Brushless DC Motor, How it works ?
Summary
TLDRThe video script provides an insightful look into the workings of Brushless DC (BLDC) motors, highlighting their advantages over traditional brushed motors in terms of reliability, efficiency, and noise reduction. BLDC motors are favored for their lighter weight and lack of wear-prone brushes that can cause sparking in conventional motors. The operation of a BLDC motor is explained through the interaction between a permanent magnet rotor and an electromagnet stator, with the process likened to a donkey chasing a carrot that perpetually moves out of reach. The script also addresses the power output limitation due to only one coil being energized at a time and explains how this is overcome by energizing a second coil to push the rotor, thus increasing torque and power output. The BLDC's constant torque nature is attributed to this configuration. The use of an electronic controller and a Hall effect sensor to determine rotor position and control coil energizing for continuous rotation is also discussed. The video concludes by differentiating between the outrunner and inrunner BLDC designs, offering viewers a comprehensive introduction to BLDC motors.
Takeaways
- 🚀 **Reliability & Efficiency**: Brushless DC (BLDC) motors are preferred for their reliability, efficiency, and lower noise levels compared to brushed motors.
- 🏋️ **Lighter Weight**: BLDC motors are lighter than brushed motors with the same power output, which can be beneficial for applications where weight is a concern.
- 🔋 **Long Life**: Conventional brushed motors have brushes that wear out and can cause sparking, making them unsuitable for applications requiring long life and high reliability.
- 🧲 **Permanent Magnet Rotor**: The rotor in a BLDC motor is a permanent magnet, which interacts with the electromagnets created by the energized stator coils.
- 🌀 **Electromagnetic Interaction**: BLDC motor operation is based on the force interaction between the permanent magnet and the electromagnets in the stator.
- 🔄 **Sequential Activation**: In BLDC motors, coils are sequentially energized, causing the rotor to rotate as each coil's magnetic field interacts with the rotor's magnetic field.
- 🥕 **Humorous Analogy**: The operation of a BLDC motor can be remembered like the story of a donkey chasing a carrot that keeps moving out of reach.
- 🔌 **Single Coil Limitation**: At any given moment, only one coil in a BLDC motor is energized, which can limit the power output.
- 🤹 **Torque Boost**: By energizing a second coil with the same polarity while the rotor is near the first coil, the motor can produce more torque and power output.
- ⚙️ **Constant Torque Nature**: BLDC motors have a constant torque nature due to the combined effect of the pushing and pulling forces from the stator coils.
- 🔄 **Simplified Stator Coil**: A small modification to the stator coil, connecting one free end of the coils together, simplifies the process of energizing two coils separately.
- 📡 **Electronic Controllers**: BLDC motors use electronic controllers with sensors, often Hall effect sensors, to determine the rotor's position and decide which coils to energize for continuous rotation.
- 🔍 **Outrunner vs Inrunner**: There are different BLDC motor designs available, such as the outrunner and inrunner types, each with their specific applications.
Q & A
Why are brushless DC (BLDC) motors considered more reliable and efficient than brushed DC motors?
-Brushless DC motors are more reliable and efficient because they do not have brushes that wear out over time and cause sparking, which can lead to reduced performance and shorter lifespan in brushed DC motors.
How does the weight of a BLDC motor compare to a brushed motor with the same power output?
-BLDC motors are lighter than brushed motors with the same power output, making them more suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor.
What is the fundamental working principle behind a BLDC motor?
-The operation of a BLDC motor is based on the force interaction between a permanent magnet (rotor) and an electromagnet (stator coil). When a DC power is applied to the coil, it energizes and attracts the opposite poles on the rotor, causing rotation.
How does the energizing sequence of the stator coils in a BLDC motor contribute to the rotor's continuous rotation?
-The stator coils are energized in a specific sequence as the rotor passes each coil. This sequential energizing creates a rotating magnetic field that keeps the rotor spinning continuously.
What is the humorous analogy used to help remember the BLDC operation?
-The humorous analogy is the story of the donkey and the carrot, where the donkey tries to reach the carrot that keeps moving out of reach, similar to how the BLDC motor's rotor continuously rotates as the magnetic field changes.
What is the drawback mentioned about BLDC motors when only one coil is energized at any instant?
-The drawback is that the two non-energized or 'dead' coils reduce the power output of the motor, as only one coil is contributing to the torque at any given time.
How can the power output and torque of a BLDC motor be improved?
-The power output and torque can be improved by energizing a second coil behind the first one with the same polarity current, which pushes the rotor and produces more torque.
What is the significance of a BLDC motor having a constant torque nature?
-A constant torque nature means that the BLDC motor can maintain a consistent output of torque regardless of changes in speed, which is beneficial for operations that require a steady and reliable power delivery.
How can the process of energizing two coils separately in a BLDC motor be simplified?
-By connecting one free end of the coils together, the process is simplified, allowing power to be applied between two coils, which then distribute the current as needed for the motor's operation.
What role does an electronic controller play in the operation of a BLDC motor?
-An electronic controller uses a sensor, often a Hall effect sensor, to determine the rotor's position and decides which stator coils to energize, ensuring continuous and efficient rotation of the rotor.
What are the two main types of BLDC motor designs mentioned in the script?
-The two main types of BLDC motor designs mentioned are the outrunner type and the inrunner type.
Why are BLDC motors preferred for applications demanding long life and reliability?
-BLDC motors are preferred for such applications because they lack the wear-prone brushes found in conventional DC motors, offer higher efficiency, and provide a longer lifespan with reduced maintenance needs.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
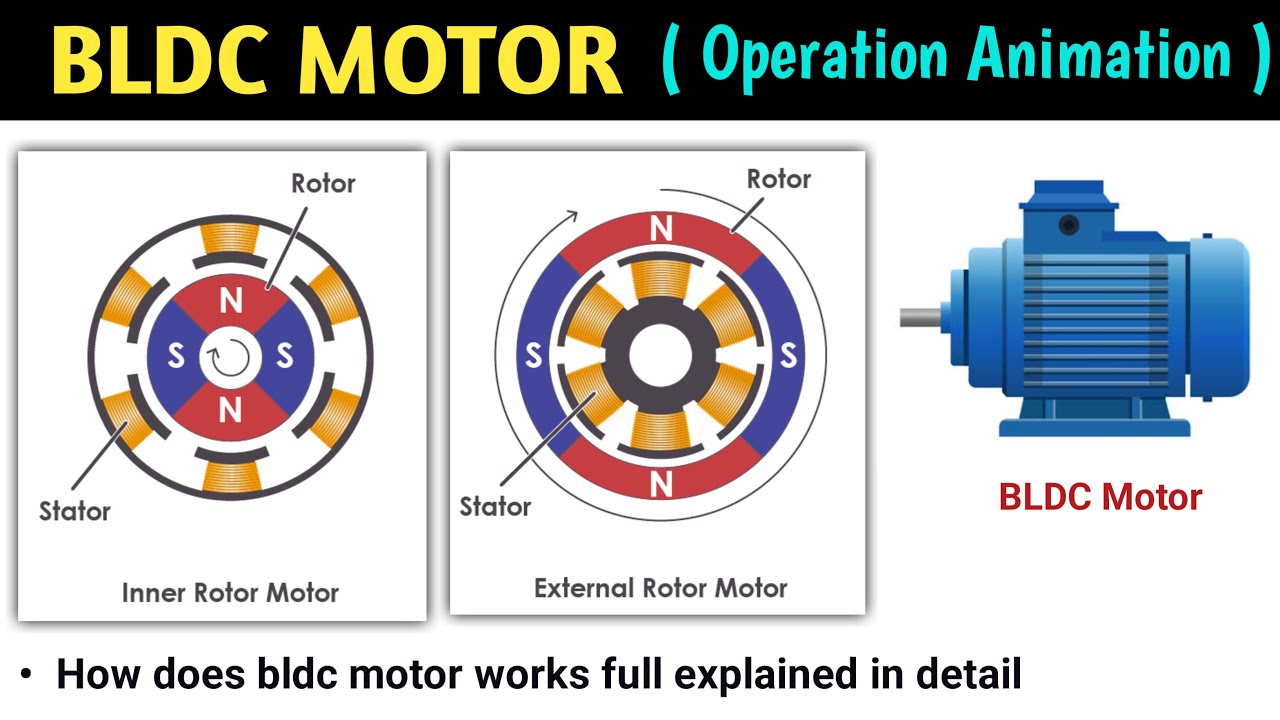
bldc motor | brushless dc motor | brushless dc motor construction and working | brushless motor
Types of Motors used in EV | Single, Dual, Three & Four Motor Configuration in EV
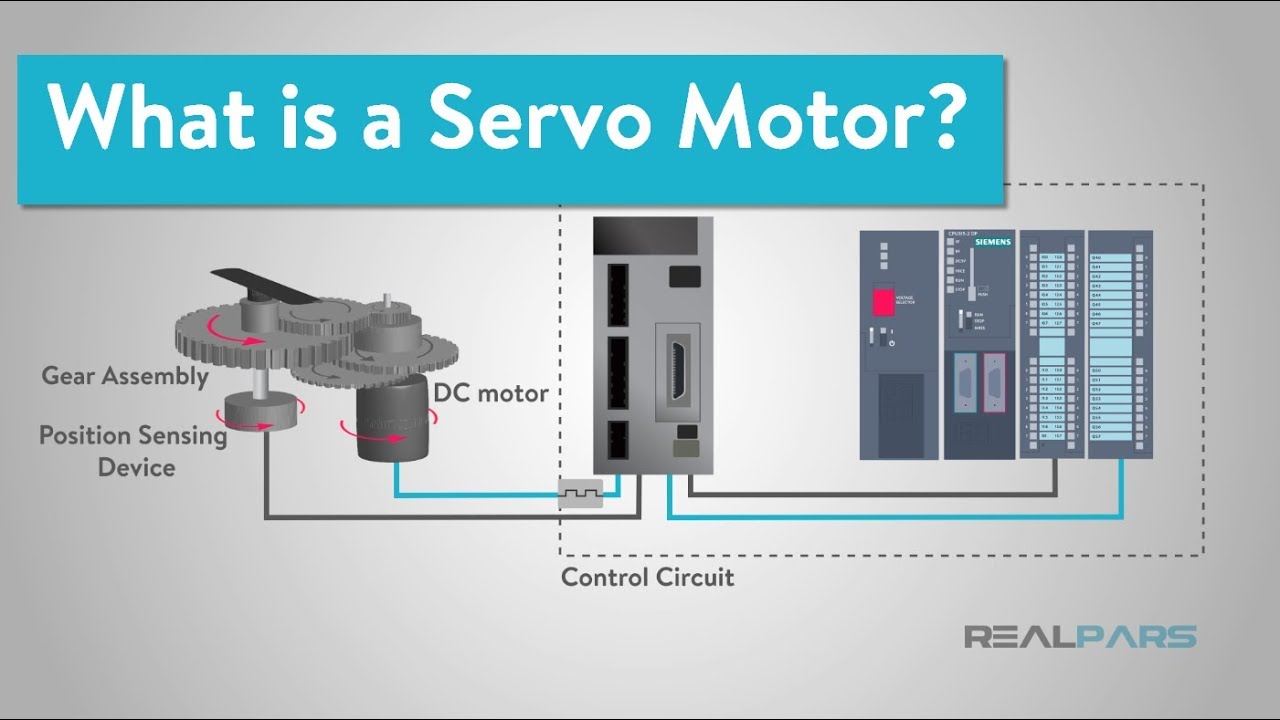
What is a Servo Motor and How it Works?

noc19-ee65-lec36

Brushless Motor - How they work BLDC ESC PWM

PID control of BLDC motor
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
