Acute Glomerulonephritis Nursing (Poststreptococcal) | Nephritic Syndrome NCLEX Review
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive overview of acute glomerulonephritis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the kidney's filtering structures. It typically arises following a streptococcal infection, leading to the formation of antigen-antibody complexes that disrupt normal filtration. Key symptoms include hematuria, mild edema, and hypertension. The video emphasizes nursing interventions such as monitoring fluid status, daily weights, and blood pressure, alongside education on the importance of prompt treatment for strep infections. The content is tailored for nursing students preparing for the NCLEX, with a quiz available at the end for reinforcement.
Takeaways
- 😀 Acute glomerulonephritis is inflammation of the nephron's filtering structure, primarily affecting the glomerulus.
- 😀 It typically develops about 14 days after a strep infection, affecting mainly children aged 2 to 10.
- 😀 The immune response to streptococcal infection leads to the formation of antigen-antibody complexes that cause inflammation in the glomeruli.
- 😀 Symptoms include hematuria (tea or cola-colored urine), mild edema (especially around the eyes), and hypertension.
- 😀 There are different types of glomerulonephritis, including nephritic and nephrotic syndromes, with differing symptoms related to protein and blood cell loss.
- 😀 The condition results in decreased glomerular filtration rate (GFR), leading to low urine output and retention of waste products in the blood.
- 😀 Patients may experience fluid overload, increasing the risk of heart failure and respiratory distress due to fluid backup in the lungs.
- 😀 Monitoring fluid status, daily weights, and strict intake/output calculations are critical nursing interventions.
- 😀 It's important to restrict potassium-rich foods in patients due to the risk of hyperkalemia from decreased kidney function.
- 😀 Education for parents and patients includes the need for prompt treatment of strep infections to prevent recurrence of glomerulonephritis.
Q & A
What is acute glomerulonephritis?
-Acute glomerulonephritis is an inflammation of the glomeruli, the filtering structures in the kidneys, which impairs their ability to filter blood properly.
What triggers the development of acute glomerulonephritis?
-It often develops approximately 14 days after a streptococcal infection, which can be from the skin or throat.
What are the primary symptoms of acute glomerulonephritis?
-Symptoms include hematuria (tea or cola-colored urine), mild edema (especially in the face), hypertension, and decreased urinary output.
How does inflammation in the glomeruli affect kidney function?
-Inflammation increases permeability, allowing proteins and red blood cells to leak into the urine, while also reducing the glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
What does the mnemonic H.A.D. S.E.E.P. represent in assessing acute glomerulonephritis?
-It stands for Hypertension, ASO titer positive, Decreased GFR, Swelling, Elevated BUN and creatinine, Edema, and Proteinuria.
What is the significance of monitoring daily weights in patients with this condition?
-Daily weights help detect fluid retention early, indicating potential fluid overload due to kidney impairment.
What dietary modifications may be necessary for patients with acute glomerulonephritis?
-Patients may need fluid and sodium restrictions to manage edema and hypertension.
What role does albumin play in fluid balance related to acute glomerulonephritis?
-Albumin helps maintain oncotic pressure; low levels due to protein loss in urine can lead to edema as fluid escapes into tissues.
Why is it important to monitor potassium levels in these patients?
-Due to impaired kidney function, patients may experience hyperkalemia (high potassium levels), which can lead to serious complications like cardiac issues.
What education should be provided to parents regarding streptococcal infections?
-Parents should be informed about the importance of seeking treatment for suspected strep infections to prevent complications like acute glomerulonephritis.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
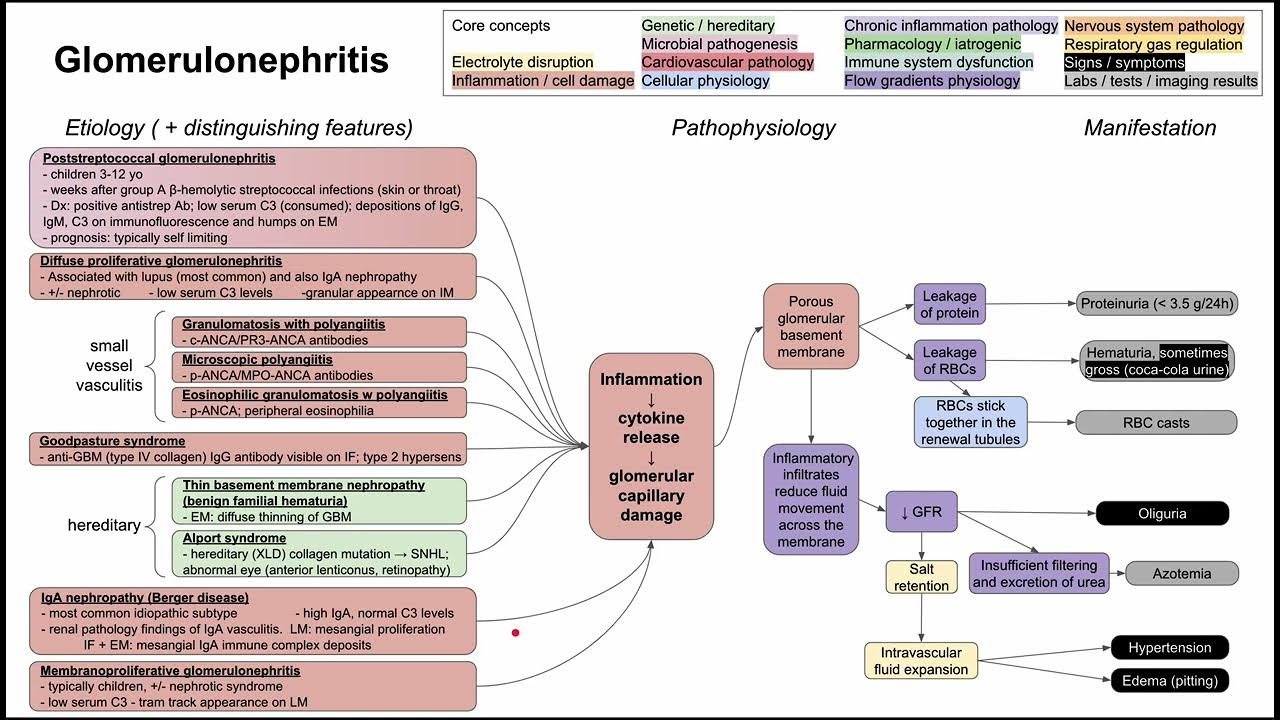
Glomerulonephritis (mechanism of disease)
Understanding Pancreatitis

Appendicitis: Introduction, Pathogenesis, Cllinical features, Lab findings, Imaging, Management

Diseases of Tonsil and Tonsillectomy (Acute Tonsillitis) by Dr. Vyshnavi | PrepLadder ENT Residency

Cholecystitis Nursing NCLEX Pathophysiology, Symptoms (T-Tube & Cholecystostomy)

Acute leukemia l Osmosis
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
