ILLUSTRATING POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS || GRADE 10 MATHEMATICS Q2
Summary
TLDRThis video lesson explains the fundamentals of polynomial functions, focusing on how to identify the degree, leading coefficient, and constant term. The instructor defines polynomial functions, provides examples in standard form, and walks through arranging terms in descending order of exponents. The lesson also covers determining whether a given function is polynomial or not, expanding factored polynomials using methods like FOIL, and identifying leading terms and coefficients. Viewers are guided step-by-step through various examples to solidify their understanding of these key concepts.
Takeaways
- 📚 A polynomial function is defined as a function of the form p(x) = a_nx^n + a_{n-1}x^{n-1} + ... + a_1x + a_0 where a_n ≠ 0.
- 🔑 The term a_nx^n is known as the leading term of the polynomial.
- 🌟 The coefficient a_n is referred to as the leading coefficient.
- 📈 The degree of a polynomial is determined by the highest power of x present in the polynomial.
- 🔢 Constant term a_0 is the term without the variable x.
- 📝 Polynomial functions can be represented in various notations such as p(x), f(x), or y.
- 📉 Polynomials are written in standard form with terms arranged in decreasing order of exponents.
- 🚫 Polynomials do not include negative exponents, fractions, or radicals in the variable's denominator.
- 🔍 To identify if a function is a polynomial, check for the absence of variables in denominators, negative exponents, and radicals.
- 📋 Examples are provided to demonstrate how to write polynomials in standard form and identify their leading term, leading coefficient, and degree.
- 🎓 The script concludes with a prompt to like, subscribe, and hit the bell button for more educational content.
Q & A
What is a polynomial function?
-A polynomial function is a function of the form p(x) = a_n x^n + a_{n-1} x^{n-1} + ... + a_1 x + a_0, where a_n ≠ 0 and n is a non-negative integer. The coefficients a_0, a_1, ..., a_n are real numbers.
What is the leading term of a polynomial function?
-The leading term of a polynomial function is the term with the highest exponent of the variable, which is a_n x^n in the polynomial p(x) = a_n x^n + a_{n-1} x^{n-1} + ... + a_1 x + a_0.
What is the leading coefficient of a polynomial function?
-The leading coefficient is the coefficient of the leading term, which is a_n in the polynomial p(x) = a_n x^n + a_{n-1} x^{n-1} + ... + a_1 x + a_0.
What is the constant term of a polynomial function?
-The constant term of a polynomial function is the term without the variable, which is a_0 in the polynomial p(x) = a_n x^n + a_{n-1} x^{n-1} + ... + a_1 x + a_0.
How do you identify the degree of a polynomial function?
-The degree of a polynomial function is the highest exponent of the variable in the polynomial. It is determined by the leading term.
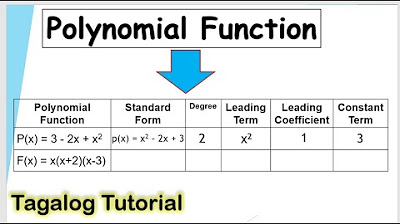
What is the standard form of a polynomial function?
-The standard form of a polynomial function is when the terms are arranged in decreasing order of the exponents of the variable, starting from the highest exponent to the constant term.
Can a polynomial function have a negative exponent?
-No, a polynomial function cannot have a negative exponent. The exponents in a polynomial function are non-negative integers.
Can a polynomial function have a variable in the denominator?
-No, a polynomial function cannot have a variable in the denominator. The variable must only appear in the numerator and raised to non-negative integer powers.
What is the difference between a polynomial function and a rational function?
-A polynomial function consists of terms with non-negative integer exponents and no variables in the denominator, while a rational function is a ratio of two polynomial functions and can have variables in the denominator.
How do you determine if a given function is a polynomial?
-A given function is a polynomial if it meets the criteria: it has non-negative integer exponents, no variables in the denominator, no fractional exponents, and no radical signs involving variables.
What are the steps to write a polynomial function in standard form?
-To write a polynomial function in standard form, you need to arrange the terms in decreasing order of the exponents of the variable, combine like terms, and ensure that the function does not contain any negative exponents, fractional exponents, radical signs, or variables in the denominator.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
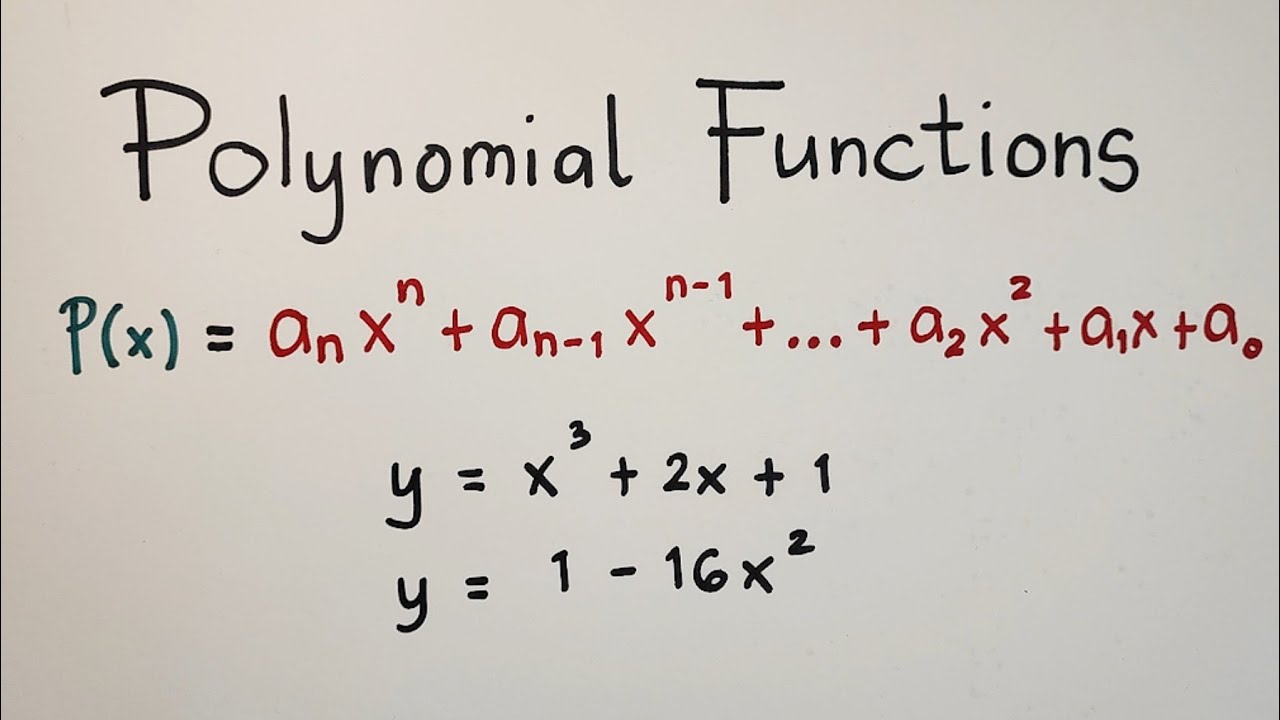
Polynomial Functions - Polynomial Function or NOT? Grade 10 Math Second Quarter

Illustrate Polynomial Functions | Second Quarter | Grade 10 MELC
[Tagalog] Write Polynomial Function into Standard Form, Determine the Degree, Leading Term, Constant

FUNÇÃO AFIM | FUNÇÃO DO 1º GRAU | LEI DE FORMAÇÃO | AULA 1 - Professora Angela Matemática

AP Precalculus – 1.6 End Behavior and Polynomial Functions
Ex1: Find an Equation of a Degree 4 Polynomial Function From the Graph of the Function
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
