Secondary Memory – Solid State Drives
Summary
TLDRThis session provides an in-depth overview of solid state drives (SSDs), covering the two primary form factors: 2.5-inch and M.2. Unlike traditional hard disk drives, SSDs offer faster data transfer rates due to their lack of moving parts, with 2.5-inch SSDs reaching up to 600 MB/s and M.2 SSDs utilizing the NVMe protocol for speeds of 2600 MB/s to 3 GB/s. The architecture of SSDs includes NAND flash memory, which allows for efficient data storage. Overall, this session highlights the advantages of SSDs in modern computing, emphasizing their role in enhancing performance and efficiency.
Takeaways
- 😀 SSDs come in two primary form factors: 2.5-inch and M.2.
- 😀 2.5-inch SSDs use SATA 3.0 interface, achieving data transfer rates up to 600 MB/s.
- 😀 M.2 SSDs utilize the NVMe protocol for optimized performance and faster speeds.
- 😀 NVMe M.2 SSDs can reach data transfer rates between 2600 MB/s to 3 GB/s.
- 😀 Unlike hard disk drives, SSDs have no moving parts, making them quieter and more efficient.
- 😀 The NAND memory in SSDs can store multiple bits per cell, enhancing data density.
- 😀 2.5-inch SSDs are generally more affordable but slower than M.2 SSDs.
- 😀 M.2 SSDs are compact and require no additional power cables.
- 😀 Compatibility can be an issue; not all motherboards support M.2 connections.
- 😀 SSDs are ideal for frequently used data, while hard drives can store infrequently accessed data.
Q & A
What are solid state drives (SSDs)?
-SSDs are a type of fixed secondary storage that use flash memory to store data, unlike hard disk drives (HDDs) which rely on moving parts.
What are the two main form factors of SSDs?
-The two main form factors of SSDs are the 2.5-inch form factor and the M.2 form factor.
How do 2.5-inch SSDs connect to the motherboard?
-2.5-inch SSDs connect to the motherboard using SATA 3.0 interfaces.
What is the maximum data transfer rate of 2.5-inch SSDs?
-2.5-inch SSDs can achieve data transfer rates of up to 600 MB/s.
What type of memory do SSDs use for storage?
-SSDs use NAND flash memory, specifically charge trap flash (CTF) technology.
How does the memory cell technology in SSDs differ from older technologies?
-Modern SSDs can store multiple bits in each memory cell (e.g., triple-level cells), compared to older technologies which typically stored only one bit.
What is the advantage of M.2 SSDs over 2.5-inch SSDs?
-M.2 SSDs, especially those using NVMe protocol, can achieve data transfer rates of 2600 MB/s to 3 GB/s, which is significantly faster than 2.5-inch SSDs.
What does NVMe stand for and why is it important?
-NVMe stands for Non-Volatile Memory Express. It is a communication protocol developed to optimize the performance of SSDs, reducing CPU overhead.
Do M.2 SSDs require power cables?
-No, M.2 SSDs typically do not require separate power cables.
What is the recommended storage strategy for optimizing performance with SSDs and HDDs?
-A recommended strategy is to store frequently used data, like operating systems, on SSDs for speed, while infrequently used data, like videos and audio files, can be stored on HDDs to save costs.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

SSD vs Hard Drive vs Hybrid Drive

Explaining SSDs: Form Factors, Interfaces & Technologies

(SSDs vs HHDs) What's The Difference Between SSD and HDD?
BTEC Level 3 IT - P04 - Storage Devices - HDD, SSD, SD, Magnetic Tape, USB Memory Stick, Optical

Mr Long Computer Terms | What's the difference between HDD and SSD?
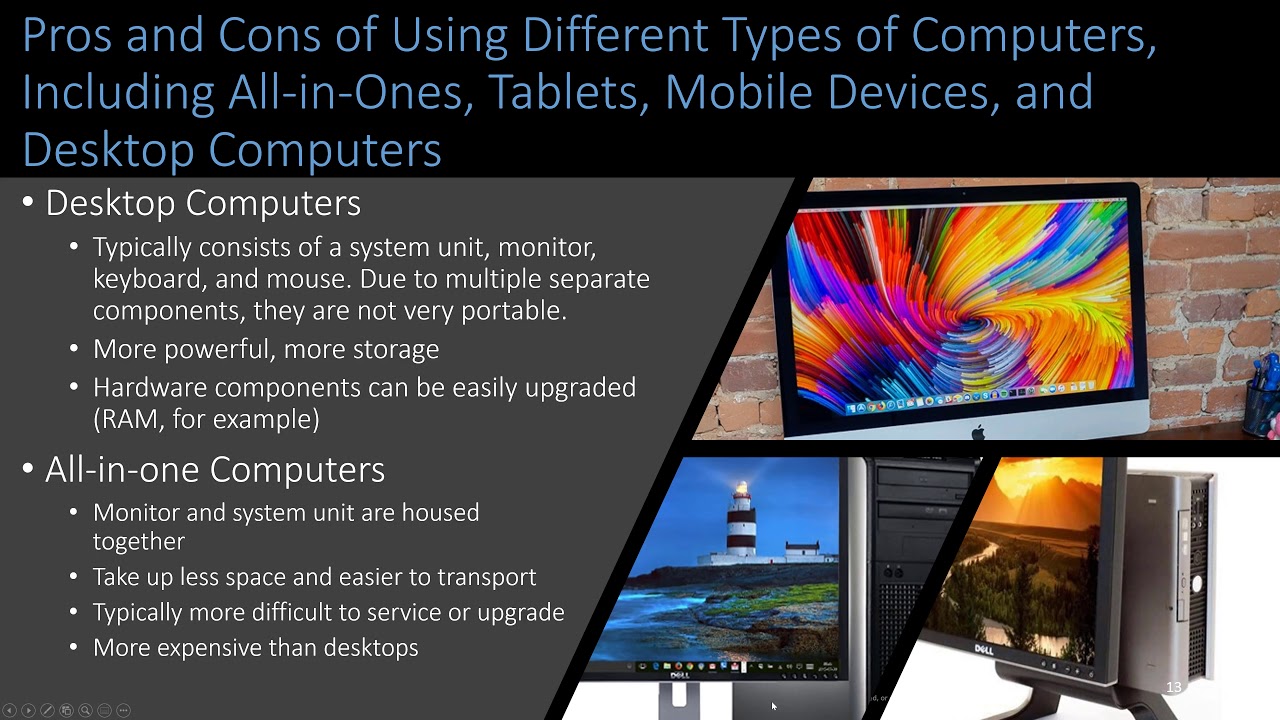
Computer Concepts - Module 3: Computer Hardware Part 1B (4K)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
