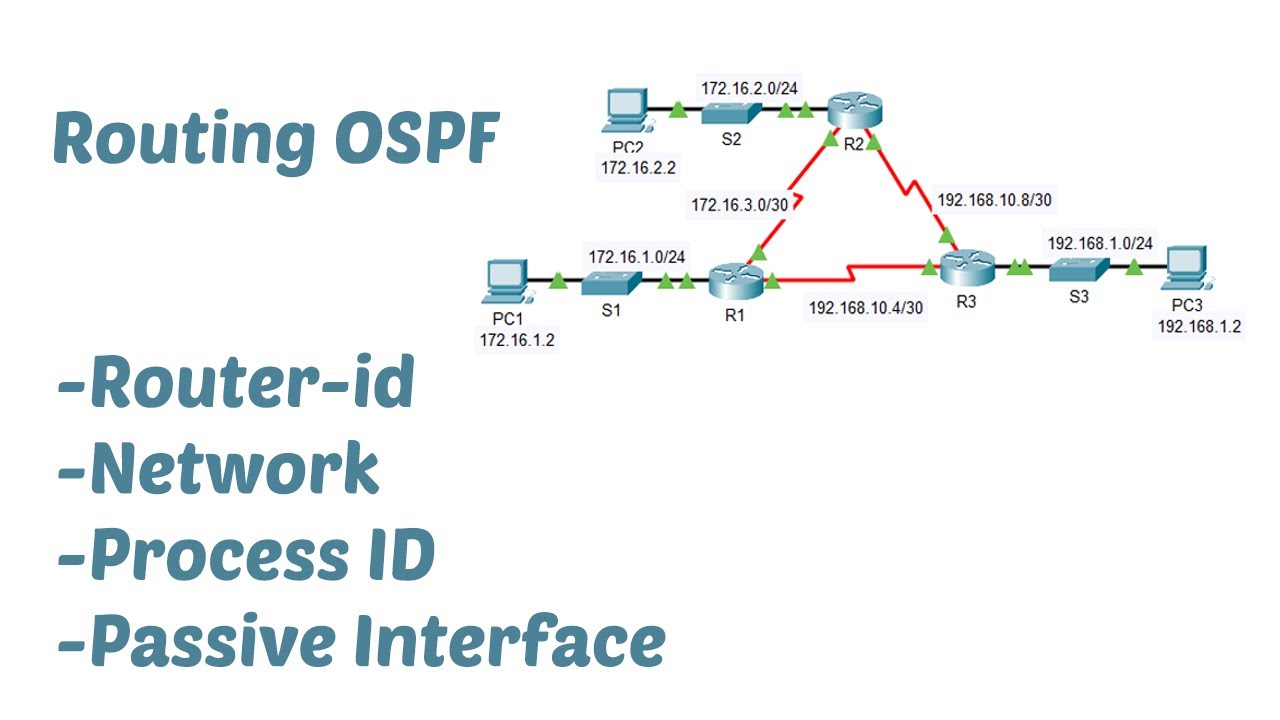
OSPF Framework & OSPF Packets: LSDB, LSA, Hello, DBD, LSR, LSU, LSAck
Summary
TLDRThis video is an introduction to OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and provides an overview of the key components involved in its operation. It explains the three main tables OSPF uses: the neighbor table, topology table (link-state database), and routing table. The lesson also covers the five types of packets involved in OSPF communication: Hello, Database Descriptor (DBD), Link State Request, Link State Update, and Link State Acknowledgment. By the end, viewers should understand these fundamental OSPF concepts and be prepared for the next lesson on OSPF areas and router types.
Takeaways
- 📊 OSPF uses three main tables: the Neighbor table, the Topology table (Link State Database - LSDB), and the Routing table.
- 🔗 The Neighbor table contains information about directly connected OSPF routers and their adjacency states.
- 🏛️ The Topology table (LSDB) holds the entire OSPF network's knowledge, including Link State Advertisements (LSAs) for each router.
- 📜 Each entry in the LSDB is a Link State Advertisement (LSA), representing specific details of routers and their networks.
- 💬 OSPF communication relies on five packet types: Hello packets, Database Descriptor (DBD) packets, Link State Requests, Link State Updates, and Link State Acknowledgements.
- 👋 Hello packets are sent periodically to the multicast address 224.0.0.5 to discover OSPF neighbors.
- 📑 Database Descriptor (DBD) packets summarize LSAs and help routers determine which LSAs they need from neighbors.
- 🔍 Link State Requests are used by routers to request specific LSAs that they don't yet have.
- 📥 Link State Update packets contain the actual LSAs, while Link State Acknowledgement packets confirm receipt of updates.
- ✅ OSPF ensures reliability by having routers exchange and acknowledge packets throughout the process, ensuring full network topology awareness.
Q & A
What are the three tables used by OSPF to accomplish its goals?
-OSPF uses the Neighbor Table, the Topology Table (also known as the Link-State Database or LSDB), and the Routing Table to accomplish its goals.
What information is stored in the Neighbor Table?
-The Neighbor Table contains a list of directly connected OSPF routers, including the state of the adjacency with each neighbor.
What command is used to view the Neighbor Table on a Cisco router?
-The command 'show ip ospf neighbor' is used to view the Neighbor Table on a Cisco router.
What is the purpose of the Topology Table in OSPF?
-The Topology Table, also known as the Link-State Database (LSDB), contains everything OSPF knows about the network, including Link-State Advertisements (LSAs), which are individual entries in the database.
What are Link-State Advertisements (LSAs)?
-Link-State Advertisements (LSAs) are individual entries within the Link-State Database (LSDB), which represent the state of each link in the OSPF topology.
Do all OSPF routers have the same Link-State Database (LSDB)?
-Yes, all OSPF routers have the same LSDB once the network has converged, meaning they all share the same view of the topology.
What is the function of the Routing Table in OSPF?
-The Routing Table contains the best routes calculated from the Topology Table. OSPF adds its best routes to the Routing Table, which is used by the router to forward packets.
What are the five packets involved in OSPF communication?
-The five packets used in OSPF communication are Hello Packets, Database Descriptor (DBD) Packets, Link-State Request Packets, Link-State Update (LSU) Packets, and Link-State Acknowledgement (LSAck) Packets.
What is the purpose of Hello Packets in OSPF?
-Hello Packets are used to discover OSPF neighbors. Routers send Hello Packets to the multicast address 224.0.0.5 to find other OSPF routers and form adjacencies.
How do Database Descriptor (DBD) Packets work in OSPF?
-DBD Packets contain summaries of the LSAs in a router’s LSDB. When two routers first discover each other, they exchange DBD Packets to summarize what they know, allowing each router to request only the LSAs it needs.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)