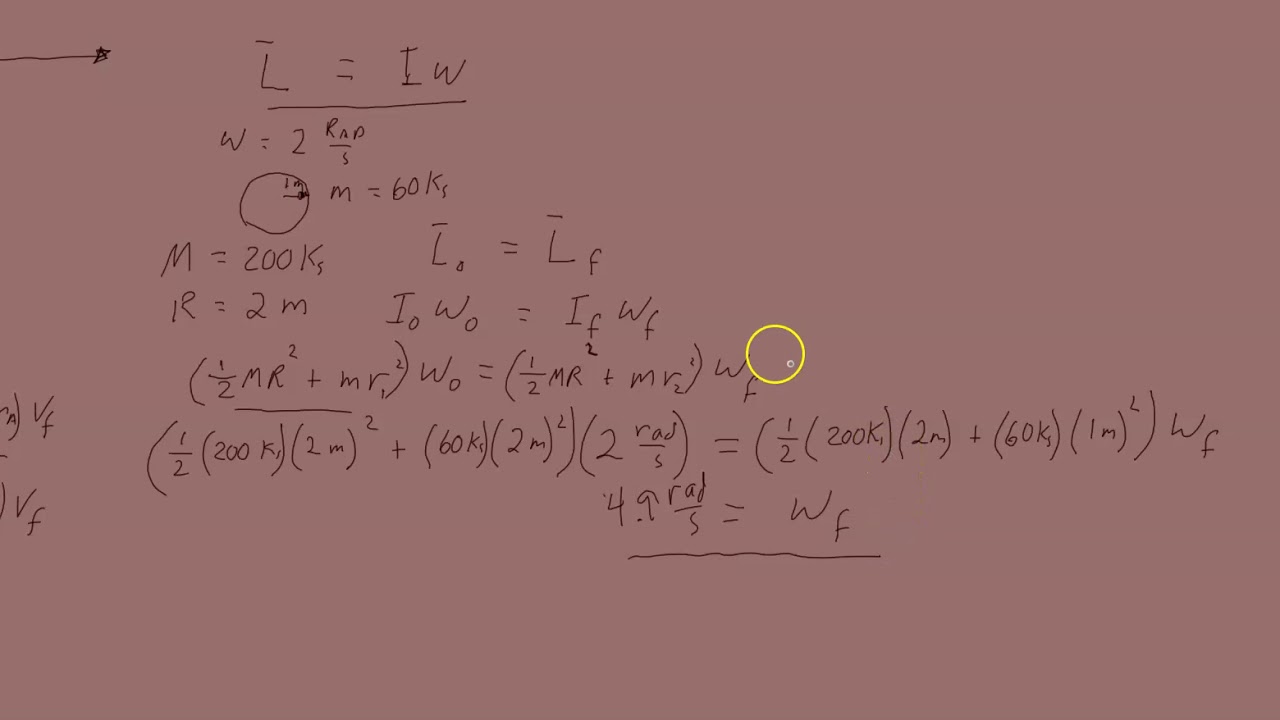konsep momentum sudut dan hukum kekekalan momentum sudut
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains the concepts of angular momentum and the law of conservation of angular momentum. It begins by introducing angular momentum, illustrating how it relates to rotational motion, and presents relevant formulas. Examples, including a solid sphere and a ballet dancer, demonstrate practical applications of these concepts, emphasizing the calculations involved in determining angular momentum and moment of inertia. The video encourages viewers to subscribe and engage with the content, highlighting its value for learners interested in physics.
Takeaways
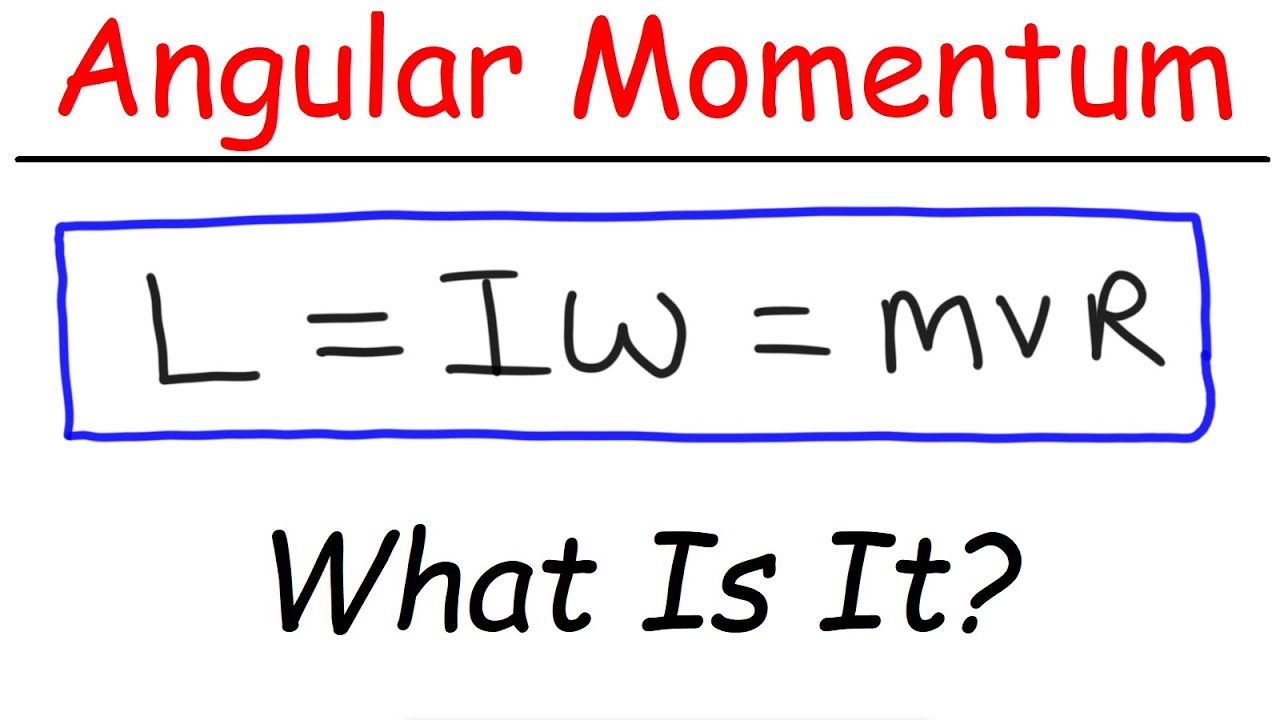
- 😀 Angular momentum is the momentum of a rotating object, calculated using the formula L = I × Ω.
- 📏 The moment of inertia (I) for a solid sphere is given by I = (2/5) m r², where m is mass and r is the radius.
- ⚙️ Linear momentum (p) for translational motion is defined as p = m × v, where v is the linear velocity.
- 🔄 An example illustrates calculating the angular momentum of a solid ball with a mass of 0.25 kg and radius of 20 cm rotating at 750 RPM.
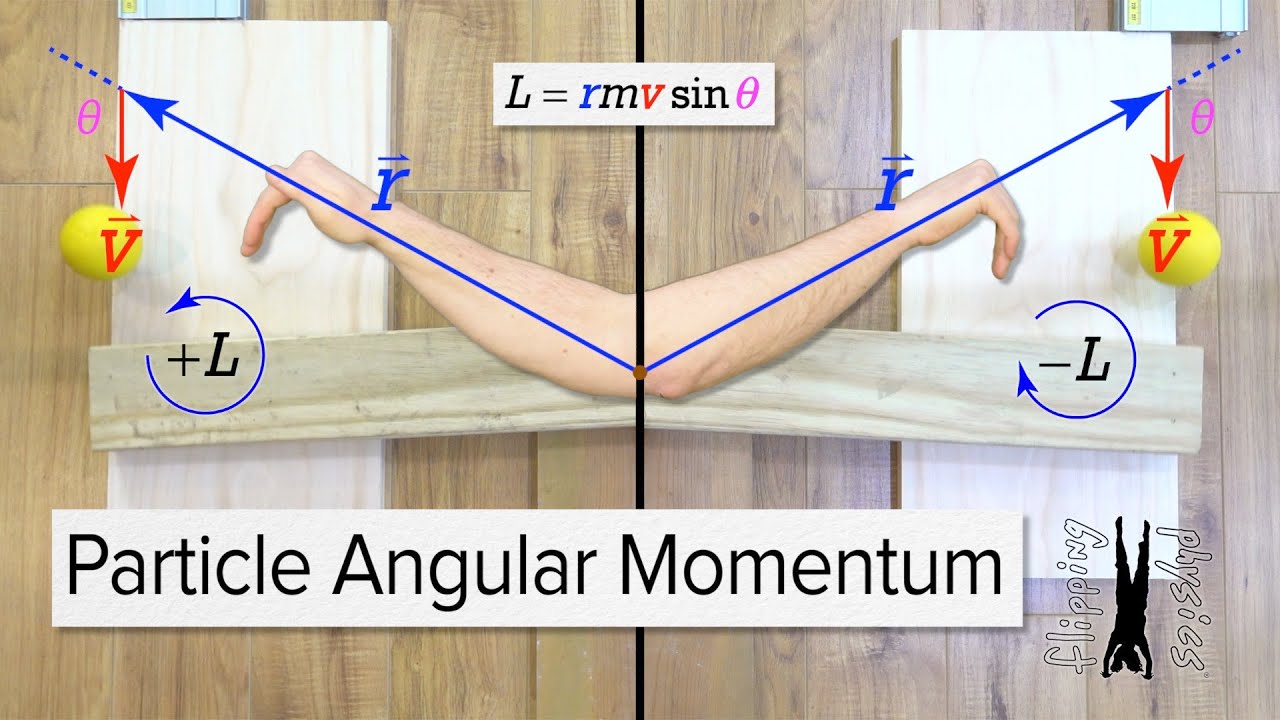
- 🔬 Another example calculates the angular momentum of a particle with a mass of 0.2 grams moving in a circular path at 10 radians per second.
- 🌀 The law of conservation of angular momentum states that if no external torque acts on a system, the total angular momentum remains constant.
- 👯♀️ An example of a ballet dancer demonstrates how pulling in her arms while spinning increases her angular speed while conserving momentum.
- 🧮 The new moment of inertia for the ballet dancer is calculated using conservation principles based on her initial and final angular speeds.
- 📈 Calculating angular momentum involves converting units, such as changing RPM to radians per second for accurate results.
- 🎥 The video concludes by encouraging viewers to subscribe and engage with educational content on physics.
Q & A
What is angular momentum?
-Angular momentum is a measure of the rotational motion of an object. It depends on the object's mass, its velocity, and the distance from the axis of rotation.
How is linear momentum different from angular momentum?
-Linear momentum is calculated using the formula p = mv, where 'p' is momentum, 'm' is mass, and 'v' is velocity. In contrast, angular momentum is represented as L = Iω, where 'L' is angular momentum, 'I' is the moment of inertia, and 'ω' is the angular velocity.
What is the formula for calculating angular momentum?
-Angular momentum can be calculated using the formulas L = Iω or L = mvr, where 'I' is the moment of inertia, 'ω' is the angular velocity, 'm' is mass, 'v' is linear velocity, and 'r' is the radius.
What are the units of angular momentum?
-The units of angular momentum are kg·m²/s (kilogram meter squared per second).
How is the moment of inertia of a solid sphere calculated?
-The moment of inertia of a solid sphere about an axis through its center is calculated using the formula I = (2/5)mR², where 'm' is mass and 'R' is the radius.
What does the conservation of angular momentum state?
-The conservation of angular momentum states that if no external torque acts on a system, the total angular momentum of that system remains constant over time.
How can we express the conservation of angular momentum mathematically?
-Mathematically, it can be expressed as L_initial = L_final, which translates to I1ω1 = I2ω2, where 'L' represents angular momentum, 'I' represents moment of inertia, and 'ω' represents angular velocity.
In the example given, how was the angular momentum of a solid sphere calculated?
-For the solid sphere with mass 0.25 kg and radius 20 cm, the angular momentum was calculated using L = Iω, where I was determined as (2/5)(0.25)(0.2²) and ω was converted from RPM to radians per second.
What was the angular momentum of the ballet dancer after changing her arm position?
-After the ballet dancer brought her arms in, her angular momentum changed based on her new moment of inertia and increased angular velocity. The calculation was based on the principle of conservation of angular momentum.
What is the importance of understanding angular momentum in physics?
-Understanding angular momentum is crucial for analyzing rotational motion, predicting the behavior of rotating systems, and applying the principles of mechanics to various fields such as engineering, sports, and astrophysics.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)