Basic Trigonometry: Sin Cos Tan (NancyPi)
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Nancy introduces viewers to the fundamental trigonometric functions: sine, cosine, and tangent, along with their reciprocals—cosecant, secant, and cotangent. She utilizes the mnemonic SOH-CAH-TOA to simplify the process of remembering the relationships between the sides of a right triangle and the angle theta. The video demonstrates how to calculate each trig function by identifying the hypotenuse, adjacent, and opposite sides relative to theta. Additionally, Nancy addresses common confusions regarding triangle orientation and emphasizes the importance of including the angle in the final answer to ensure clarity, making the content both informative and accessible.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video introduces the six basic trigonometric functions: sine (sin), cosine (cos), tangent (tan), and their reciprocals: cosecant (csc), secant (sec), and cotangent (cot).
- 🔑 The memory trick SOH-CAH-TOA is explained to help remember the relationships between the sides of a right triangle and the trigonometric functions: Sine (Opposite/Hypotenuse), Cosine (Adjacent/Hypotenuse), and Tangent (Opposite/Adjacent).
- 📐 All trigonometric functions involve right triangles, where the longest side is the hypotenuse, the side next to the angle theta is the adjacent side, and the side opposite theta is the opposite side.
- 🔍 To find sin(theta), divide the length of the opposite side by the length of the hypotenuse.
- 📏 To find cos(theta), divide the length of the adjacent side by the length of the hypotenuse.
- 📘 To find tan(theta), divide the length of the opposite side by the length of the adjacent side.
- 🔄 To find the reciprocal functions (csc, sec, cot), take the reciprocal of sin, cos, and tan respectively, which involves flipping the numerator and denominator.
- 📌 The video clarifies that the orientation of the right triangle does not affect the definitions of opposite, adjacent, and hypotenuse sides.
- ⚠️ A common mistake is forgetting to include the angle (theta) when writing the answer, which is crucial for the function to have meaning.
- 👍 The presenter encourages viewers to like or subscribe if the video helped them understand the trigonometric functions.
Q & A
What are the six basic trigonometric functions?
-The six basic trigonometric functions are sine, cosine, tangent, and their reciprocals, which are cosecant, secant, and cotangent.
What is the memory trick for remembering the ratios of sine, cosine, and tangent?
-The memory trick for remembering the ratios of sine, cosine, and tangent is SOH-CAH-TOA, which stands for Sine equals Opposite over Hypotenuse, Cosine equals Adjacent over Hypotenuse, and Tangent equals Opposite over Adjacent.
What is a right triangle and why is it important in trigonometry?
-A right triangle is a triangle with one angle measuring 90 degrees. It is important in trigonometry because the definitions of sine, cosine, and tangent are based on the ratios of the sides of a right triangle relative to one of its non-right angles, typically denoted as theta.
What is the hypotenuse of a right triangle?
-The hypotenuse of a right triangle is the longest side of the triangle, which is opposite the right angle.
How do you determine the adjacent and opposite sides relative to an angle in a right triangle?
-The adjacent side is the side of the right triangle that is next to the angle (theta) but not the hypotenuse. The opposite side is the side that is directly opposite the angle (theta).
If the hypotenuse of a right triangle is 5 and the opposite side is 4, what is the sine of the angle?
-The sine of the angle (sin(theta)) is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse. So, sin(theta) = 4/5.
How do you find the cosine of an angle in a right triangle if the adjacent side is 3 and the hypotenuse is 5?
-The cosine of the angle (cos(theta)) is the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. Therefore, cos(theta) = 3/5.
What is the formula for calculating the tangent of an angle in a right triangle?
-The tangent of an angle (tan(theta)) is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side. So, tan(theta) = opposite/adjacent.
How can you find the values of cosecant, secant, and cotangent using the basic trigonometric functions?
-To find the values of cosecant (csc), secant (sec), and cotangent (cot), first find the values of their respective basic trigonometric functions (sin, cos, tan) and then take the reciprocal of those values.
Why is it important to include the angle when writing the value of a trigonometric function?
-It is important to include the angle when writing the value of a trigonometric function to specify which angle the function refers to, as the value of the function can change depending on the angle being considered. For example, you should write sin(theta) instead of just sin to indicate the sine of a specific angle theta.
What can confuse people when dealing with different orientations of right triangles in trigonometry?
-Different orientations of right triangles, such as when the triangle is drawn sideways, on its hypotenuse, or with the hypotenuse horizontal, can confuse people because the positions of the opposite, adjacent, and hypotenuse sides relative to the angle theta can change, requiring careful identification of these sides to correctly apply the trigonometric functions.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Identitas Trigonometri: Identitas Kebalikan, Perbandingan dan Pythagoras - SMA Kelas 10
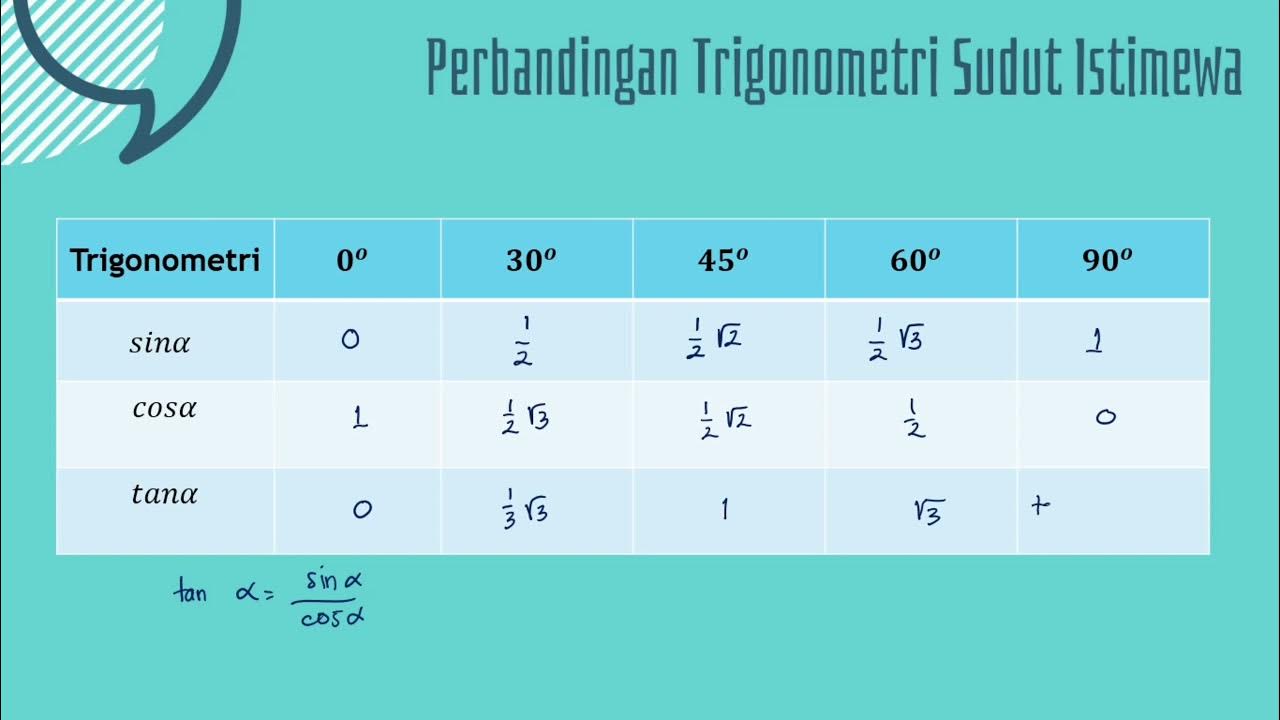
Perbandingan Trigonometri Sudut Istimewa

Identitas Trigonometri - Part 1
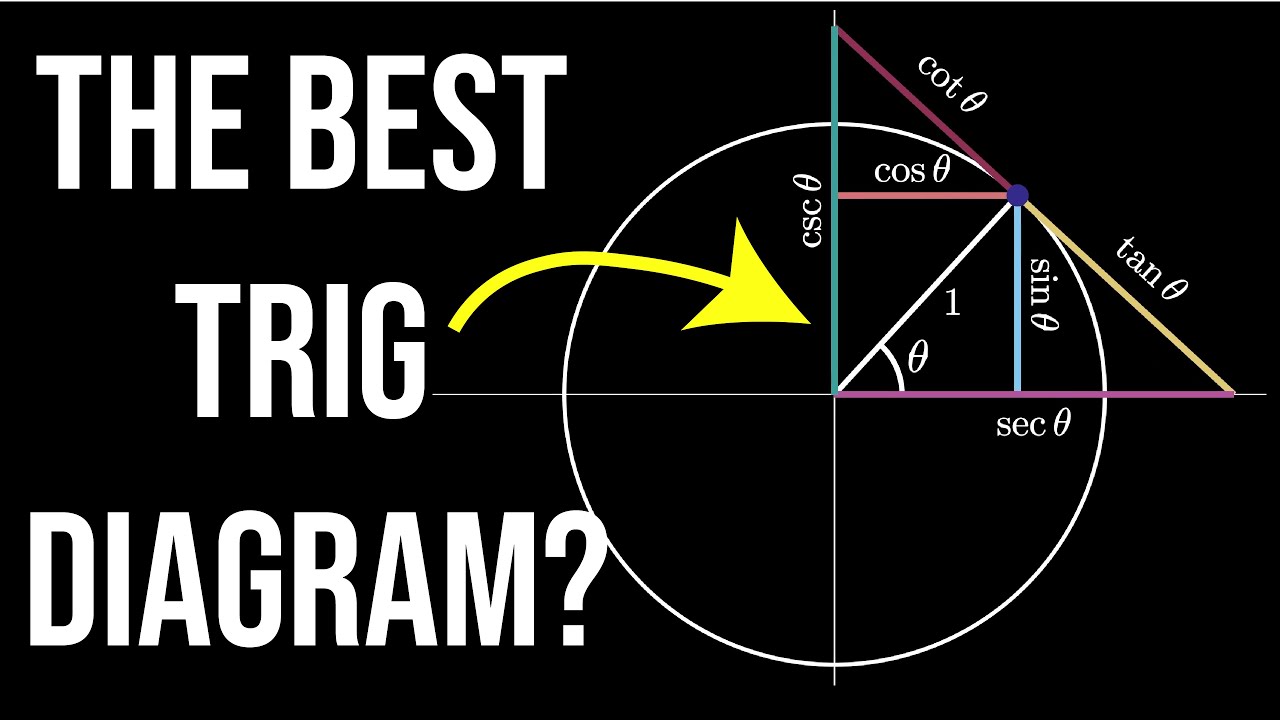
Trig Visualized: One Diagram to Rule them All (six trig functions in one diagram)
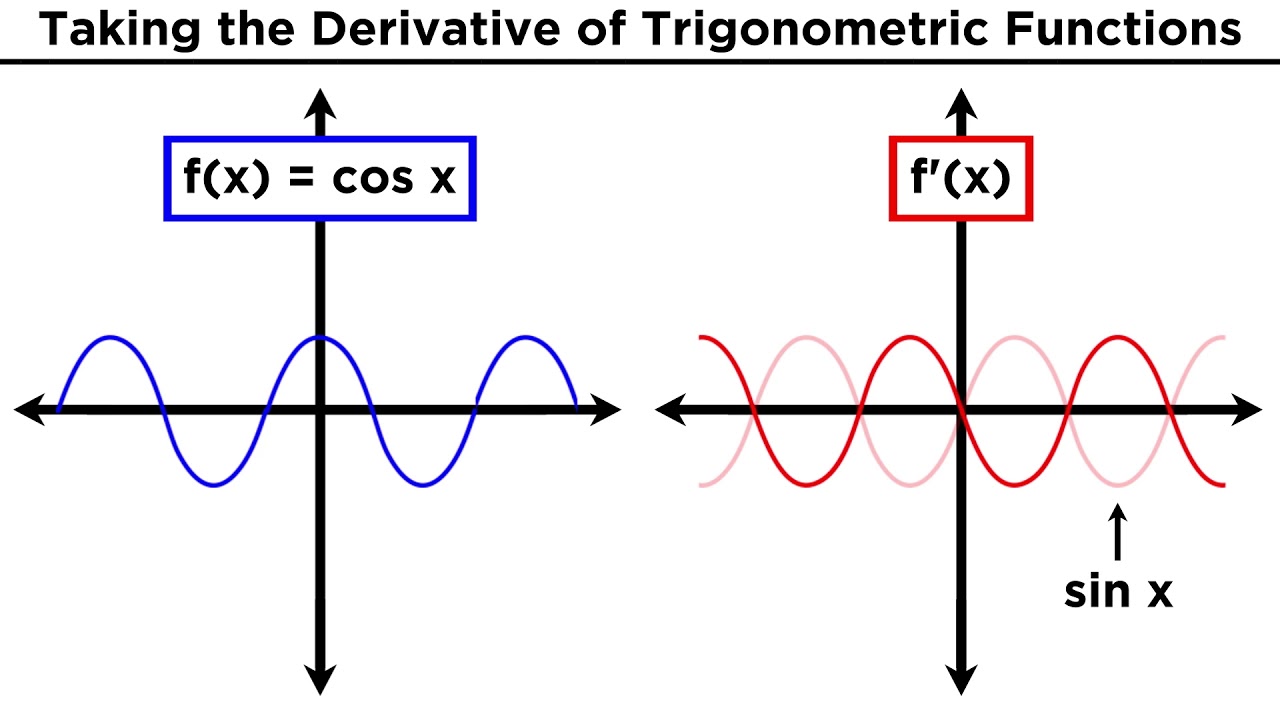
Derivatives of Trigonometric Functions

Trigonometric Ratios (Tagalog Math)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
