Salt Hydrolysis | Buffer : Definition & Action | SK015 Chapter 7.1 Part III
Summary
TLDRIn this informative video, the host explores the reactions between strong acids and bases, focusing on concepts such as neutralization and buffer solutions. Key examples include the formation of sodium ions from sodium hydroxide and chloride ions from hydrochloric acid, resulting in a neutral pH of 7. The discussion also covers the combination of strong acids with weak bases, leading to exothermic reactions, and explains the importance of buffer solutions in maintaining pH levels in various environments. The video is enriched with engaging explanations and music, making complex chemistry concepts accessible and interesting.
Takeaways
- 😀 The reaction of a strong acid with a strong base results in a neutral pH of 7.
- 😀 Strong acids, like HCl, and strong bases, like NaOH, dissociate completely in solution.
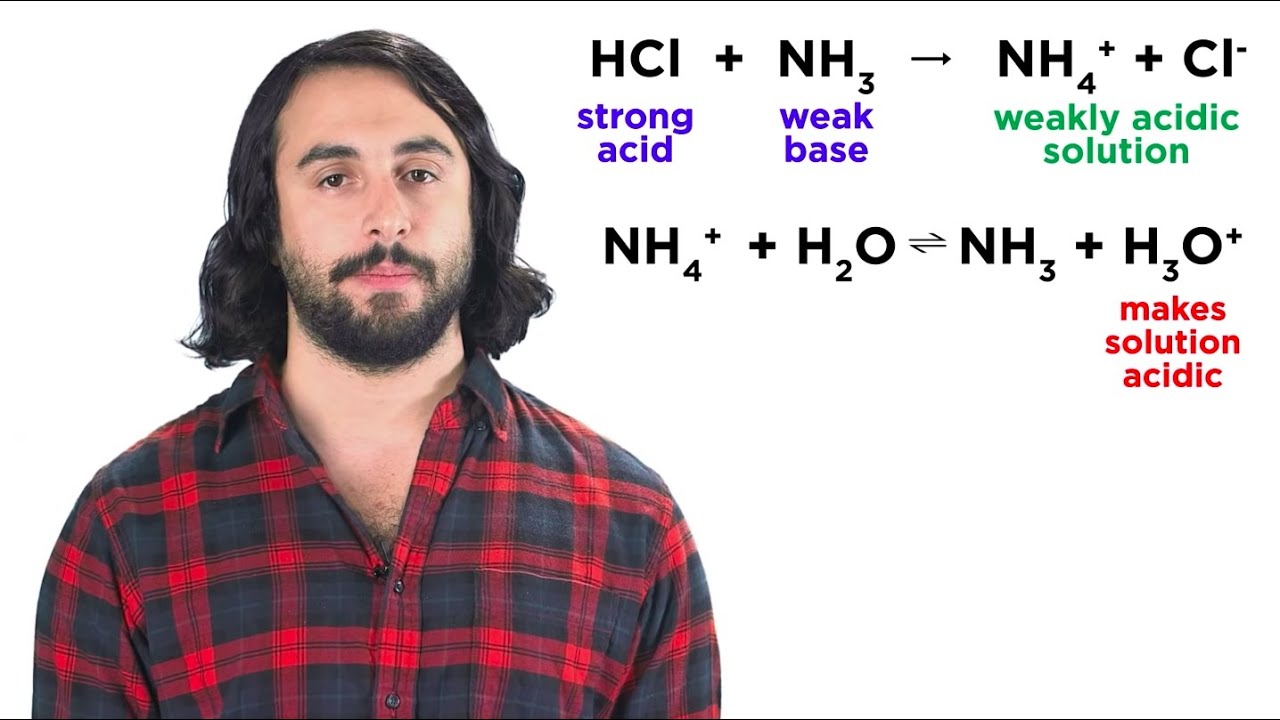
- 😀 A combination of a strong acid and a weak base generates exothermic reactions, leading to varying pH levels.
- 😀 Basic solutions can be derived from weak bases such as ammonia (NH3).
- 😀 Buffer solutions maintain pH stability in the body, and there are two types: acidic and basic buffers.
- 😀 Acidic buffers consist of weak acids and their conjugate bases, like HCN and NaCN.
- 😀 Full dissociation occurs in strong acids and bases, while weak acids only partially dissociate.
- 😀 When strong acids are mixed with buffer solutions, the pH remains relatively unchanged.
- 😀 The addition of a strong base to a buffer will also not significantly alter the pH, demonstrating the buffer's effectiveness.
- 😀 The script discusses specific chemical reactions and their products, emphasizing the importance of understanding acid-base chemistry.
Q & A
What are the products of the reaction between strong acids and strong bases?
-The reaction between strong acids and strong bases typically produces a neutral solution with a pH of 7, as seen with the example of NaOH (strong base) and HCl (strong acid).
What occurs during the hydrolysis of a weak base and a strong acid?
-During the hydrolysis of a weak base and a strong acid, an exothermic reaction may occur, resulting in the production of more heat, and this can lead to a decrease in pH.
Can you explain what buffer solutions are?
-Buffer solutions are special solutions that resist changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acid or base. They contain a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
What types of buffer solutions are mentioned in the transcript?
-The transcript mentions two types of buffer solutions: acidic buffers and basic buffers, which contain a weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its conjugate acid, respectively.
How do buffer solutions maintain pH when strong acids or bases are added?
-Buffer solutions maintain their pH by reacting with added strong acids or bases. For example, when a strong acid is added, the buffer will react to neutralize the acid, preventing significant changes in pH.
What happens when a strong base is added to an acidic buffer?
-When a strong base is added to an acidic buffer, the base will react with the weak acid present in the buffer, allowing the buffer to maintain a relatively stable pH despite the addition of the base.
What is the significance of conjugate acids and bases in buffer solutions?
-Conjugate acids and bases are crucial in buffer solutions because they help to neutralize added acids or bases, thereby stabilizing the pH of the solution.
What does full dissociation mean in the context of strong acids and bases?
-Full dissociation refers to the complete separation of an acid or base into its ions in solution. For example, a strong acid like HCl fully dissociates into H+ and Cl- ions in water.
How does the presence of weak acids and bases affect the behavior of a buffer solution?
-The presence of weak acids and bases in a buffer solution allows it to resist changes in pH by providing equilibrium between the weak acid and its conjugate base, which can react with added acids or bases.
What role does NH3 (ammonia) play in buffer systems?
-NH3 (ammonia) acts as a weak base in buffer systems. It can react with added acids to form NH4+, thus helping to maintain the pH of the solution.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)