Metabolismo dos lipídeos (Jejum e Bem alimentado) - Bioquímica
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the metabolism of lipids, focusing on triglycerides and cholesterol. It explains how fatty acids, the core of most lipids, are classified into saturated and unsaturated types, and how they are metabolized through processes like esterification. The video also covers the digestion and absorption of lipids, their transport in lipoproteins, and the roles of different proteins like HDL and LDL in managing cholesterol. It touches on lipid synthesis (lipogenesis) and the breakdown of lipids (lipolysis) in response to metabolic states like feeding and fasting, emphasizing the importance of cholesterol in hormone production and cellular structure.
Takeaways
- 😀 Fatty acids are the main components of lipids and can be classified as saturated (no double bonds) or unsaturated (one or more double bonds).
- 😀 Saturated fats, like butter, are solid at room temperature, while unsaturated fats, such as vegetable oils, are liquid.
- 😀 Triglycerides and cholesterol are both lipids; triglycerides are simple lipids, and cholesterol is a compound lipid when bound with other molecules.
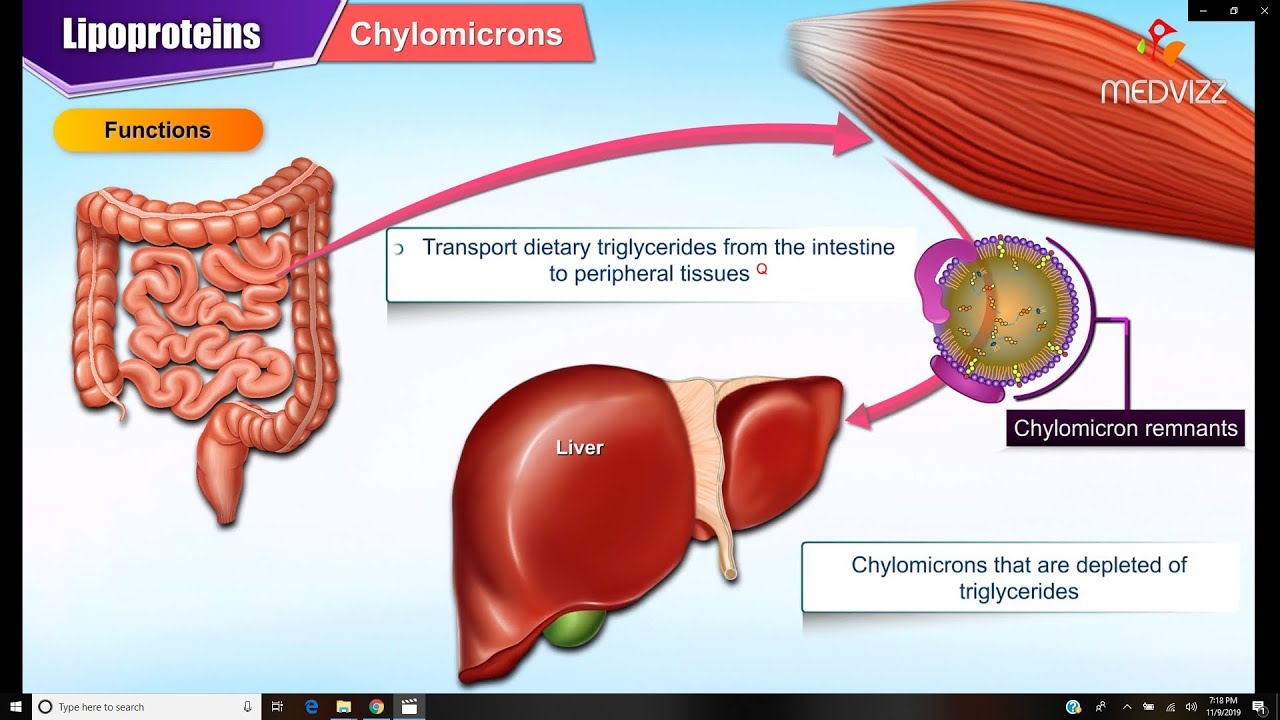
- 😀 Lipids are absorbed into the bloodstream via chylomicrons, which are complexes of lipids and proteins.
- 😀 Lipoproteins, such as LDL (bad cholesterol) and HDL (good cholesterol), transport lipids throughout the body. LDL carries cholesterol to cells, while HDL removes excess cholesterol from the body.
- 😀 Insulin stimulates the synthesis of fatty acids from glucose (lipogenesis), which are stored as fat in the body during the fed state.
- 😀 Cholesterol is synthesized in the liver and is essential for hormone production and the integrity of cell membranes.
- 😀 The process of cholesterol synthesis occurs in four stages, starting from acetyl-CoA and regulated by enzymes like HMG-CoA reductase.
- 😀 In the fasting state, lipolysis occurs, breaking down triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol, which are used for energy.
- 😀 Fatty acids are oxidized in the mitochondria to produce ATP, and if excess fatty acids are not fully oxidized, they are converted into ketones in the liver, which provide alternative energy.
- 😀 Lipid metabolism is regulated by hormones like insulin and glucagon, which influence lipogenesis (fat storage) and lipolysis (fat breakdown).
Q & A
What are the main components of lipids, and how are they classified?
-Lipids are primarily composed of fatty acids, which are formed by long carbon chains. These fatty acids can be classified as saturated or unsaturated. Saturated fatty acids have only single bonds between carbon atoms, while unsaturated fatty acids contain one or more double bonds between carbon atoms.
What happens during the esterification of fatty acids?
-During esterification, fatty acids undergo a chemical reaction with alcohol, typically glycerol, to form triglycerides. If the resulting compound contains only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, it is classified as a simple lipid, such as triglycerides.
How are lipids transported in the body?
-Lipids are transported in the form of chylomicrons, which are composed of cholesterol, triglycerides, lipids, and proteins. These chylomicrons are absorbed from the digestive system and carry lipids to various tissues, where they are utilized or stored.
What is the role of HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein)?
-HDL is known as 'good cholesterol' because it helps remove excess cholesterol from the body, carrying it back to the liver for processing and disposal. Higher HDL levels are considered beneficial for cardiovascular health.
What is the difference between LDL and VLDL in terms of cholesterol content?
-LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) and VLDL (Very Low-Density Lipoprotein) are types of lipoproteins that transport cholesterol. LDL has about 50% cholesterol content and is responsible for delivering cholesterol to cells. VLDL, on the other hand, has a higher triglyceride content and delivers fat to cells.
What is lipogenesis, and when does it occur?
-Lipogenesis is the process of synthesizing lipids from excess glucose, typically occurring after meals when glucose levels are high. This process mainly happens in adipose tissue and involves the conversion of glucose into fatty acids, which are then stored as fat.
What are the key steps involved in cholesterol synthesis?
-Cholesterol synthesis involves four main steps: 1) Formation of mevalonate from acetyl-CoA, 2) Formation of isoprenoid units, 3) Formation of squalene, and 4) Conversion of squalene into cholesterol. The enzyme HMG-CoA reductase plays a crucial role in the first step and is regulated by insulin.
How does the body process lipids during fasting?
-During fasting, the hormone glucagon is predominant, and lipolysis occurs, breaking down triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol. These fatty acids are used by muscles for energy. Excess fatty acids are processed in the liver to produce ketone bodies as an alternative energy source.
What is the role of insulin in lipid metabolism?
-Insulin promotes lipid synthesis, including the synthesis of cholesterol and fatty acids, by stimulating enzymes involved in lipogenesis. It also facilitates the storage of excess lipids in adipose tissue.
What are ketone bodies, and when are they produced?
-Ketone bodies (acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone) are produced during the breakdown of fatty acids in the liver when glucose availability is low, such as during fasting or prolonged exercise. They serve as an alternative energy source for tissues like the brain and muscles.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Konsep Dasar Lipid(Lemak) : Kolesterol, Trigliserida, Fosfolipid

LIPOPROTEÍNAS - QUILOMÍCRONS, VLDL, LDL E HDL

1: Lipids: Definition, Classification, functions |Lipid Chemistry-1| Biochemistry
Lipoproteins and Apolipoproteins - Structure , function and metabolism : Medical Biochemistry

Lipids Part 1
A-Level Biology - Lipids: Triglycerides & Phospholipids | Cholesterol (2026/27 exams)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
