3. Plato's Theory of Forms
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into Plato's theory of forms, explaining the existence of a perfect, eternal realm separate from our physical world. Forms are non-physical, eternal, and unchanging ideas that serve as archetypes for the imperfect, mutable particulars we encounter. Plato suggests that we recognize similarities among different things because they all participate in the same form. The video also touches on the hierarchy of forms, with forms of ideals being higher than forms of phenomena, and hints at the upcoming discussion on the form of the good.
Takeaways
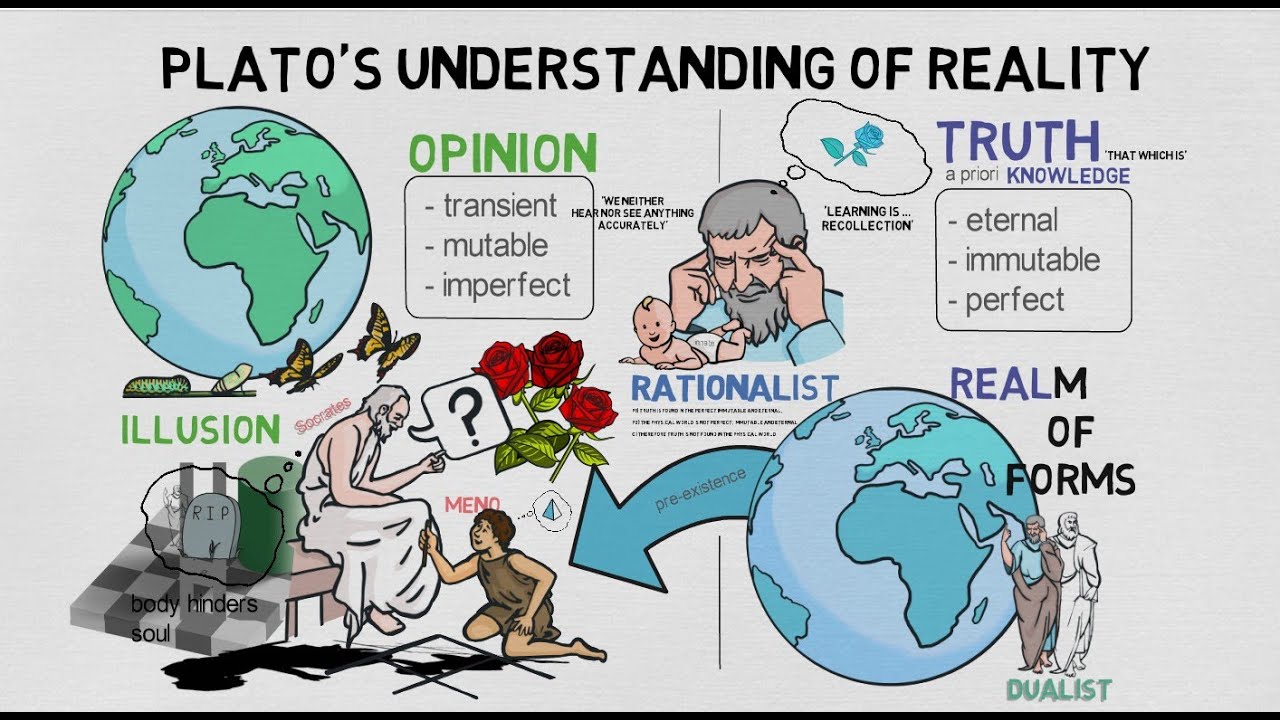
- 🌐 Plato introduced the concept of a perfect, eternal, and unchanging realm called the 'realm of the forms'.
- 💭 Forms are non-physical, eternal, perfect, unchanging, and non-extended ideas that serve as archetypes for the physical world.
- 🔍 Our physical world consists of imperfect copies or 'particulars' that are reflections or shadows of the forms.
- 🔑 Each form acts as a blueprint for the archetypes, and particulars participate in or instantiate these forms.
- 👁️ We recognize things as the same despite their differences because they share a common form, such as multiple horses sharing the form of 'horse'.
- 📚 Plato held the realist position that there is a distinction between the world of forms and the physical world of particulars.
- 🌳 Particulars can instantiate multiple forms, such as a horse embodying the forms of 'horse', 'beauty', and 'black'.
- 💐 Some particulars instantiate forms better than others, leading to a hierarchy where some are more 'beautiful' or 'just' than others.
- 🌟 Forms exist necessarily, while particulars are contingent and dependent on forms for their existence and identity.
- 📈 There is a hierarchy of forms, with forms of phenomena (like trees and houses) being lower than forms of ideals (like beauty and justice).
Q & A
What is the main topic of the second video on Plato?
-The main topic of the second video on Plato is his theory of forms, which includes an explanation of what forms are, the hierarchy among them, and the concept of particulars.
What is the realm of the forms according to Plato?
-The realm of the forms is a perfect, eternal, and immutable realm that Plato posited as separate from the physical world. It is where the abstract, non-physical entities called forms exist.
How are forms different from the physical objects we experience?
-Forms are non-physical, eternal, perfect, unchanging, and non-extended, meaning they do not occupy space. In contrast, physical objects are imperfect, mutable, extended, and take up space.
What is the relationship between forms and particulars?
-Particulars are imperfect copies or reflections of the forms. They participate in or instantiate the forms, meaning the form is somehow present within the particular.
Why are we able to recognize different things as the same?
-We are able to recognize different things as the same because they share a common form. For instance, different horses are recognized as horses because they all participate in the form of a horse.
What is the ontological status of forms and particulars according to Plato?
-Forms exist necessarily, meaning they must exist and cannot not exist. Particulars, on the other hand, are contingent and dependent on forms for their existence.
Can one particular instantiate multiple forms?
-Yes, one particular can instantiate multiple forms. For example, a single horse can instantiate the form of horse, the form of beauty, and the form of black.
What is the difference between forms of phenomena and forms of ideals?
-Forms of phenomena are related to physical objects like trees, houses, and horses, while forms of ideals are abstract concepts like beauty, justice, and goodness. Forms of phenomena are considered lower than forms of ideals because they participate in the latter.
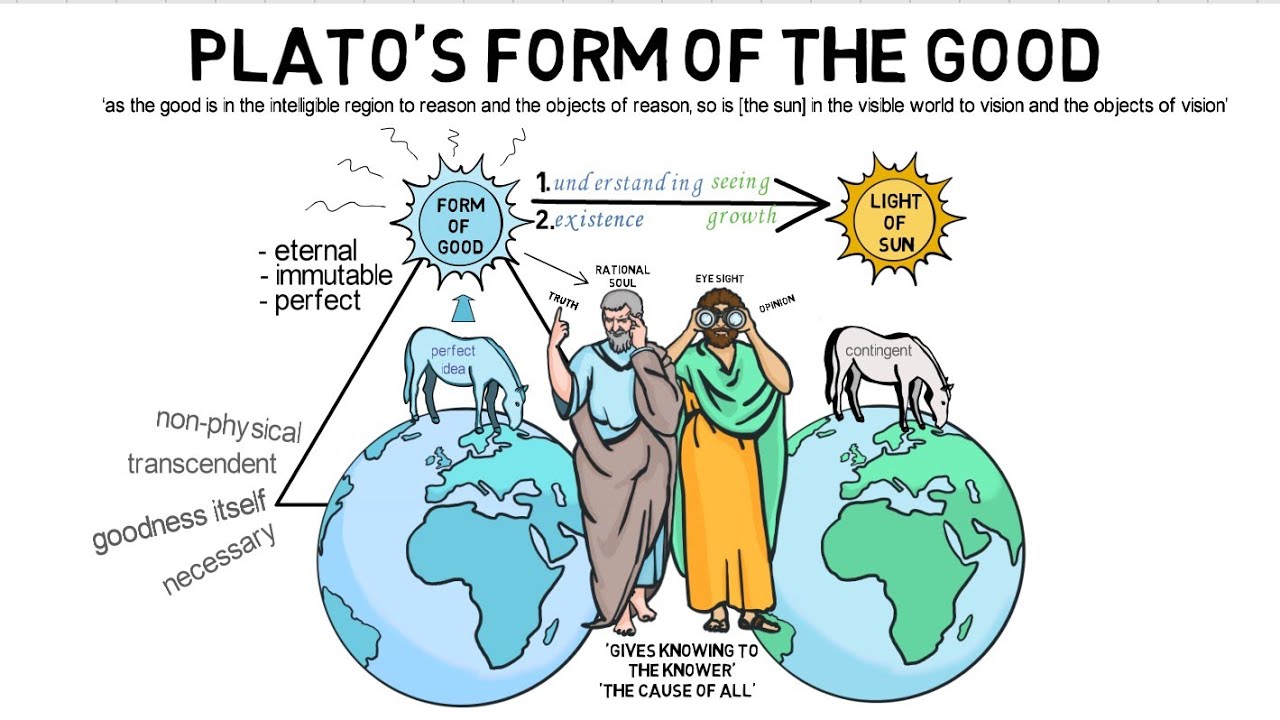
What is the highest form according to Plato?
-The highest form according to Plato is the form of the good, which is said to be above all other forms. It will be discussed further in a separate video.
How does the concept of forms relate to the realist position in metaphysics?
-Plato's concept of forms aligns with the realist position in metaphysics, which asserts that there is a reality independent of our perceptions and experiences, and that our knowledge of this reality is possible.
What is the role of the form of the good in Plato's philosophy?
-The form of the good is central to Plato's philosophy as it represents the highest principle of value and is the source of all other forms. It is discussed in a separate video as it is a complex and significant concept.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)