How a Power Supply *ACTUALLY* works.
Summary
TLDRThis video explains how a computer's power supply works, detailing its role in converting alternating current (AC) from a wall outlet into direct current (DC) for the computer's components. It describes how the power supply distributes different voltages to various parts like the processor, RAM, and fans, and why certain appliances need varying levels of electricity. Additionally, it touches on how power supplies manage heat and why it's important to keep them ventilated. The video invites viewers to explore more about electricity and its principles.
Takeaways
- 🔌 Your computer needs electricity to function, just like any other powered appliance.
- 🔄 Unlike simple appliances, computers require different amounts of electricity in different places.
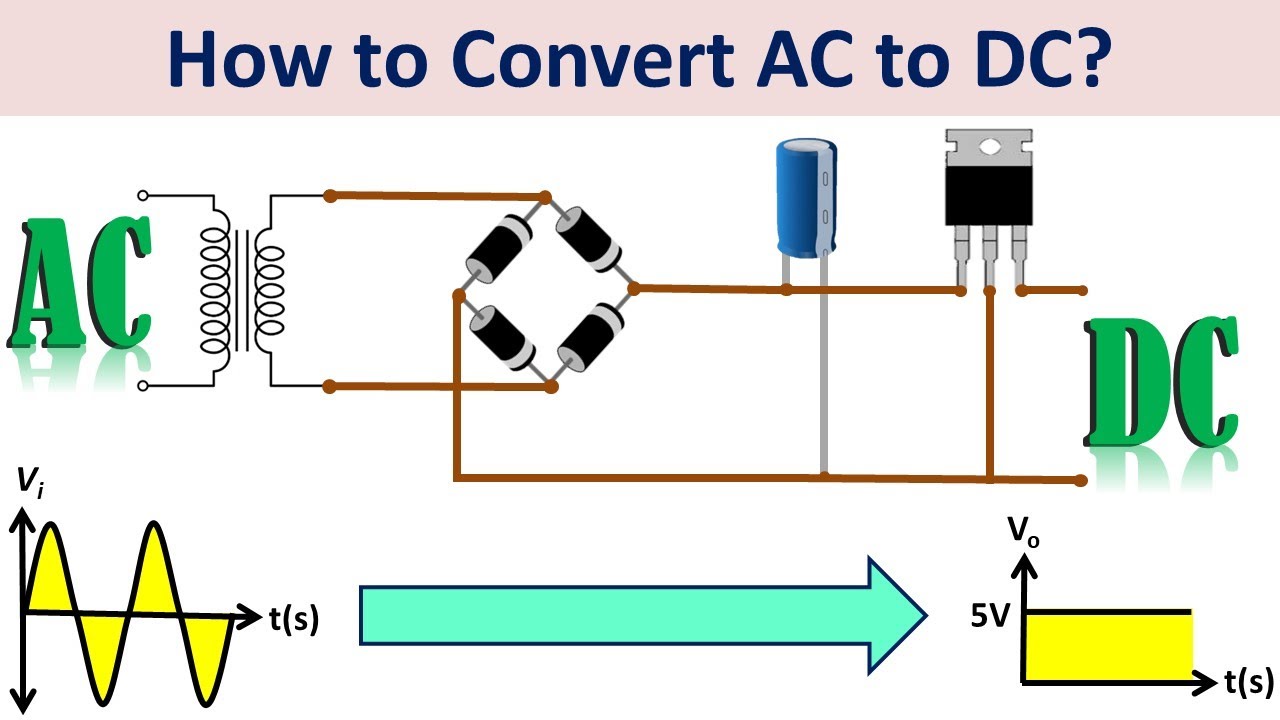
- ⚡ A power supply converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) to power the computer's components.
- 🌊 Alternating current flows back and forth like water, while direct current flows in one direction like a river.
- 📦 Many appliances, including computers, have power supply units that convert AC from the wall into DC for use.
- 📉 The power supply ensures the correct amount of electricity is delivered to prevent overloading.
- 🧮 Different computer components require varying power levels, like tiny switches needing less electricity, while cooling fans require more.
- 🔋 The power supply stores electricity and distributes it to components based on their needs, using voltages of 3.3, 5, and 12 volts.
- 🔥 Power supply units generate heat, which is managed by built-in fans that keep the system cool.
- 🖥️ Keeping your computer slightly elevated helps airflow, especially if the power supply intake is facing down.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a computer's power supply?
-The primary function of a computer's power supply is to convert alternating current (AC) from the wall outlet into direct current (DC) for the computer's components and to manage the distribution of electricity to different parts of the computer.
Why is direct current (DC) more suitable for computer components than alternating current (AC)?
-Direct current (DC) is more suitable for computer components because it maintains a constant flow of electrons in one direction, unlike alternating current (AC) which reverses direction periodically. This consistency is necessary for the reliable operation of electronic components.
How does a power supply manage the electricity fed to the device to prevent overloading?
-A power supply manages the electricity fed to the device by regulating the voltage and current levels, ensuring that each component receives only the amount of power it requires to function properly without being overloaded.
What are the three main voltages provided by a computer's power supply, and what are they used for?
-The three main voltages provided by a computer's power supply are 3.3 volts, 5 volts, and 12 volts. 3.3 volts and 5 volts are mostly used for low-power circuitry, while 12 volts are typically used for fans and disk drives.
How do the 'small calculators' on a computer's motherboard communicate with the power supply?
-The 'small calculators' on a computer's motherboard, which are actually voltage regulators, communicate with the power supply to inform it of the current needs of the components, allowing the power supply to adjust the power distribution accordingly.
Why do power supply units (PSUs) get very hot, and how do they manage heat?
-Power supply units (PSUs) get very hot because they handle and convert high amounts of electricity, which generates heat as a byproduct. They manage heat through built-in fans that push hot air away from the circuitry and draw in cool air to prevent overheating.
What is the significance of keeping a computer slightly elevated in relation to its power supply?
-Keeping a computer slightly elevated can be beneficial because it allows for better airflow around the power supply, which typically has its intake pointed downwards. This helps in cooling the power supply and maintaining efficient operation.
How does the power supply know which levels of current to send to which components?
-The power supply determines which levels of current to send to which components based on the requirements of each component and the communication from the voltage regulators on the motherboard.
What role do the power cables' 'big boxes' play in the operation of appliances like computers?
-The 'big boxes' on power cables, known as power adapters or transformers, extract alternating current from the power outlet and convert it into direct current. They also manage the amount of electricity fed to the device to prevent overloading.
Why is alternating current (AC) better suited for power lines in the electrical grid compared to direct current (DC)?
-Alternating current (AC) is better suited for power lines in the electrical grid because it can be transmitted over long distances with less loss of energy compared to direct current (DC), and it's easier to step up or step down the voltage for different uses.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)