Metabolism | The Metabolic Map: Lipids
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the focus is on the metabolism of triglycerides and fats, detailing how they are stored and broken down in the body. The process of lipolysis is explained, where triglycerides are split into glycerol and fatty acids. The video also covers lipogenesis, the synthesis of triglycerides, and how these processes are reversible. Key metabolic pathways such as glycolysis, beta-oxidation, ketogenesis, and ketolysis are discussed, along with the synthesis of cholesterol and its importance. The next video will delve into how proteins and amino acids are integrated into metabolic pathways and cover gluconeogenesis.
Takeaways
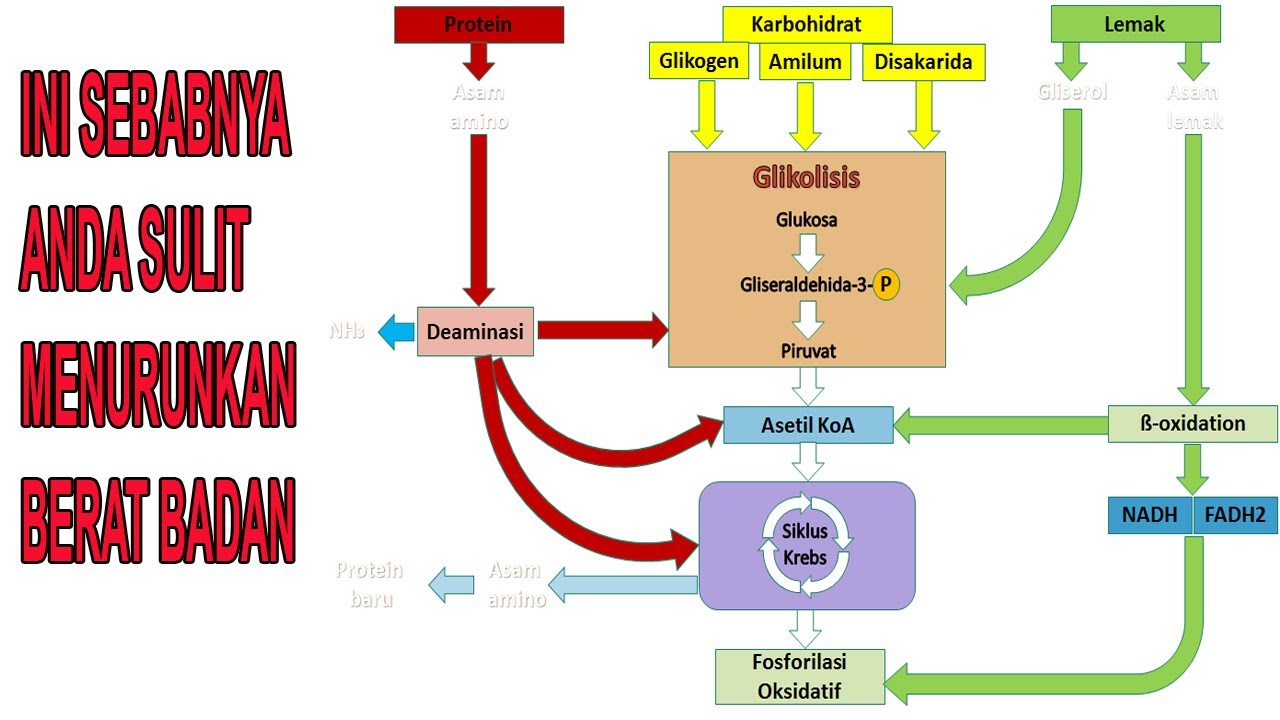
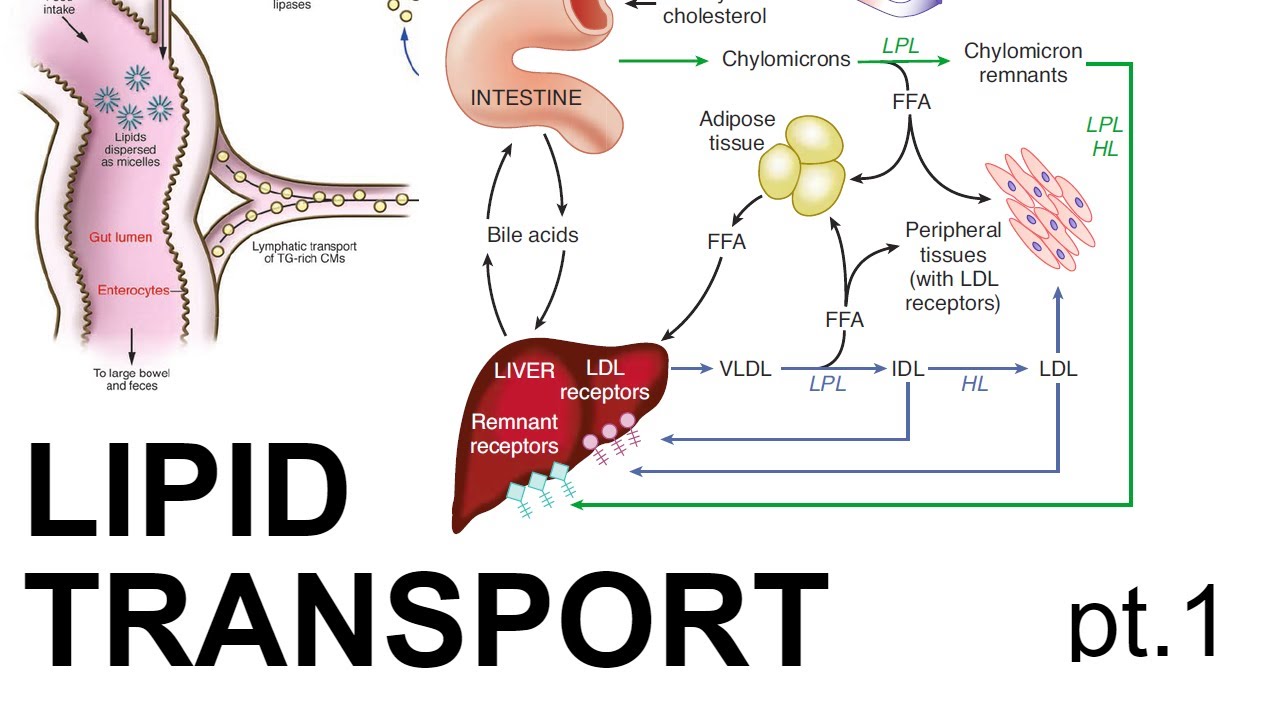
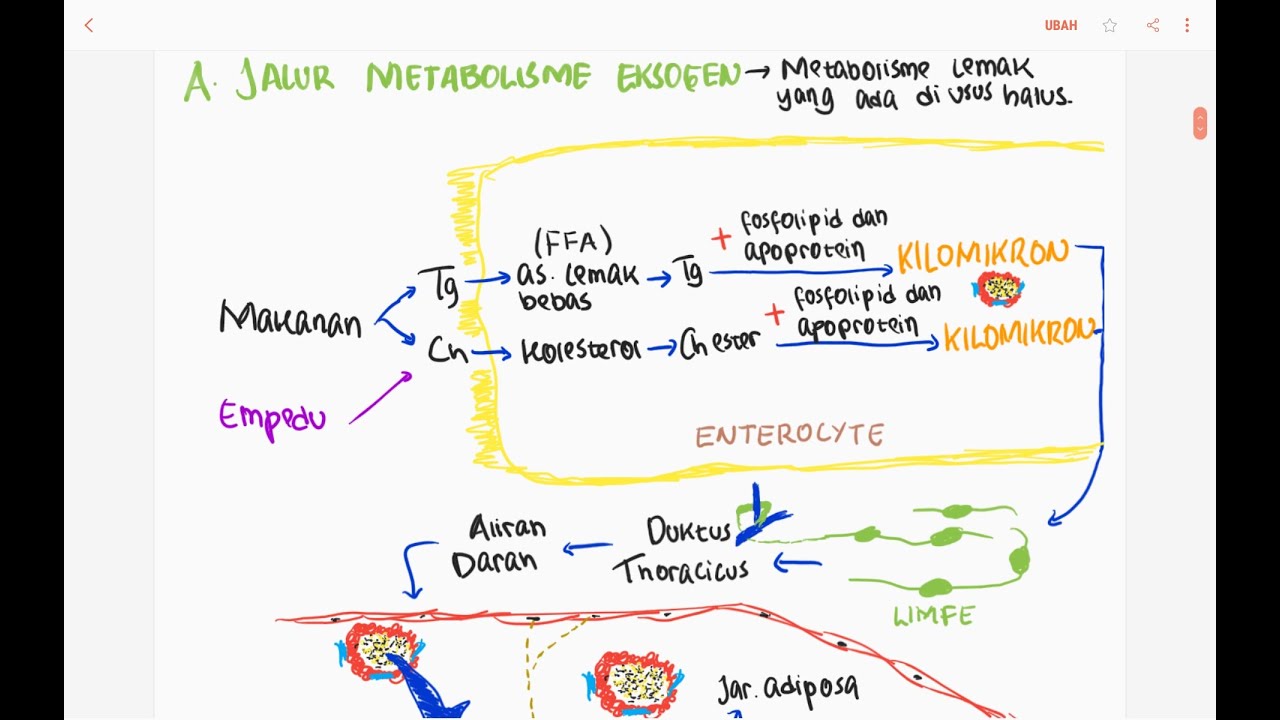
- 🧪 Triglycerides, or triacylglycerols (TAG), are the main form of stored fat in the body, consisting of glycerol and fatty acids.
- ⚙️ During fasting or energy demand, triglycerides are broken down into glycerol and fatty acids through lipolysis.
- 🔄 Lipolysis is the process of breaking down triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids, while lipogenesis is the reverse, where fatty acids and glycerol are used to form triglycerides.
- 🔬 Glycerol is a three-carbon structure that can be converted to dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP), entering glycolysis to produce energy.
- 💡 Fatty acids are broken down into two-carbon units through beta oxidation, leading to the formation of acetyl-CoA, which enters the Krebs cycle to produce ATP.
- 🍽️ In a fed state, excess glucose can be converted into fatty acids (lipogenesis), which combine with glycerol to form triglycerides.
- 🧠 In conditions of low glucose (e.g., diabetes, starvation), the body can convert acetyl-CoA into ketone bodies (ketogenesis), which can be used by the brain and muscles for energy.
- ⚛️ Ketolysis is the process where ketone bodies are broken down into acetyl-CoA for energy production in the brain and muscles.
- 🌟 Acetyl-CoA is also a precursor for cholesterol synthesis, which is essential for cell membranes, bile salts, and steroid hormones.
- 💥 Excess acetyl-CoA in the body, due to a lack of oxaloacetate (OAA), can be converted into ketone bodies, providing an alternative energy source when glucose is low.
Q & A
What are triglycerides commonly referred to in scientific terms?
-Triglycerides are commonly referred to as lipids in scientific terms. More specifically, they are also called triacylglycerols (TAG).
How are triglycerides broken down in the body?
-Triglycerides are broken down into glycerol and fatty acids through a process called lipolysis. This involves breaking the ester bond between the glycerol 'head' and the fatty acid 'tails'.
What happens to glycerol after it is released during lipolysis?
-After glycerol is released, it is converted into dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP), which can enter glycolysis or gluconeogenesis pathways.
What is beta-oxidation, and what role does it play in fat metabolism?
-Beta-oxidation is the process by which long-chain fatty acids are broken down into two-carbon fragments, specifically acetyl-CoA. This acetyl-CoA then enters the Krebs cycle to produce energy.
What occurs in the body when there is an excess of glucose intake?
-When there is an excess of glucose, the body converts some of the DHAP into glycerol and some of the acetyl-CoA into fatty acids. These two components combine to form triglycerides through a process called lipogenesis.
What is ketogenesis, and when does it occur?
-Ketogenesis is the process of converting acetyl-CoA into ketone bodies, such as acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate. This occurs when there is a lack of carbohydrates, such as during starvation or diabetes, and the body needs an alternative energy source for the brain and muscles.
What is the role of ketone bodies in energy metabolism?
-Ketone bodies provide an alternative energy source during periods of low carbohydrate availability. They are transported to tissues like the brain, skeletal muscles, and cardiac muscles, where they are broken down back into acetyl-CoA through a process called ketolysis to generate energy.
How is cholesterol synthesized in the body?
-Cholesterol is synthesized from acetyl-CoA in a process called cholesterol synthesis. This cholesterol is essential for forming bile salts, steroid hormones, and maintaining the structural integrity of cell membranes.
What is the importance of acetyl-CoA in fat metabolism?
-Acetyl-CoA is a key molecule in fat metabolism. It is produced during beta-oxidation of fatty acids, and it serves as a substrate for the Krebs cycle, ketogenesis, cholesterol synthesis, and fatty acid synthesis.
What is the significance of lipogenesis in the fed state?
-In the fed state, when insulin is produced, lipogenesis occurs. During this process, excess glucose is converted into fatty acids and glycerol, which combine to form triglycerides for long-term energy storage.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)