¿Qué es la INTEGRAL? | SIGNIFICADO de la integral definida (Lo que no te enseñan sobre la integral)
Summary
TLDREl script explora el concepto de integral en cálculo, enfocándose en su significado más allá de los cálculos. Expone que el área bajo la curva de una función, comúnmente asociada a la integral, representa áreas como la distancia recorrida en un viaje o la energía consumida por un sistema. Utiliza ejemplos prácticos, como el viaje en coche a diferentes velocidades y el cambio de energía, para ilustrar cómo calcular áreas y distancias a través de integrales. El video busca que el espectador entienda la belleza y utilidad de las matemáticas, promoviendo una comprensión más profunda y atractiva del cálculo diferencial.
Takeaways
- 📚 El cálculo integral es un tema relevante en el estudio del cálculo, pero a menudo se enfoca más en el cálculo que en su significado y utilidad.
- 📉 La integral de una función se asocia comúnmente con el área bajo la curva de esa función, pero su significado y aplicación pueden ser más amplios.
- 🚗 El ejemplo de un viaje en coche con velocidad constante muestra cómo calcular la distancia recorrida a partir de la velocidad y el tiempo.
- 📊 La representación gráfica de la velocidad vs. tiempo permite visualizar la distancia recorrida como el área bajo la curva de velocidad.
- 🔄 En situaciones donde la velocidad varía, la distancia recorrida se puede calcular como la suma de áreas de figuras geométricas simples, como rectángulos y trapecios.
- 🚦 La integral se utiliza para calcular áreas bajo curvas, lo cual es útil para determinar distancias cuando la velocidad no es constante.
- 📐 El proceso de aproximación de áreas mediante rectángulos se mejora al disminuir el ancho de estos, acercando el resultado a la verdadera área bajo la curva.
- 🔢 La integral definida es el límite de la suma de áreas de rectángulos cuando su ancho tiende a cero, lo que nos da el área exacta bajo la curva.
- ⏱ La integral de la velocidad con respecto al tiempo nos da la distancia recorrida, mientras que la integral de la potencia con respecto al tiempo nos da la energía.
- 🌐 La integral puede representar diferentes conceptos dependiendo de la función que se está integrando, como distancia, energía o otros.
- 🌟 Comprender la intuición detrás de las integrales y su significado puede hacer que el aprendizaje de cálculo sea más agradable y significativo.
Q & A
¿Qué es un integral en cálculo y por qué es relevante?
-Un integral en cálculo es una medida de la área bajo la curva de una función dada, y es relevante porque representa conceptos como la distancia recorrida, la energía consumida o el acumulo de una cantidad en un intervalo de tiempo.
¿Por qué es importante entender más allá de los cálculos el significado de los integrales?
-Es importante entender el significado de los integrales porque permite ver la conexión entre matemáticas y el mundo real, lo que facilita una comprensión más profunda y una apreciación de su utilidad en diferentes contextos.
¿Cómo se relaciona el área bajo la curva de una función con la distancia recorrida por un vehículo?
-El área bajo la curva de la función de velocidad en función del tiempo da la distancia recorrida, ya que multiplicar la velocidad (altura de la curva) por el tiempo (base) nos da la distancia total.
En el caso de un viaje en auto con velocidad constante, ¿cómo se calcula la distancia recorrida?
-Para un viaje con velocidad constante, la distancia recorrida se calcula multiplicando la velocidad por el tiempo transcurrido.
¿Cómo se representa gráficamente la distancia recorrida por un vehículo con velocidad constante?
-Gráficamente, la distancia recorrida se representa como el área rectangular bajo la curva de velocidad constante en el eje de tiempo.
Si la velocidad de un vehículo varía con el tiempo, ¿cómo se calcula la distancia total recorrida?
-Cuando la velocidad varía, la distancia total se calcula sumando las áreas de las figuras geométricas correspondientes a los intervalos de tiempo en los que la velocidad es constante o se puede aproximar como tal.
¿Qué es un rectángulo en el contexto de calcular áreas bajo curvas para aproximar distancias recorridas?
-Un rectángulo en este contexto es una aproximación de la área bajo una curva, donde se considera que la velocidad es constante en un intervalo de tiempo pequeño, y se calcula la distancia como la base (tiempo) multiplicada por la altura (velocidad).
¿Cómo se representa gráficamente la distancia recorrida por un vehículo con velocidad que cambia con el tiempo?
-Se representa sumando las áreas de figuras geométricas como rectángulos y trapecios, que corresponden a intervalos de tiempo en los que la velocidad es constante o puede ser aproximada como tal.
¿Qué es un integral definido y cómo se relaciona con el cálculo de áreas bajo curvas?
-Un integral definido es la suma límite de áreas de infinitos rectángulos horizontales cuando su ancho tiende a cero, lo que se usa para calcular áreas bajo curvas y, por ejemplo, la distancia recorrida cuando la velocidad es una función del tiempo.
¿Cómo se relaciona el integral de una función de potencia con el cálculo de energía?
-El integral de una función de potencia en un intervalo de tiempo da la energía consumida por un sistema, ya que la potencia (en vatios) multiplicada por el tiempo (en segundos) da la energía (en julios).
¿Por qué es beneficioso entender la matemática de manera intuitiva y relacionada con el mundo real?
-Entender la matemática intuitivamente y relacionada con el mundo real ayuda a apreciar su belleza y utilidad, lo que puede hacer que el aprendizaje sea más agradable y significativo.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
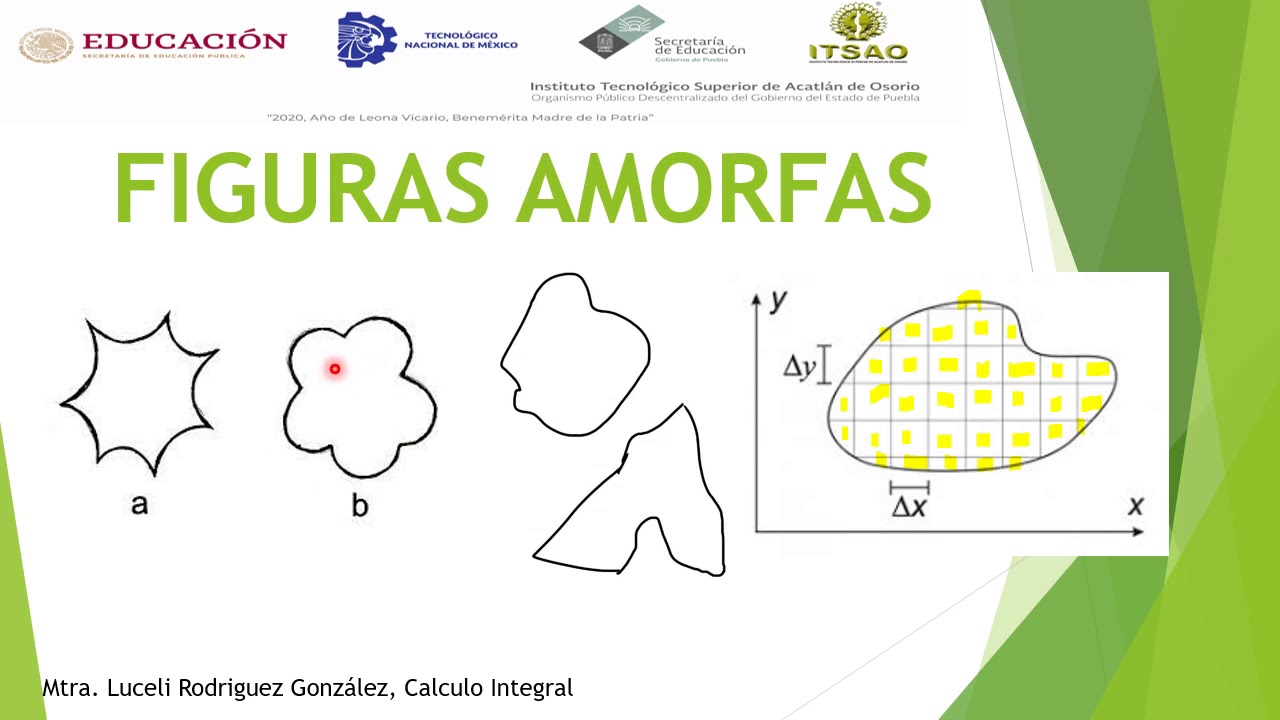
Figuras amorfas y notación sumatoria

Volumen de paraboloide con integral triple | COORDENADAS CILÍNDRICAS | Modelado con GEOGEBRA

Sumatorias
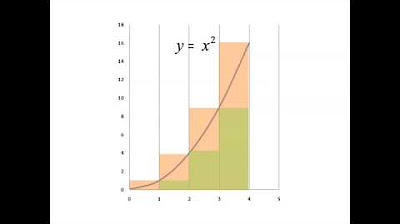
Cálculo Integral 01:Área bajo una curva. Area under a curve
El determinante | Esencia del álgebra lineal, capítulo 5

¿QUÉ ES EL CALCULO INTEGRAL? Super facil - Para principiantes

Calculo integral
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)