METABOLISME LIPID (JALUR EKSOGEN)
Summary
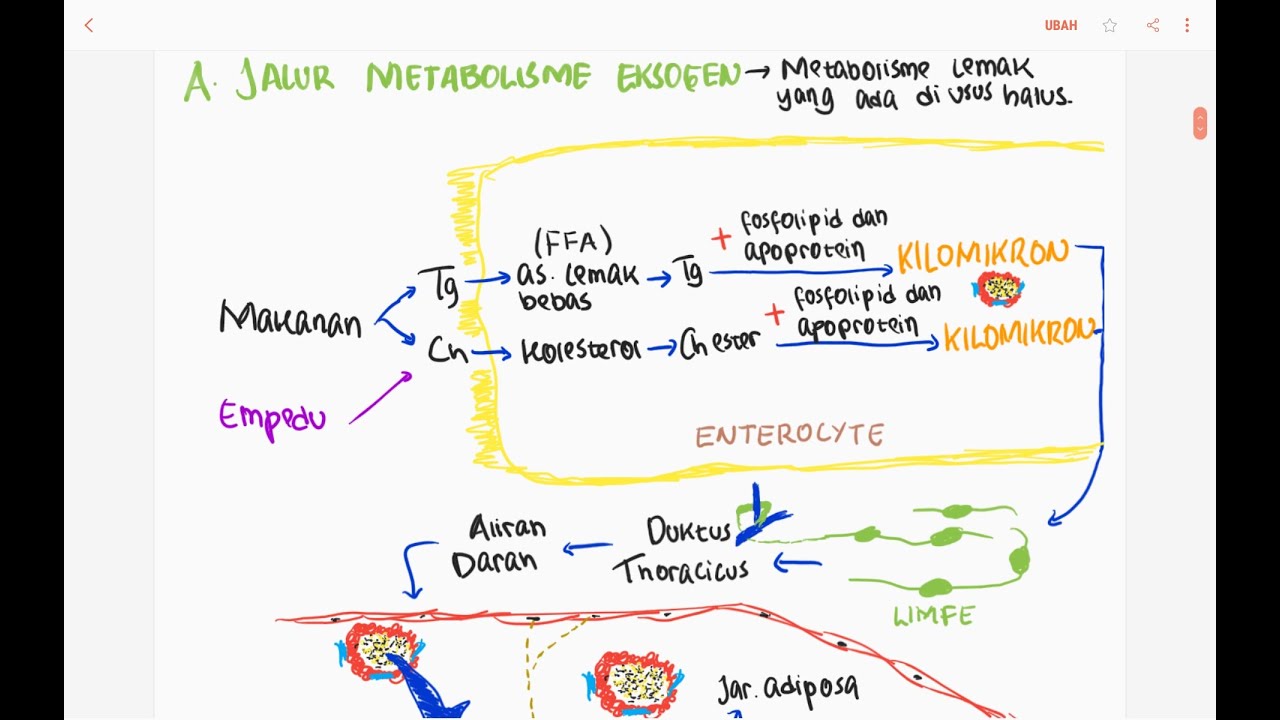
TLDRThis video explains lipid metabolism via the exogenous pathway, detailing how the body processes fats from food. It begins with the absorption of triglycerides and cholesterol in the small intestine, followed by their conversion into chylomicrons. These chylomicrons enter the lymphatic system and bloodstream, where triglycerides are broken down by lipoprotein lipase. The free fatty acids can either be stored in adipose tissue or transported to the liver. Cholesterol, unlike triglycerides, remains in the chylomicrons and is directed to the liver, completing the process of lipid metabolism.
Takeaways
- 😀 Metabolism is the process where the body converts absorbed nutrients into energy for bodily functions.
- 😀 Lipid metabolism involves the synthesis and breakdown of lipids in cells, which includes fat storage and energy production.
- 😀 Exogenous lipid metabolism begins in the small intestine where triglycerides and cholesterol from food are absorbed.
- 😀 Cholesterol from food and bile secreted from the liver both enter the small intestine and contribute to lipid absorption.
- 😀 Triglycerides in the small intestine are absorbed as free fatty acids, while cholesterol is absorbed as cholesterol.
- 😀 Free fatty acids are re-esterified into triglycerides, and cholesterol undergoes esterification to form cholesterol esters.
- 😀 These lipids, along with phospholipids and apolipoproteins, form chylomicrons that enter the lymphatic system and eventually the bloodstream.
- 😀 In the bloodstream, triglycerides in chylomicrons are broken down by lipoprotein lipase into free fatty acids.
- 😀 Free fatty acids can be stored as triglycerides in adipose tissue or taken by the liver for further processing.
- 😀 Cholesterol remains in the chylomicrons and is eventually transported to the liver as chylomicron remnants rich in cholesterol esters.
- 😀 The process of lipid digestion, absorption, and transport is essential for energy storage and regulating cholesterol levels in the body.
Q & A
What is lipid metabolism?
-Lipid metabolism refers to the processes in which the body synthesizes and breaks down lipids (fats) to produce energy needed for various bodily functions.
What are the two main pathways of lipid metabolism?
-The two main pathways of lipid metabolism are the exogenous pathway and the endogenous pathway.
What is the exogenous pathway in lipid metabolism?
-The exogenous pathway in lipid metabolism involves the digestion and absorption of dietary lipids (fats), including triglycerides and cholesterol, which are then transported in the body.
How do triglycerides and cholesterol get into the bloodstream?
-Triglycerides and cholesterol from food and bile are absorbed in the small intestine, converted into chylomicrons, and enter the lymphatic system before being transported into the bloodstream.
What is the role of chylomicrons in lipid metabolism?
-Chylomicrons are lipid-protein complexes that transport dietary triglycerides and cholesterol through the lymphatic system and bloodstream to various tissues, including the liver.
What happens to triglycerides in the bloodstream?
-Triglycerides in the bloodstream undergo hydrolysis by the enzyme lipoprotein lipase, breaking them down into free fatty acids, which can be stored in adipose tissue or used for energy.
What role does the liver play in lipid metabolism?
-The liver processes the free fatty acids and cholesterol received from chylomicrons, using them to form new triglycerides or other lipids that are needed for various bodily functions.
How is cholesterol handled differently from triglycerides?
-Unlike triglycerides, which are stored in adipose tissue, cholesterol remains within the chylomicrons and is transported to the liver for further processing.
What is the process of esterification of cholesterol?
-Esterification of cholesterol involves the chemical attachment of fatty acids to cholesterol, forming cholesterol esters, which are then incorporated into chylomicrons for transport in the bloodstream.
What is the function of lipoprotein lipase in lipid metabolism?
-Lipoprotein lipase is an enzyme that breaks down triglycerides in chylomicrons into free fatty acids and glycerol, which can be utilized by tissues for energy or storage.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Metbolisme Lipid 1 : Jalur Eksogen

Tiga Jalur Metabolisme Lipid dalam Tubuh

Lipids and Lipoproteins - Part 2 (Exogenous Pathway)
CARBOHYDRATE, FAT AND PROTEIN METABOLISM PATHWAYS

Fat Digestion and Absorption | Triglycerides

METABOLISMO ENERGÉTICO - (FISIOLOGIA DE GUYTON) - FORMAÇÃO DE ATP - FISIOLOGIA HUMANA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)