Quantum Numbers
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the four quantum numbers that describe the position and characteristics of electrons in an atom. It covers the principal quantum number (n), which represents the energy level, the angular momentum quantum number (l) for sublevel shapes, the magnetic quantum number (ml) that specifies the orbital, and the electron spin quantum number (ms), which denotes the electron's spin. Through detailed examples, the video illustrates how these quantum numbers work together to define the unique 'address' of an electron, following the Pauli exclusion principle.
Takeaways
- 🔢 The video discusses four key quantum numbers that describe the 'address' of an electron in an atom.
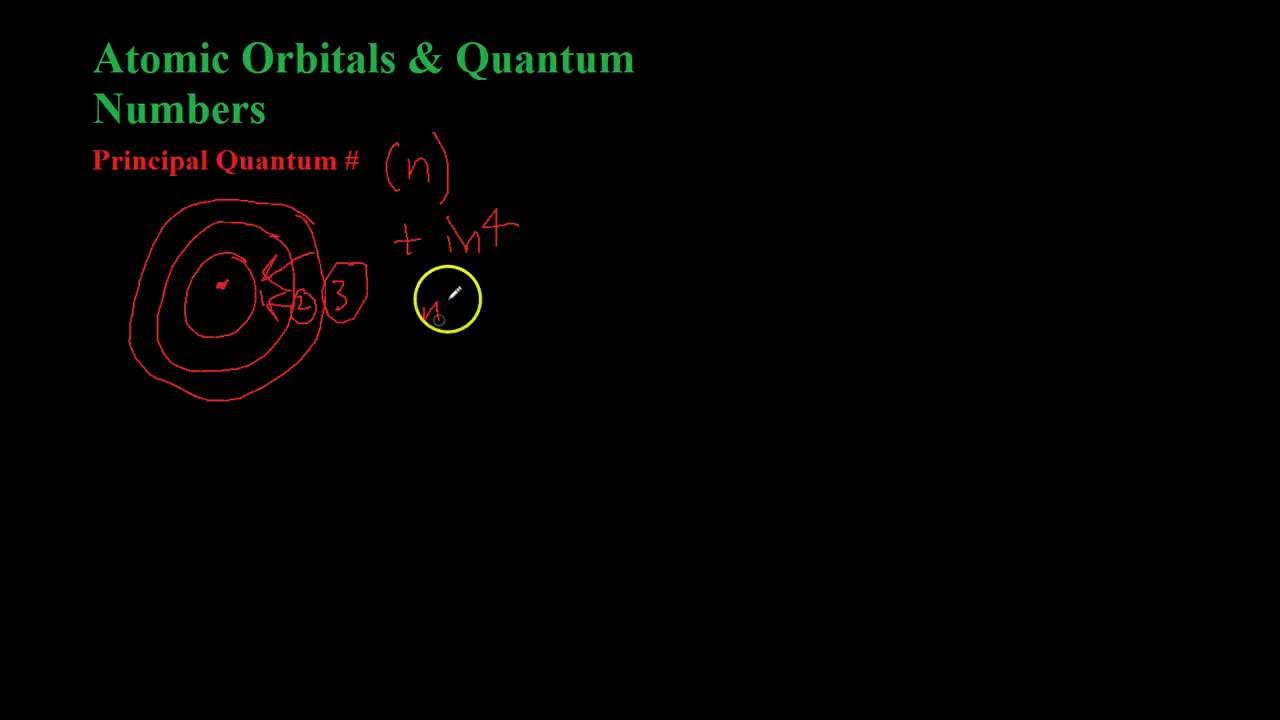
- 🔬 The first quantum number, 'n' (principal quantum number), defines the energy level of the electron, which can be any integer starting from 1.
- ⚛️ The second quantum number, 'l' (angular momentum quantum number), defines the shape of the electron's sublevel and is dependent on 'n'. The value of 'l' can range from 0 to n-1.
- 🌀 The 's', 'p', 'd', and 'f' sublevels have specific 'l' values: for 's', l=0; for 'p', l=1; for 'd', l=2; and for 'f', l=3.
- 🔗 The value of 'l' determines the possible sublevels within an energy level: for example, when n=3, l can be 0, 1, or 2, corresponding to the 's', 'p', and 'd' sublevels.
- 🧲 The third quantum number, 'ml' (magnetic quantum number), describes the specific orbital within a sublevel. It ranges between -l and +l.
- 🎯 The number of orbitals within each sublevel varies: 's' has 1 orbital, 'p' has 3, 'd' has 5, and 'f' has 7.
- 🔄 The fourth quantum number, 'ms' (spin quantum number), describes the spin of the electron, which can be either +1/2 or -1/2.
- 🌀 Each orbital can hold two electrons, one with an up spin (+1/2) and one with a down spin (-1/2).
- 🧪 In specific examples (like 3d electrons), quantum numbers can be assigned based on the electron’s position in the sublevel, with 'ms' indicating its spin.
Q & A
What are the four quantum numbers used to describe the address of an electron in an atom?
-The four quantum numbers are: 1) Principal quantum number (n), 2) Angular momentum quantum number (l), 3) Magnetic quantum number (m_l), and 4) Electron spin quantum number (m_s).
What does the principal quantum number (n) represent?
-The principal quantum number (n) represents the energy level of an electron within an atom. It is an integer (1, 2, 3, etc.) and determines the size and energy of the electron's orbit.
What is the angular momentum quantum number (l), and what does it describe?
-The angular momentum quantum number (l) describes the shape of the sublevel within a given energy level. It can take values from 0 to n-1, where n is the principal quantum number. The values correspond to sublevels: s (l=0), p (l=1), d (l=2), and f (l=3).
How are the values of the angular momentum quantum number (l) related to the principal quantum number (n)?
-The angular momentum quantum number (l) must be less than or equal to n-1. For example, if n=3, l can be 0, 1, or 2.
What is the magnetic quantum number (m_l), and what does it determine?
-The magnetic quantum number (m_l) describes the orientation of the orbital within a sublevel. It takes integer values ranging from -l to +l. For example, when l=2 (d sublevel), m_l can be -2, -1, 0, 1, or 2.
What are the possible values for the electron spin quantum number (m_s), and what do they represent?
-The electron spin quantum number (m_s) can be either +1/2 or -1/2, representing the two possible spin states of an electron within an orbital: spin up (+1/2) or spin down (-1/2).
How do you determine the quantum numbers for an electron in the 3d sublevel?
-For an electron in the 3d sublevel, the principal quantum number (n) is 3, the angular momentum quantum number (l) is 2 (because d sublevel corresponds to l=2), and the magnetic quantum number (m_l) can range from -2 to +2. The electron spin (m_s) can be either +1/2 or -1/2.
Why is there no 1p or 2d sublevel in electron configurations?
-There is no 1p sublevel because when n=1, l must be 0 (s sublevel only), and there is no 2d sublevel because when n=2, l can only be 0 (s) or 1 (p), but not 2 (d).
What is the maximum number of orbitals in the d and f sublevels, and how many electrons can they hold?
-The d sublevel has 5 orbitals, and the f sublevel has 7 orbitals. Since each orbital can hold 2 electrons, the d sublevel can hold a maximum of 10 electrons, and the f sublevel can hold a maximum of 14 electrons.
What are the quantum numbers for an electron in the 4f sublevel?
-For an electron in the 4f sublevel, the principal quantum number (n) is 4, the angular momentum quantum number (l) is 3 (because f sublevel corresponds to l=3), and the magnetic quantum number (m_l) can range from -3 to +3. The electron spin (m_s) can be either +1/2 or -1/2.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Cara Mudah‼️Menentukan Bilangan Kuantum (Utama, Azimut, Magnetik, Spin)
4.2 Quantum Model of the Atom

BILANGAN KUANTUM

3.5.3 - Composição de um orbital atômico: Número quântico principal (camada ou nível de energia)

BILANGAN KUANTUM

How To Determine The 4 Quantum Numbers From an Element or a Valence Electron
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
