#2: Learning about linear operators
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the fundamental properties of linear operators, detailing their definitions and key examples such as the identity operator, zero operator, and differentiation and integration operators. It explains important concepts like null spaces, inverse operators, and bounded linear operators, highlighting their significance in preserving the structure of vector spaces. The discussion emphasizes the linearity and dimensionality associated with these operators, providing a solid foundation for understanding their role in functional analysis and mathematics.
Takeaways
- 😀 A linear operator maps elements between vector spaces while preserving the operations of addition and scalar multiplication.
- 😀 The identity operator leaves elements unchanged and maps a vector space to itself.
- 😀 The zero operator maps every element of a vector space to the zero element in the target space.
- 😀 Differentiation and integration are examples of linear operators applied to polynomials and continuously differentiable functions, respectively.
- 😀 A matrix can define a linear operator that acts on vectors through matrix multiplication, establishing a connection between linear algebra and operator theory.
- 😀 The null space of a linear operator consists of all elements that are mapped to the zero element of the range.
- 😀 The range of a linear operator is also a vector space, and its dimension is always less than or equal to that of the domain.
- 😀 A bounded linear operator exists if there is a constant that limits the operator's output relative to its input norms.
- 😀 An inverse operator exists if the original operator is both injective (one-to-one) and surjective (onto), preserving the structure of vector spaces.
- 😀 Understanding the properties of linear operators is fundamental in functional analysis and essential for exploring deeper mathematical concepts.
Q & A
What are the key elements that make up fire?
-The key elements that make up fire include heat, fuel, and oxygen, which together create the combustion process.
How does the combustion process initiate?
-The combustion process initiates when a material reaches its ignition temperature, causing a chemical reaction between the fuel and oxygen.
What role does oxygen play in fire?
-Oxygen is essential for fire as it supports the combustion process; without sufficient oxygen, a fire cannot sustain itself.
Can fire be extinguished by removing one of its elements?
-Yes, fire can be extinguished by removing one of its essential elements: heat, fuel, or oxygen.
What are some common methods to extinguish a fire?
-Common methods to extinguish a fire include using water to cool the heat, smothering it to cut off oxygen, or using fire extinguishers containing chemicals that disrupt the combustion process.
What is the significance of the fire triangle in understanding fire dynamics?
-The fire triangle is significant in understanding fire dynamics as it visually represents the three necessary components of fire: heat, fuel, and oxygen, which helps in fire prevention and control strategies.
What safety precautions should be taken around fire?
-Safety precautions around fire include keeping flammable materials away from heat sources, having fire extinguishers accessible, and being aware of the nearest exits in case of an emergency.
How does fire behave in different environments, such as indoors vs outdoors?
-Fire behaves differently in various environments; indoors, it can spread quickly due to confined spaces and available fuels, whereas outdoors, wind can influence its direction and intensity.
What are the environmental impacts of fire?
-The environmental impacts of fire include destruction of habitats, air pollution from smoke, and potential contribution to climate change through carbon emissions.
How can controlled burns be beneficial?
-Controlled burns can be beneficial for managing forests and grasslands, promoting new growth, and reducing the risk of larger, uncontrolled wildfires by removing excess fuel.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

CPE 112 Lecture 18 - Unary Operators

☕️ Curso de Java na prática - Operadores Aritméticos - Atribuições - aula 6 - Fundamentos Parte 2/5

C_14 Operators in C - Part 2 | Arithmetic & Assignment Operators | C Programming Tutorials

Operator Overloading in C++ Programming | C++ Programming for Beginners
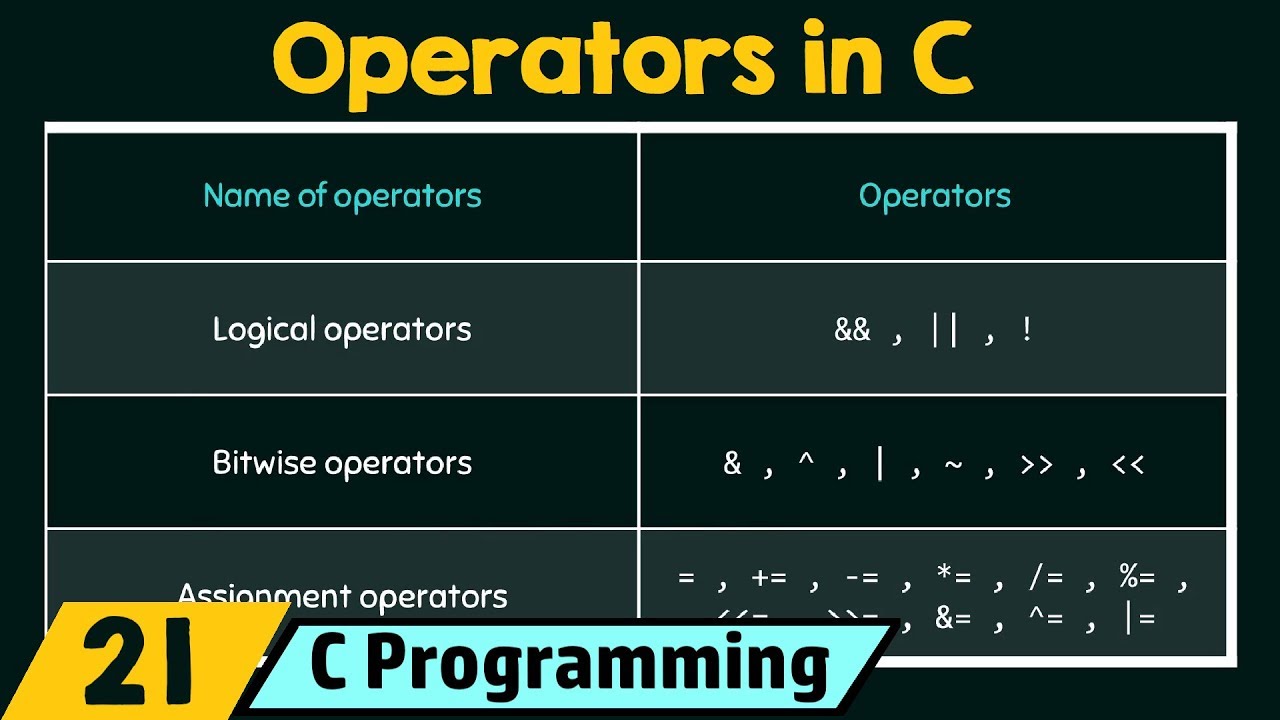
Introduction to Operators in C

Linguagem C - Aula 3.2 - Aprenda a realizar cálculos em C (2022)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
