JENIS-JENIS MANUSIA PURBA INDONESIA
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the fascinating discoveries of ancient human species in Indonesia, highlighting key findings such as Meganthropus Paleojavanicus, Pithecanthropus, and Homo species. Notable researcher Gustav Heinrich von Koenigswald uncovered significant fossils, revealing the characteristics and lifestyles of these early humans. From the robust Meganthropus to the small-statured Homo floresiensis, each species showcases a unique aspect of human evolution. Viewers are encouraged to engage with the content by subscribing, liking, and commenting, fostering a deeper interest in prehistoric studies.
Takeaways
- 😀 The existence of prehistoric humans in Indonesia is supported by real research and discoveries.
- 🌍 The Meganthropus Paleojavanicus was discovered by Gustav Heinrich von Koenigswald between 1936 and 1941 in Sangiran, Central Java.
- 🔍 Meganthropus was characterized by a large, robust body and a strong jaw, with a small brain size compared to other prehistoric humans.
- 🦧 The Pithecanthropus erectus, also known as 'the upright ape man,' was first discovered by Eugène Dubois in 1890 near Trinil, East Java.
- 📏 Pithecanthropus had a height of about 165 to 180 cm and features similar to both apes and modern humans.
- 🧠 The Homo species, meaning 'human,' includes several varieties, showing a higher intelligence level than earlier species.
- 🧬 Fossils of Homo Wajakensis, found in 1889, indicate that this group had a brain volume of 1630 cc, distinguishing them as Homo sapiens.
- ⏳ Homo Soloensis fossils, discovered between 1931 and 1939, date back to around 900,000 to 300,000 years ago.
- 🏞️ Homo floresiensis, or 'the Hobbit,' was discovered in Liang Bua cave in 2004, notable for its small stature of about 100 cm.
- 📅 The timeline of these species ranges from 1.9 million years ago to as recently as 13,000 years ago, showcasing a diverse evolutionary history in Indonesia.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video transcript?
-The transcript discusses the existence of prehistoric humans in Indonesia and highlights various discoveries and research related to ancient human species.
Who discovered the Meganthropus Paleojavanicus, and where was it found?
-Meganthropus Paleojavanicus was discovered by German-Dutch researcher Gustav Heinrich von Koenigswald between 1936 and 1941 in Sangiran, Central Java.
What are the key physical characteristics of Meganthropus Paleojavanicus?
-Meganthropus Paleojavanicus had a large and sturdy body, a strong jaw, a prominent brow ridge, and no chin. Its brain volume was estimated to be small compared to other prehistoric humans.
What distinguishes Pithecanthropus from other prehistoric human species?
-Pithecanthropus, particularly Pithecanthropus erectus, is noted for showing ape-like features while also having adaptations for bipedalism, making it a significant link in human evolution.
Which researcher is associated with the discovery of Pithecanthropus, and where was it found?
-Pithecanthropus was discovered by Dutch researcher Eugene Dubois in 1890 near Trinil, a village on the banks of the Solo River in East Java.
What does the term 'Homo' refer to in the context of this transcript?
-In this context, 'Homo' refers to the genus of modern humans and their close relatives, indicating an evolutionary advancement in terms of intelligence and physical traits.
What evidence supports the classification of Homo Wajakensis as Homo sapiens?
-Homo Wajakensis was classified as Homo sapiens due to its skull features, which included a flat face, broad nose, and a larger brain volume of 1630 cc, indicating advanced cognitive abilities.
What is notable about Homo floresiensis, also known as the Liang Bua man?
-Homo floresiensis is notable for its small stature, standing only about 100 cm tall, and its brain volume of 380 cc. It was discovered in 2004 in Liang Bua cave in Flores, Indonesia.
What time period do the fossil remains of Homo floresiensis date back to?
-The fossil remains of Homo floresiensis are estimated to date back to between 94,000 and 13,000 years ago.
How does the transcript conclude, and what does it encourage viewers to do?
-The transcript concludes by inviting viewers to support the channel through subscriptions, likes, and constructive comments, and ends with a friendly farewell.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Manusia Purba Indonesia dan Dunia || Sejarah Peminatan Kelas 10 IPS

Manusia Purba di Indonesia

6 Jenis Manusia Purba yang Pernah Hidup di Indonesia

JENIS-JENIS MANUSIA PURBA DI INDONESIA

Mengenal Jejak Manusia Purba | Sejarah Kelas 10 - KHATULISTIWA MENGAJAR
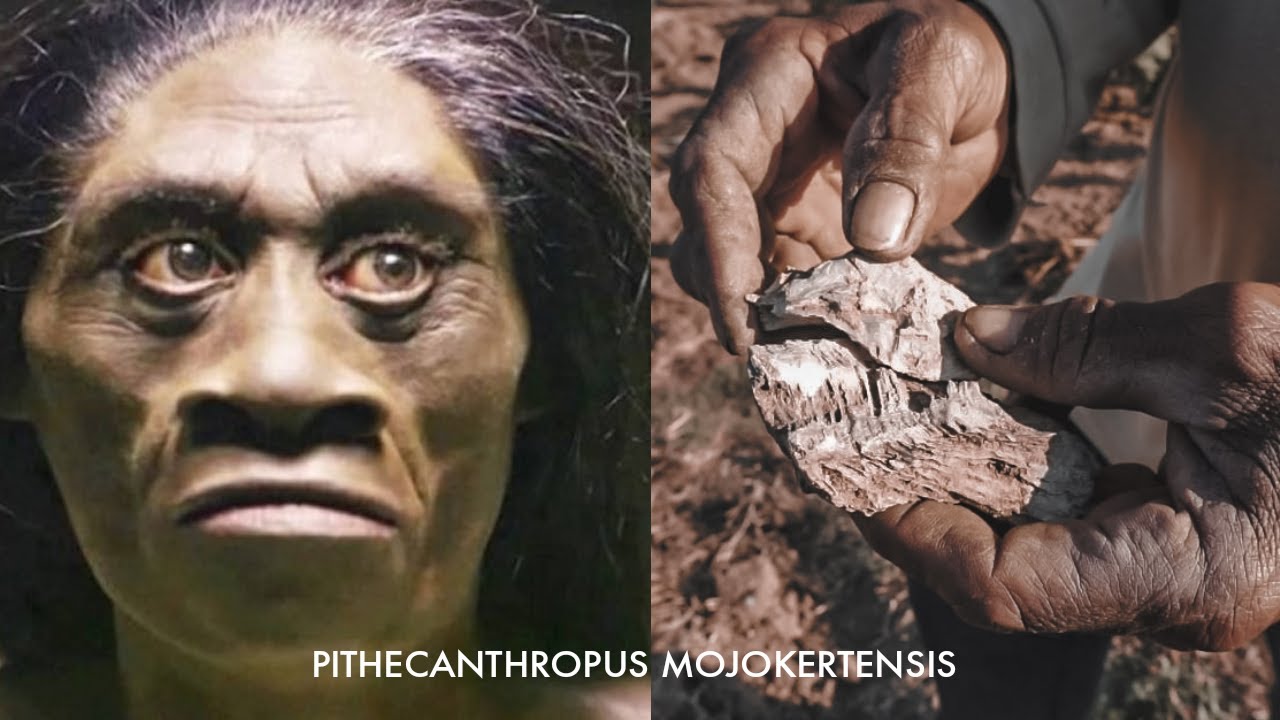
Ternyata Begini Jejak Manusia Purba PITHECANTHROPUS MOJOKERTENSIS Manusia Kera Dari Mojokerto
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
