Cardiac (Heart) MRI scan positioning, protocols and planning. Cardiac flow and myocardial T2 mapping
Summary
TLDRThis detailed guide outlines the steps involved in performing a cardiac MRI scan, focusing on patient preparation, electrode placement, and imaging protocols. It covers the process of positioning the patient, applying ECG electrodes, selecting the right MRI sequences, and ensuring proper planning for multiple views, including the four-chamber, two-chamber, short-axis, and cine scans. The script also highlights the use of contrast agents, delayed scans, and advanced techniques like myocardial mapping and flow studies, providing a comprehensive framework for conducting high-quality cardiac MRI exams.
Takeaways
- 😀 Ensure patient safety by completing a safety questionnaire and confirming their ability to undergo the MRI scan.
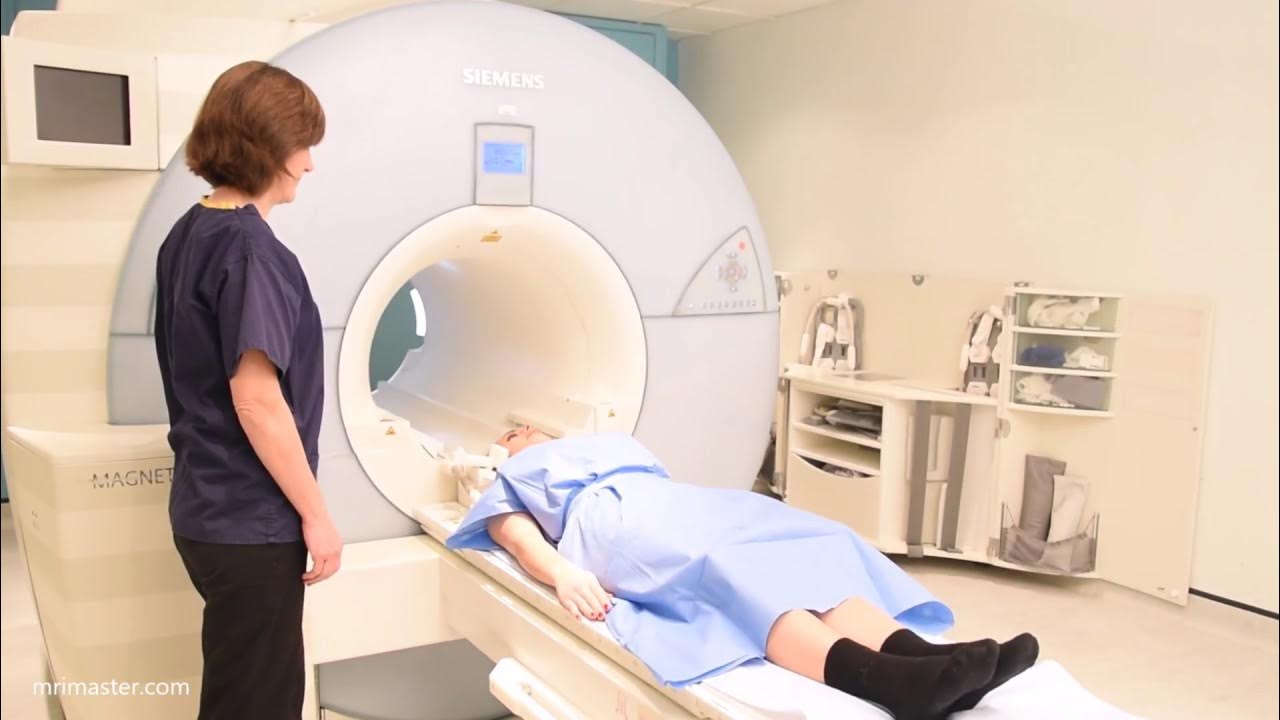
- 😀 Have the patient change into a hospital gown with the opening at the front and position them head first, supine on the MRI table.
- 😀 If necessary, shave hair from the chest area for proper placement of ECG electrodes.
- 😀 Apply ECG electrodes according to manufacturer’s guidelines and verify signal quality on the scanner display.
- 😀 Provide the patient with an emergency buzzer, ear protection (headphones and earplugs), and ensure they understand its use.
- 😀 Move the patient slowly into the MRI magnet, center the laser beam on the mid chest, and ensure they are comfortable.
- 😀 Register the patient’s details, including height, weight, and position (head first, supine) for accurate specific absorption rate calculations.
- 😀 Select the appropriate MRI protocol and start with the three-plane T2 localizer, ensuring good localizer images are obtained.
- 😀 Use precise planning for obtaining heart images in multiple views (e.g., two-chamber, four-chamber, short axis) with breath hold techniques.
- 😀 Perform post-contrast scans if applicable, including delayed PSIR sequences and free-breathing options for superior spatial resolution.
- 😀 Implement advanced imaging techniques, such as myocardial mapping (T1, T2), and flow studies for vascular analysis, following proper planning methods.
Q & A
What is the first step in preparing a patient for an MRI scan?
-The first step is to ensure the patient has completed a safety questionnaire and is deemed safe to undergo an MRI scan.
Why is it important to shave hair from the chest area before entering the scanner room?
-Shaving the chest hair ensures that the electrocardiogram (ECG) electrodes will stick properly to the skin, providing an accurate signal during the scan.
What should be done if the ECG signal quality is not satisfactory?
-If the ECG signal is not consistent or satisfactory, the electrodes should be repositioned to improve the signal quality.
What is the purpose of placing a spacer cushion over the patient's chest before the MRI scan?
-The spacer cushion is placed to help secure the body coil in position, ensuring proper imaging during the scan.
What is the recommended patient positioning for the MRI scan?
-The patient should be positioned head-first and supine on the MRI table for the scan.
What is the significance of obtaining good localizer images in MRI?
-Good localizer images are crucial for proper planning and alignment of the imaging slices, ensuring the accuracy of the scan. If necessary, re-plan and repeat the localizer images.
How do you plan the imaging slices for cardiac MRI?
-The imaging slices are planned using localizer scans in multiple orientations (axial, coronal, and sagittal) with the positioning blocks carefully aligned to anatomical landmarks such as the mitral valve, left ventricular apex, and interventricular septum.
What is the role of expiration breath holds during the scan?
-Expiration breath holds are used during the scans to minimize motion artifacts and ensure high-quality images, especially for cardiac imaging where precise timing is critical.
Why is gadavist contrast injected during the MRI scan?
-Gadavist contrast is injected to enhance image quality, particularly for visualizing blood clots, tumors, or other abnormalities post-contrast.
What is the purpose of the TI scout in cardiac MRI?
-The TI scout is used to identify the myocardial nulling TI value, which helps in selecting the appropriate timing for myocardial imaging to minimize artifacts.
What are the benefits of free-breathing PSIR sequences?
-Free-breathing PSIR sequences offer superior spatial resolution and reduce the need for long breath holds, making the scan more comfortable for patients and improving image quality.
How is phase contrast flow measurement used in MRI?
-Phase contrast flow measurements are used to assess vascular flow, such as aortic flow, by identifying the most accurate flow velocity through a scout sequence and applying it to the flow imaging sequence.
What is the purpose of myocardial mapping sequences in MRI?
-Myocardial mapping sequences, like T1 and T2 mapping, are used to assess myocardial tissue characteristics, including fibrosis and edema, both before and after contrast injection.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

PELAYANAN MRI KONTRAS RSPON Prof. Dr. dr. MAHAR MARDJONO JAKARTA

RADIOGRAFER, TEKNIK PEMERIKSAAN CT SCAN KEPALA TANPA KONTRAS, PROSEDUR REGISTER HINGGA CETAK FILM

IAC’s
Brain MRI scan protocols, positioning and planning

CARDIAC ARREST EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT, UNCONSCIOUS PULSELESS PATIENT TREATMENT ACLS RHYTHM REVIEW 2021

Pemeriksaan Elektrokardiografi (EKG)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
