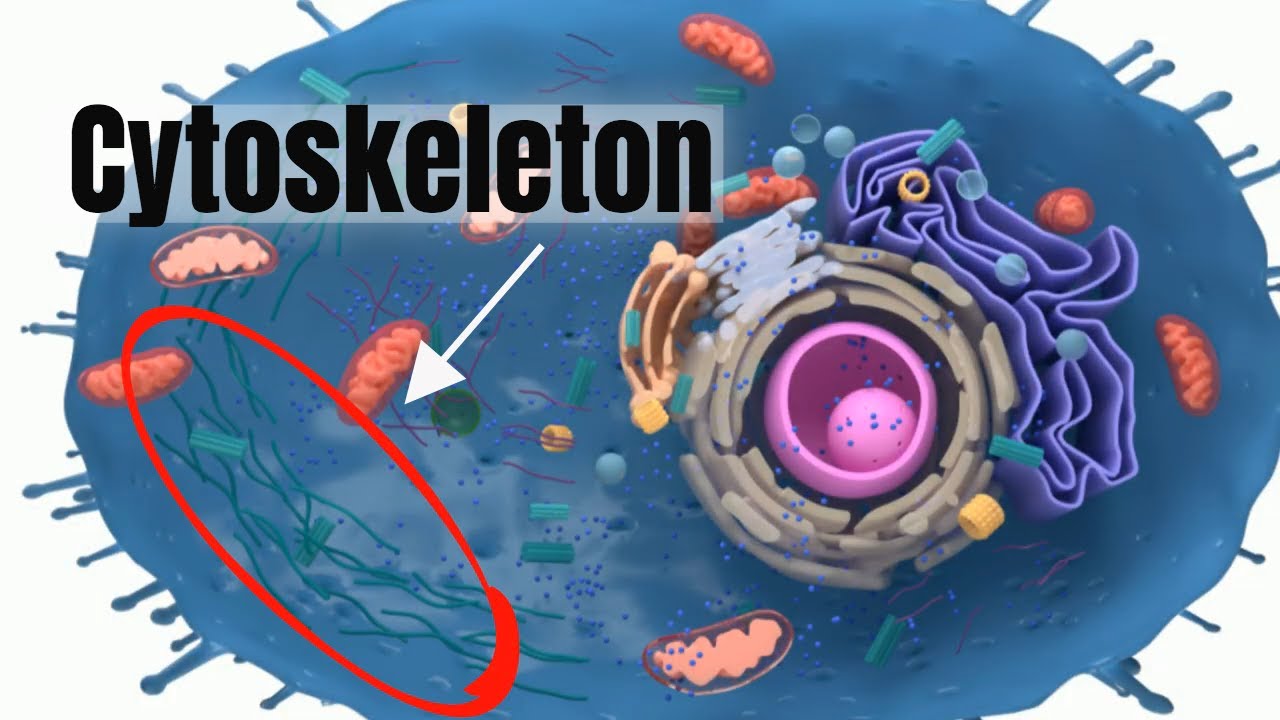
- 😀 The cytoskeleton is a network of protein fibers that provides structure, support, and transportation within cells.
- 😀 The term 'cytoskeleton' comes from 'cyto' meaning cell and 'skeleton' referring to structural support, just like bones in a human body.
- 😀 The cytoskeleton's primary functions include providing cell structure, facilitating movement, and supporting organelles inside the cell.
- 😀 Prokaryotic cells (like bacteria) do not have a cytoskeleton, unlike eukaryotic cells that possess it.
- 😀 The cytoskeleton enables cell motility (movement) and internal transport of substances within vesicles.
- 😀 Microtubules, one of the types of cytoskeletal fibers, are important for chromosome movement during cell division (mitosis and meiosis).
- 😀 Microtubules also facilitate the internal movement of organelles and vesicles within the cell, functioning like transportation highways.
- 😀 Intermediate filaments, formed mainly of keratin, provide mechanical strength and structural integrity to the cell, including around the nucleus.
- 😀 Microfilaments are the smallest cytoskeletal fibers and play a key role in cell shape changes, amoeboid movement, and the process of cytokinesis during cell division.
- 😀 The cytoskeleton supports both the cell’s external structure and internal organization, ensuring the proper positioning and function of organelles.
Q & A
What discovery in the 1950s revolutionized our understanding of cells?
-In the 1950s, the discovery that cells have a skeleton, called the cytoskeleton, which supports organelles, facilitates the transport of substances, and gives shape to the cell, significantly advanced our understanding of cell biology.
What is the cytoskeleton made of?
-The cytoskeleton is made of a network of protein fibers that help in various cellular functions such as support, movement, and transport of substances inside the cell.
What is the main function of the cytoskeleton in a cell?
-The cytoskeleton provides structural support, helps maintain cell shape, enables cellular movement, and facilitates the internal transport of substances, including organelles and vesicles.
Do prokaryotic cells have a cytoskeleton?
-Prokaryotic cells, such as bacterial cells, do not have a cytoskeleton, at least not in the same way eukaryotic cells do. While they may have some structural fibers, they are not considered part of a full cytoskeleton in prokaryotes.
How does the cytoskeleton contribute to cell motility?
-The cytoskeleton enables cell motility by allowing cells to move or change shape. For example, it aids in amoeboid movement, where the cell changes shape to move, and also helps cells like macrophages travel through tissues or the bloodstream.
What is the role of microtubules in cell division?
-Microtubules play a crucial role in cell division, particularly in the process of mitosis and meiosis. They help organize and separate chromosomes during the division process, ensuring accurate cell division.
What are the three main types of protein fibers that make up the cytoskeleton?
-The three main types of protein fibers that make up the cytoskeleton are microtubules, intermediate filaments, and microfilaments. Each type has distinct roles in maintaining cell structure, movement, and transport.
What are microtubules, and what are they made of?
-Microtubules are tube-like structures made of protein subunits called tubulins. They are the thickest of the cytoskeletal fibers and are involved in processes such as cell division, organelle movement, and vesicle transport within the cell.
What are intermediate filaments, and how do they contribute to cell structure?
-Intermediate filaments are protein fibers made of keratin that are intermediate in size between microtubules and microfilaments. They provide structural support to the cell, help maintain its shape, and stabilize the position of organelles, including the nucleus.
How do microfilaments function within the cell?
-Microfilaments, the thinnest of the cytoskeletal fibers, are involved in cell shape changes, movement (like amoeboid movement), and processes such as cytoplasmic streaming in plant cells. They also play a role in cell division by facilitating the cleavage of the cell during cytokinesis.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Cytoskeleton Structure and Function | Role in Motility
Cytoskeleton: The skeleton of the cell PLUS MORE

Biologia Celular-Ensino Superior-Aula 21:Citoesqueleto II- Microfilamentos

Connective Tissue | Connective Tissue Proper | Body Tissues | Human Histology

Cell Cytoskeleton Structure & Functions || Microtubules || Thin, Thick and Intermediate Filaments

Cell Organelles and Structures - A Tour of the Cell
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)