BTEC Applied Science Level 3 - Unit 9: Ventilation and gas exchange - BioTeach.
Summary
TLDRThis video from BioTeach focuses on the BTEC Assignment Unit 9, delving into human regulation and reproduction, specifically gas exchange and the ventilation system. It explains how the lungs' alveoli, with their thin walls and vast surface area, facilitate efficient gas exchange. The video also describes the respiratory system's structure, comparing it to an upside-down tree, and details the mechanics of ventilation, including the roles of the diaphragm, intercostal muscles, and rib cage in the processes of inspiration and expiration. Aimed at helping viewers understand and complete their assignment, the video offers a clear and educational overview of the respiratory system.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video focuses on Unit 9 of the BTEC assignment, which is about human regulation and reproduction, specifically gas exchange and the ventilation system.
- 🔍 Learning Aim A of the unit explores the inter-relationship and nervous control of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
- 🌟 Gas exchange in humans primarily occurs in the lungs, specifically in the alveoli, which are adapted for efficient gas exchange with a large surface area and a single layer of cells.
- 🌬️ The alveoli are surrounded by a network of blood capillaries, creating a concentration gradient that facilitates efficient diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
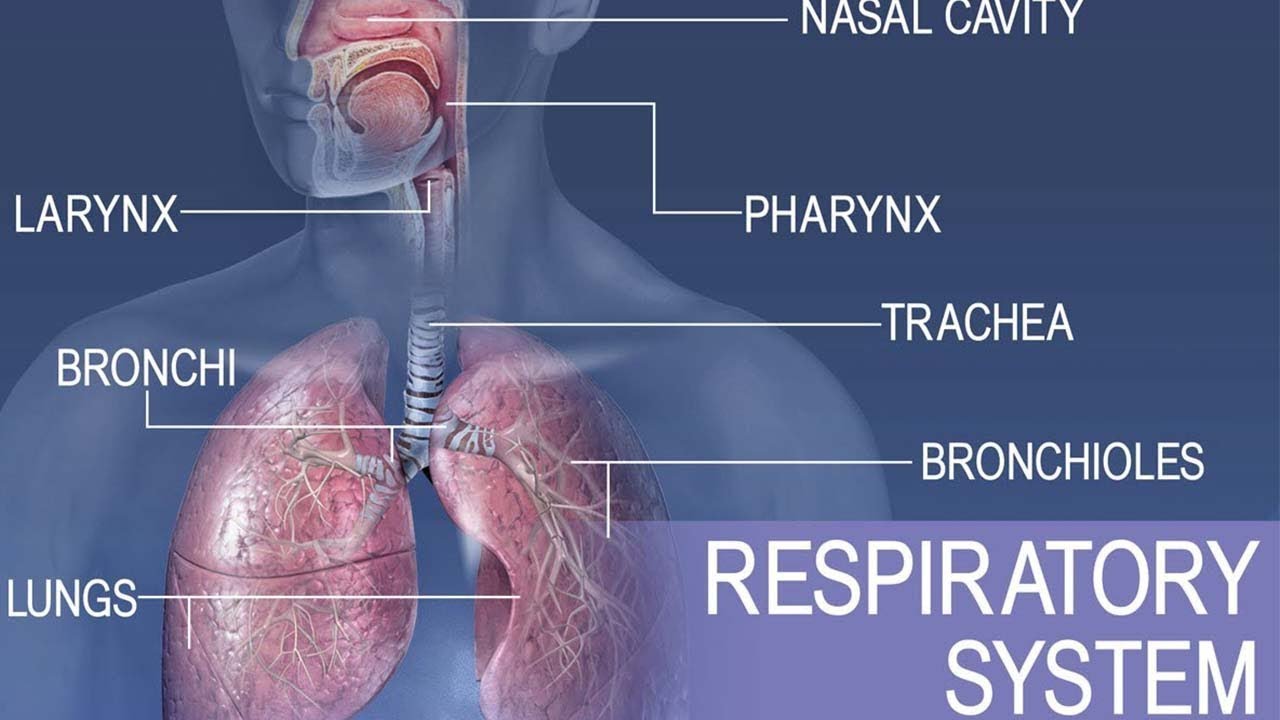
- 👃 Humans use their nose and mouth as primary breathing pathways, with the trachea being the main tube that supports air passage and is kept open by C-shaped cartilage rings.
- 🔗 The bronchi and bronchioles branch off from the trachea into the lungs, with the bronchioles having muscle that can contract to control air movement.
- 🍃 The alveoli are composed of flattened epithelial cells surrounded by collagen and elastic tissue, allowing them to stretch and recoil during the breathing process.
- 🌳 The structure of the respiratory system can be likened to an upside-down tree, with the bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli corresponding to branches, smaller branches, and leaves, respectively.
- 🏋️♂️ Ventilation, which includes inspiration (breathing in) and expiration (breathing out), is controlled by the diaphragm, intercostal muscles, and the rib cage.
- 🔄 Inspiration is an active process requiring energy, where the diaphragm contracts and the rib cage expands to draw air into the lungs, while expiration is a passive process where these actions reverse, pushing air out.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the BTEC assignment unit 9 discussed in the video?
-The main focus of the BTEC assignment unit 9 is human regulation and reproduction, with a specific emphasis on the inter-relationship and nervous control of the cardiovascular and respiratory system.
What is the primary location for gas exchange in humans?
-The primary location for gas exchange in humans is the lungs, specifically within specialized organs known as the alveoli.
How are the alveoli adapted for efficient gas exchange?
-The alveoli are adapted for efficient gas exchange by having a single layer of cells for a fast and short diffusion pathway, a large surface area due to millions of alveoli in each lung, and a network of blood capillaries that provide an excellent blood supply.
What is the role of the trachea in the respiratory system?
-The trachea is a tube supported by C-shaped rings of cartilage that prevent kinking and allow it to remain open for the passage of air.
How do the bronchi and bronchioles contribute to the ventilation system?
-The bronchi, leading into each lung, have a similar structure to the trachea with cartilage to keep them open. Bronchioles, at the end of the bronchi, have no cartilage but contain muscle that can contract to control air movement.
What is the composition of the lining of the alveolus?
-The lining of the alveolus is composed of flattened epithelial cells surrounded by collagen and elastic tissue, allowing the alveoli to stretch and recoil during breathing.
Can you describe the ventilation process in humans?
-Ventilation in humans consists of inspiration (breathing in) and expiration (breathing out), controlled by the movements of the diaphragm, internal and external intercostal muscles, and the rib cage.
What is the difference between inspiration and expiration in terms of energy requirement?
-Inspiration is an active process that requires energy as the diaphragm contracts and the ribcage moves up and out to draw air into the lungs. Expiration is a passive process that does not require energy as the diaphragm relaxes and the ribcage moves down and in, forcing air out of the lungs.
How does the structure of the respiratory system relate to an upside-down tree?
-The structure of the respiratory system can be likened to an upside-down tree, with the bronchi being the primary and secondary branches, the bronchioles as the smaller branches, and the alveoli as the leaves or fruit.
What advice does the video provide for students completing their assignment?
-The video suggests that students should pause the video to write down the information discussed, and to include a table summarizing the points in their assignment, ensuring to put things in their own words.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

🫁 INTRODUÇÃO À FISIOLOGIA DO SISTEMA RESPIRATÓRIO | MK Fisiologia

Sistema Respiratório 1/6: Introdução | Anatomia e etc

Struktur Dan Fungsi Sistem Pernapasan Manusia : Organ Pernapasan Manusia

Sistema respiratório - Visão geral - Fisiologia veterinária - Aula 1
Anatomy and physiology of Respiratory system

Fish Respiration
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
