OSI Model for dummies | EASY to understand | autometeNow
Summary
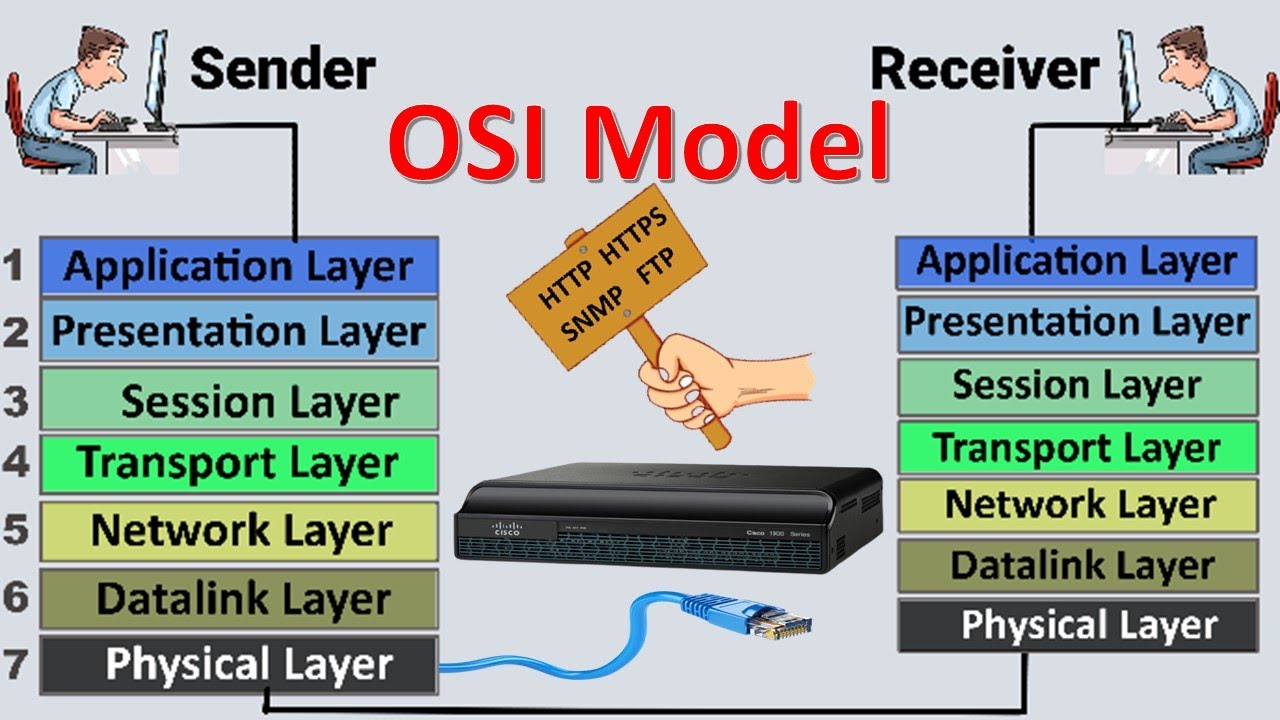
TLDRThe OSI model, introduced in the mid-80s, revolutionized electronic communication by standardizing data transmission across networks. It consists of seven layers: Physical (hardware transmission), Data Link (error correction, flow control), Network (routing using IP), Transport (end-to-end data delivery via TCP/UDP), Session (communication management), Presentation (data formatting), and Application (network services for apps). The model facilitates everyday tasks like sending emails and browsing the web, with a memorable acronym: 'Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away'.
Takeaways
- 🌐 OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnection and is a model introduced in the mid-80s to facilitate communication between electronic devices.
- 📈 The OSI model consists of seven layers, each with a specific role in the process of data transmission and reception over a network.
- 🔌 The Physical Layer (Layer 1) is responsible for the actual transmission of raw data bits over the physical medium.
- 📦 The Data Link Layer (Layer 2) ensures reliable delivery of data across a physical link, using techniques like error detection, correction, and flow control.
- 🛤️ The Network Layer (Layer 3) handles the routing of data between different networks using IP and ICMP protocols, similar to GPS routing.
- 🚚 The Transport Layer (Layer 4) provides end-to-end data delivery, using protocols like TCP for reliability and UDP for speed.
- 🔐 The Session Layer (Layer 5) manages communication sessions between applications, ensuring secure and authorized access, akin to entering a code on a keypad.
- 🎭 The Presentation Layer (Layer 6) formats and presents data, including encryption, compression, and data format conversion, much like video encoding for streaming.
- 💌 The Application Layer (Layer 7) is the most familiar layer, providing network services for applications like email, file transfer, and web browsing.
- 🍕 A mnemonic to remember the OSI model layers is 'Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away', with 'P' for Physical and 'A' for Application.
Q & A
What is the OSI model and why was it introduced?
-The OSI model, or Open Systems Interconnection model, is a conceptual framework that describes how data is transmitted and received over a network. It was introduced in the mid-1980s to allow electronic devices to communicate with one another, enabling modern activities like sending emails.
How does the OSI model help in network communication?
-The OSI model divides network communication into seven layers, each responsible for different aspects of data transmission. This separation makes it easier to troubleshoot and manage communication processes between devices.
What is the role of the Physical Layer (Layer 1) in the OSI model?
-The Physical Layer is responsible for the physical transmission of data over a network. This includes electrical, optical, or wireless signals that carry the data from one device to another.
How does the Data Link Layer (Layer 2) ensure reliable data transmission?
-The Data Link Layer ensures reliable transmission of data by using error detection and correction techniques, as well as flow control. It also uses MAC addresses to label and send data between devices, similar to mailing addresses.
What does the Network Layer (Layer 3) do, and how is it similar to GPS?
-The Network Layer is responsible for routing data between different networks using protocols like IP. It's similar to a GPS system, which selects the best route based on traffic and distance, ensuring efficient data delivery across networks.
What is the difference between TCP and UDP in the Transport Layer (Layer 4)?
-In the Transport Layer, TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) ensures reliable, ordered data delivery, while UDP (User Datagram Protocol) allows faster, but less reliable, transmission without ensuring the data arrives in the correct order.
How does the Session Layer (Layer 5) manage communication between applications?
-The Session Layer manages communication between applications by establishing, maintaining, and terminating sessions. It ensures secure communication using protocols like SSL and TLS.
What is the function of the Presentation Layer (Layer 6)?
-The Presentation Layer is responsible for formatting and presenting data. It handles tasks such as encryption, compression, and conversion of data formats, making sure that the data is readable and secure during transmission.
Why is the Application Layer (Layer 7) the most familiar to users?
-The Application Layer provides access to network services that are directly used by end-users, such as email, file transfer, web browsing, and social media. It allows interaction with the network through familiar applications.
How can you remember the order of the seven OSI layers easily?
-A helpful mnemonic to remember the OSI layers in order is 'Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away,' where each word corresponds to one of the OSI layers, from Physical to Application.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Understanding the OSI Model - CompTIA Network+ N10-009 - 1.1

CARA KERJA OSI LAYER

Belajar Dasar Jaringan Komputer dari nol - Part 3/8 | OSI Layer
OSI Model | OSI Model Explained | OSI Animation | OSI Model in easiest Way | OSI 7 Layers

OSI Model animated, What is osi model in networking? 7 OSI layers explained

TCP/IP Protocol Explained | What Is TCP/IP Address? | TCP/IP Configuration Tutorial | Simplilearn
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
