SISTEM KOORDINASI (SYARAF) PADA MANUSIA - BIOLOGI 11 SMA
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains the nervous system, focusing on its components and functions. It covers the structure of neurons, how they transmit impulses, and the different types of neurons involved in sensory, motor, and reflex activities. The video also describes the central and peripheral nervous systems, including the brain's lobes and their functions. It further explores the autonomic nervous system and provides examples of nervous system disorders, such as meningitis, Alzheimer's, and Parkinson's. Designed for 11th-grade students, this video offers clear insights into the coordination of body functions through the nervous system.
Takeaways
- 😀 The nervous system coordinates body functions by sending electrical signals quickly to regulate organ activity.
- 😀 Neurons are the basic cells that transmit impulses; they consist of dendrites, a cell body, an axon, and a myelin sheath.
- 😀 Impulses travel through neurons via three phases: polarization (resting), depolarization (signal entry), and repolarization (reset).
- 😀 Sensory neurons carry impulses from receptors to the brain, while motor neurons transmit responses from the brain to effectors.
- 😀 Interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons, playing a crucial role in processing impulses.
- 😀 Voluntary movements involve conscious control by the brain, whereas reflex movements occur automatically for quick responses.
- 😀 The central nervous system (CNS) includes the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system (PNS) connects the CNS to the body.
- 😀 The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary actions, with two opposing parts: the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
- 😀 Common diseases of the nervous system include meningitis (brain membrane infection), encephalitis (brain inflammation), and Parkinson’s disease (motor function degeneration).
- 😀 Alzheimer's disease causes memory loss and cognitive decline, and Parkinson’s disease leads to tremors and motor issues.
- 😀 The brain has several lobes with specific functions, including the frontal lobe (motor control), parietal lobe (sensory input), and occipital lobe (vision).
Q & A
What is the main function of the coordination system in the body?
-The main function of the coordination system is to regulate the activities of the organs in the body, ensuring that they work together to support proper bodily functions.
What are the three components of the coordination system?
-The three components of the coordination system are the nervous system, sensory system, and endocrine system (hormones).
What is the role of neurons in the nervous system?
-Neurons, or nerve cells, transmit electrical impulses from receptors to the brain and send responses from the brain to effectors, facilitating communication within the nervous system.
What are the main parts of a neuron and their functions?
-The main parts of a neuron include the dendrites (receive stimuli), the cell body (processes stimuli), the axon (transmits impulses to the next neuron), and the myelin sheath (insulates and speeds up signal transmission).
How do electrical impulses travel in a neuron?
-Electrical impulses travel from the dendrites to the cell body, then along the axon, and across synaptic gaps to other neurons using neurotransmitters.
What is the process of impulse transmission in neurons?
-Impulse transmission in neurons involves three stages: polarization (resting state), depolarization (when the neuron is stimulated), and repolarization (when the neuron returns to its resting state).
What is the difference between conscious movement and reflex movement?
-Conscious movements involve processing in the brain and require more time, while reflex movements are automatic and fast, processed by the spinal cord for quick responses to immediate stimuli.
What are the main divisions of the nervous system?
-The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which includes sensory and motor neurons.
What is the function of the cerebrum?
-The cerebrum is responsible for voluntary motor activities, problem-solving, thinking, speaking, and sensory processing such as touch, pressure, temperature, and pain.
What are some common disorders of the nervous system?
-Common disorders include meningitis (inflammation of the brain membranes), encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), Alzheimer's disease (cognitive decline), Parkinson's disease (motor dysfunction), and epilepsy.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

central nervous system mcqs with answers | mcq on central nervous system | nervous system mcqs

#sistemsaraftepi #sarafperifer #biologismakelas11 SISTEM REGULASI | SISTEM SARAF TEPI (PERIFER)

Sistem Saraf_ (Sistem Koordinasi Bagian 1)_Biologi SMA XI
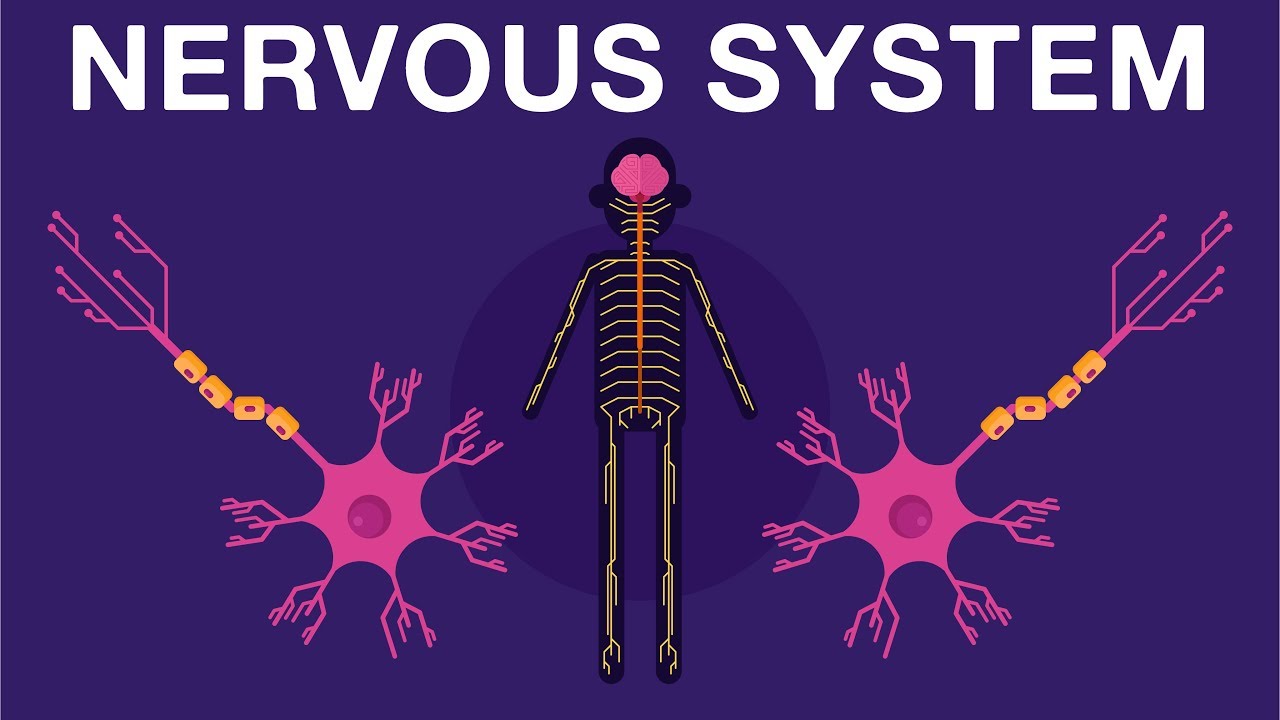
Nervous System - Get to know our nervous system a bit closer, how does it works? | Neurology
Sistem Saraf Tepi

Sistem Saraf Pada Manusia| Sistem Koordinasi part 1 - Biologi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
