Renal System Examination
Summary
TLDRIn this medical examination, a student assesses a patient's kidney function through a thorough physical exam. The student first checks the patient's hands for signs of abnormalities, such as palmar erythema, and performs tests for clubbing and tremors. They proceed to inspect the face, neck, chest, abdomen, and limbs, checking for edema, scars, and other signs of disease. The examination also includes palpation of organs like the liver, spleen, and kidneys, as well as percussing the abdomen. The student concludes with listening to the patient's lungs and renal arteries, followed by inspection of the legs for edema.
Takeaways
- 😀 The speaker introduces themselves as a medical student and asks the patient's permission to examine their kidneys.
- 🩺 The patient is observed to be comfortable, alert, breathing normally, and of normal weight.
- ✋ The examination begins with an inspection of the patient's hands for signs like palmar erythema, muscle wasting, and clubbing, all of which are normal.
- 👁 The speaker checks the patient's face for signs like periorbital edema, epistaxis, and oral health, all of which are normal.
- 🫀 The speaker palpates the patient's neck for lymph nodes and checks for raised jugular venous pressure (JVP), which is normal.
- 🩻 The heart examination includes checking the apex beat and listening for pericardial rubs, both of which are normal.
- 🩺 The speaker examines the patient's lungs for pleural effusion and auscultates lung bases, finding no abnormalities.
- 🫁 The abdomen is inspected for scars, masses, and distension, followed by superficial and deep palpation, liver, spleen, and kidney examination.
- 👂 The speaker listens for bruits in the renal arteries and assesses bowel sounds across four areas, which are all normal.
- 🦵 The legs are inspected for asymmetry, discoloration, and edema, and the patient does not exhibit any signs of pain during the examination.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of the medical examination described in the script?
-The main purpose of the examination is to assess the patient's kidneys and overall health, including pulse rate, blood pressure, and various physical signs related to kidney function.
Why does the examiner ask the patient to remove their shirt before starting the examination?
-The examiner asks the patient to remove their shirt to properly assess the chest, arms, and abdomen for any physical signs such as scars, bruises, or abnormalities that might indicate an underlying health condition.
What does the absence of palmar erythema and muscle wasting in the patient's hands indicate?
-The absence of palmar erythema (redness of the palms) and muscle wasting suggests that the patient does not have liver disease or malnutrition, which can manifest through such physical signs.
Why is the skin turgor checked, and what does a normal result indicate?
-Skin turgor is checked to assess the patient’s hydration status. A normal skin turgor (where the skin returns to its original position within 3 seconds) indicates that the patient is well-hydrated.
What is the significance of the examiner testing for clubbing and capillary refill time?
-Clubbing of the fingers can indicate chronic respiratory or cardiovascular diseases, while capillary refill time tests blood flow and circulation. Normal findings suggest healthy cardiovascular and respiratory function.
Why does the examiner check for periorbital edema and a butterfly rash on the face?
-Periorbital edema (swelling around the eyes) can indicate kidney issues, and a butterfly rash can be a sign of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an autoimmune disorder. The absence of these signs suggests the patient does not have these conditions.
What does the absence of a raised jugular venous pressure (JVP) indicate?
-The absence of a raised JVP suggests that the patient does not have fluid overload or heart failure, as elevated JVP is a common sign of these conditions.
Why does the examiner palpate the abdomen and perform percussion?
-The examiner palpates and percusses the abdomen to check for masses, organ enlargement (such as liver or spleen), and abnormal fluid accumulation. These are important for assessing the health of internal organs like the kidneys, liver, and spleen.
What is the purpose of the Murphy's punch test during the examination?
-The Murphy's punch test is performed to check for tenderness in the kidneys, which may indicate kidney infection or inflammation. The absence of pain during this test suggests the kidneys are not tender or inflamed.
Why is it important to assess the legs for edema and asymmetry?
-Assessing the legs for edema (swelling) and asymmetry helps identify fluid retention, which can be a sign of heart or kidney problems. Pitting edema, for instance, may indicate heart failure or renal dysfunction.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
Hand Examination - OSCE Guide (old version) | UKMLA | CPSA

Cardiovascular Examination | OSCE Guide | UKMLA | CPSA | PLAB 2

Pemeriksaan Fisik Neurologis | Tugas Ujian Online Stase Saraf

PEMERIKSAAN FISIK EKSTREMITAS
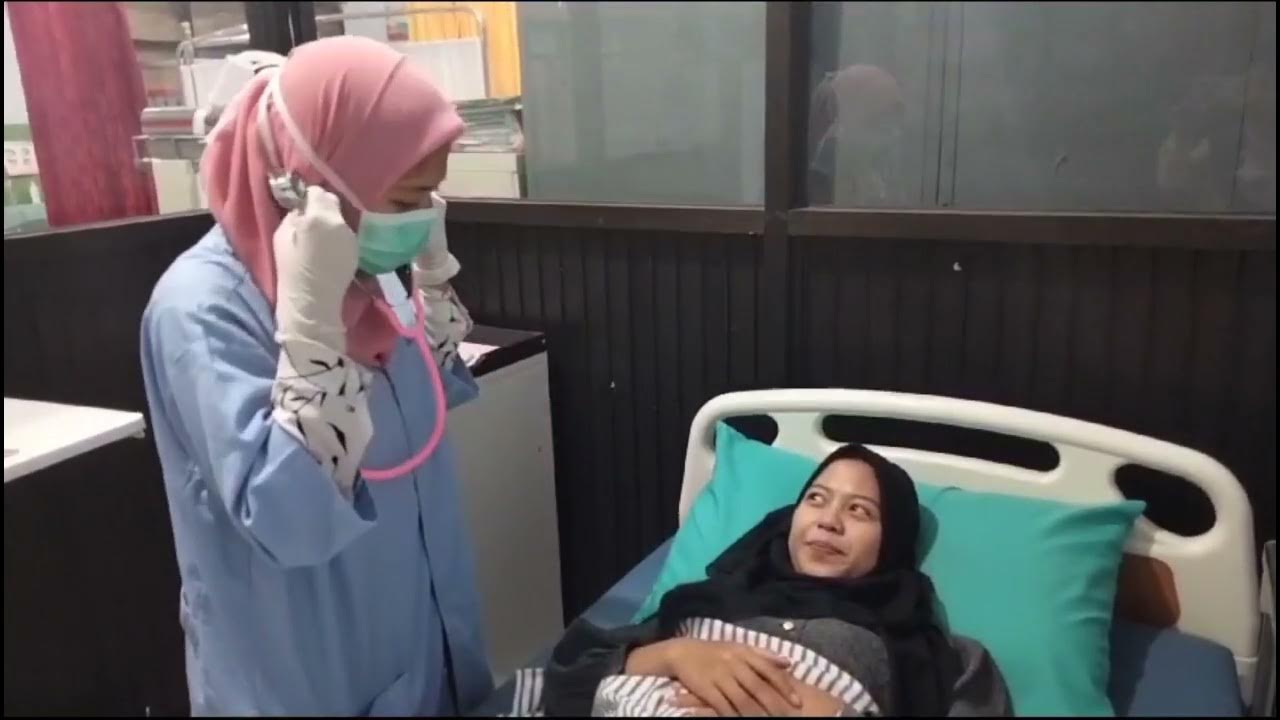

PEMERIKSAAN FISIK DAN KECUKUPAN OKSIGEN

GALS examination (Gait, Arms, Legs, Spine) - OSCE Guide | UKMLA | CPSA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
