BIOLOGI Kelas 12 - Mutasi dan Jenis-jenisnya | GIA Academy
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores various genetic mutations, focusing on their types and causes. The speaker discusses chromosomal mutations like insertion, deletion, duplication, and translocation, explaining how these changes can affect an organism. Special emphasis is placed on the mechanisms behind these mutations and their potential consequences. The video concludes with a promise to continue the discussion on the effects of mutations in the next video, encouraging viewers to stay tuned for more insights.
Takeaways
- 😀 Mutations are permanent changes in the genetic material of an organism.
- 😀 Mutations can occur in both somatic and germ cells, with germline mutations being passed on to offspring.
- 😀 Mutations can be categorized into gene mutations, chromosomal mutations, and genome mutations.
- 😀 Gene mutations include point mutations, which involve changes in a single base pair.
- 😀 Chromosomal mutations can lead to structural changes in chromosomes, such as translocations, inversions, or deletions.
- 😀 A specific type of chromosomal mutation discussed is translocation, where a segment of one chromosome is transferred to a non-homologous chromosome.
- 😀 Translocations can result in new chromosome formations, potentially causing genetic disorders or changes in the organism.
- 😀 Inversions, a type of chromosomal mutation, involve a segment of a chromosome being flipped in orientation.
- 😀 Mutations can have various effects, ranging from beneficial to harmful, and can influence an organism's fitness.
- 😀 The video discusses how mutations can occur naturally or as a result of environmental factors like radiation or chemicals.
- 😀 The speaker concludes by promising further discussions on the effects of mutations in upcoming videos.
Q & A
What is mutation, and how does it occur?
-Mutation is a sudden change in the genetic material of an organism, which can result from environmental changes. It involves alterations in DNA or chromosome structure, leading to genetic variations that may be passed on to offspring.
What are the two main types of genetic variation caused by mutation?
-The two main types of genetic variation are genetic variation, caused by changes in genetic material that can be inherited, and environmental variation, which results from changes in the environment and is not inherited.
How can mutations be categorized based on genetic material?
-Mutations can be classified into two main categories: gene mutations, which affect the structure of DNA bases, and chromosome mutations, which involve changes in chromosome structure or number.
What are the types of gene mutations, and what are their effects?
-Gene mutations can be point mutations, such as substitution, deletion, and insertion of DNA bases. These mutations may result in silent mutations, missense mutations (which change an amino acid), or nonsense mutations (which introduce a stop codon and truncate protein synthesis).
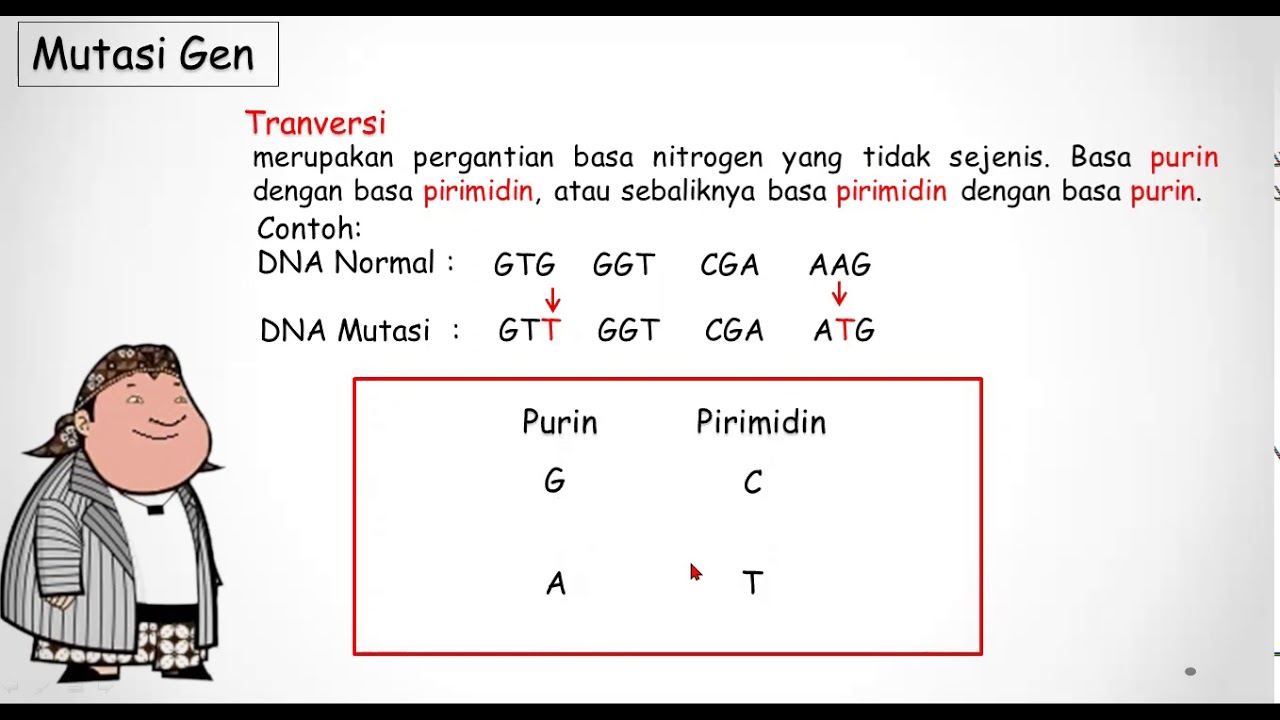
What is the difference between transition and transversion in substitution mutations?
-In transition mutations, one purine is replaced by another purine, or one pyrimidine is replaced by another pyrimidine. In transversion mutations, a purine is substituted by a pyrimidine or vice versa, which alters the base pairing more significantly.
How do chromosome mutations differ from gene mutations?
-Chromosome mutations involve changes in the structure or number of chromosomes, such as deletions, duplications, inversions, translocations, and katenations, whereas gene mutations specifically affect the DNA sequence within a gene.
What are the types of chromosomal mutations and their effects?
-Chromosomal mutations can involve structural changes (deletion, duplication, inversion, translocation, katenation) or changes in chromosome number, leading to conditions like aneuploidy or polyploidy.
What is the difference between euploidy and aneuploidy?
-Euploidy refers to changes in the number of entire sets of chromosomes, such as triploidy or tetraploidy. Aneuploidy refers to changes in the number of individual chromosomes, like trisomy (an extra chromosome) or monosomy (a missing chromosome).
What are somatic mutations and how do they differ from gametic mutations?
-Somatic mutations occur in non-reproductive cells and are not passed on to offspring. They can lead to diseases like cancer. Gametic mutations occur in the sex cells (sperm or eggs) and can be inherited by the next generation.
How do environmental factors influence mutations?
-Environmental factors, such as cosmic rays, UV radiation, and chemicals, can cause mutations by damaging DNA or altering chromosome structure. These factors are considered mutagens, which can lead to both natural and induced mutations.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)