4. Plato's Form of the Good
Summary
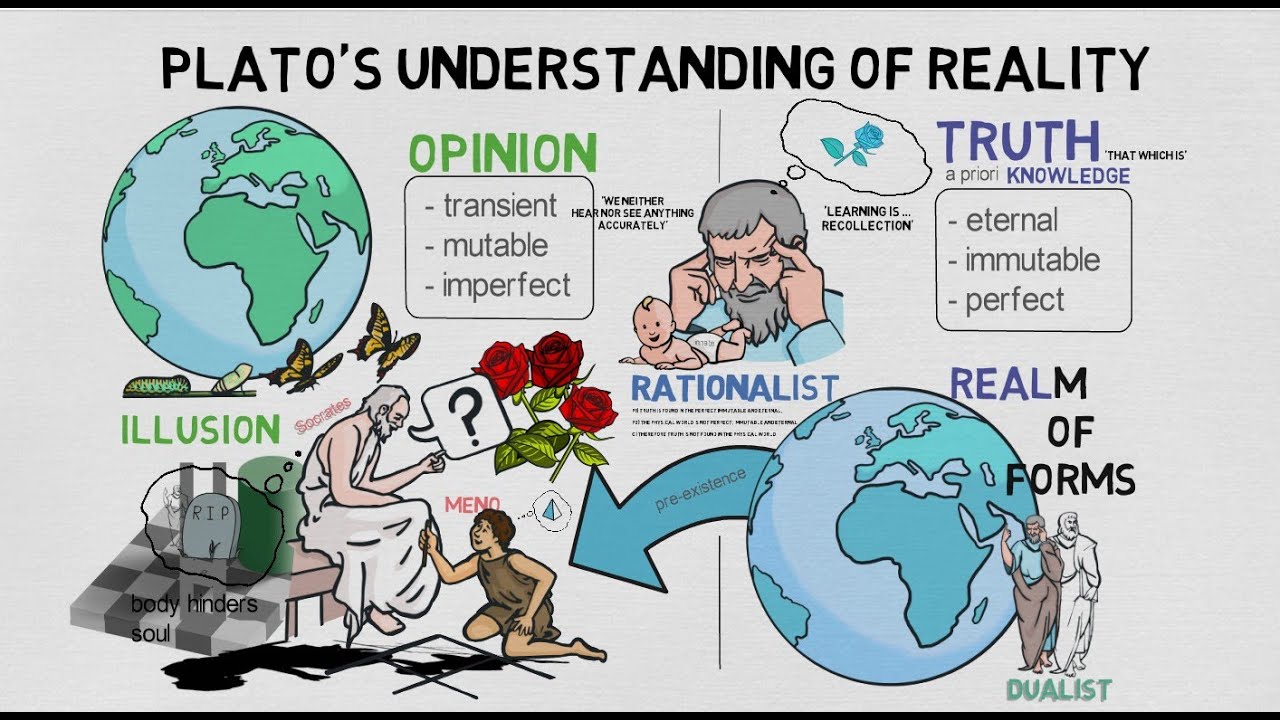
TLDRIn this video, the speaker explores Plato's Form of the Good, the highest form in his theory of forms, which transcends and underpins all existence. The Form of the Good illuminates knowledge, enabling the soul to grasp truths in the intelligible realm, similar to how the Sun enables visibility in the physical world. The video discusses the Form's characteristics: it is immutable, necessary, eternal, and non-physical, emphasizing its role as the source of goodness and existence for all particulars. Understanding this concept is crucial for comprehending Plato's philosophy and the nature of reality.
Takeaways
- 🌟 The Form of the Good is the highest form in Plato's theory, transcending all other forms.
- 🔗 Particulars, like a horse, participate in their respective forms, which ultimately connect to the Form of the Good.
- 💡 The Form of the Good is essential for knowledge, illuminating the rational soul's understanding of truths.
- 🌞 Plato compares the Form of the Good to the Sun, which enables visibility and comprehension in the physical world.
- 📈 The more one focuses on the realm of forms, the clearer the truths become, enhancing the understanding of knowledge.
- 🎁 The Form of the Good is the source of existence for all forms, providing them with essence and beauty.
- 🔄 The Form of the Good is immutable and incorruptible, meaning it does not change over time.
- 🛡️ Its goodness is intrinsic and does not depend on external factors, making it eternally good.
- 🌌 The Form of the Good is non-physical and cannot be perceived through the senses, as it is immaterial.
- 🧠 Plato emphasizes that while ideas can be conceptualized, they cannot be physically seen, highlighting their non-sensible nature.
Q & A
What is the Form of the Good in Plato's theory?
-The Form of the Good is the highest form in Plato's hierarchy of forms, transcending all others and representing the ultimate idea of perfection and complete goodness.
How does Plato explain the relationship between particulars and the Form of the Good?
-Particulars, such as individual objects, participate in their respective forms, which in turn participate in the Form of the Good. This creates a hierarchy where all forms are contingent upon the Form of the Good.
What analogy does Plato use to explain the dependence of forms on the Form of the Good?
-Plato compares the Form of the Good to the Sun, stating that just as the Sun illuminates visible things, allowing them to be seen, the Form of the Good illuminates the rational part of the soul, enabling understanding of truths in the realm of forms.
What happens to our understanding when we focus on corruptible particulars instead of the Form of the Good?
-When we focus on corruptible and elusive particulars in the material world, our understanding becomes limited, leading us to possess only opinions rather than true knowledge.
How does the Form of the Good contribute to knowledge and truth?
-The Form of the Good is the cause of knowledge and truth, allowing us to grasp and understand these concepts, much like the Sun provides visibility to objects.
What characteristics make the Form of the Good immutable?
-The Form of the Good is immutable because it is intrinsically good, meaning it is good for its own sake and does not change, reflecting its position in the realm of forms, which is associated with unchanging truth.
How does Plato describe the necessity of the Form of the Good?
-Plato describes the Form of the Good as necessary existence, meaning it does not depend on anything else for its existence, is eternal, and has always been.
What is the nature of the Form of the Good in terms of substance?
-The Form of the Good is immaterial and non-physical, distinguishing it from physical objects that are subject to change and corruption.
How does Plato view the perceptibility of the Form of the Good?
-Plato asserts that the Form of the Good cannot be perceived through the senses; it can only be understood through thought, as it is non-sensible.
What role does the Form of the Good play in the hierarchy of forms?
-The Form of the Good is at the top of the hierarchy of forms, influencing and giving existence and essence to all other forms and particulars in the world.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)