GCSE Biology: Revision Guide | Plant, Animal, Bacteria Cells & Orders of Magnitude
Summary
TLDRThis script offers a concise guide to cell structures, highlighting the distinction between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. It explains that eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi, have a nucleus for genetic material, while prokaryotes like bacteria do not. The script delves into size scales, comparing micrometers to millimeters and meters, and uses orders of magnitude to illustrate relative sizes. It also describes the unique structures of animal, plant, and bacterial cells, such as the cell wall in plants and the absence of a nucleus in bacteria, providing a fundamental understanding of cellular biology.
Takeaways
- 🌐 All living organisms are composed of cells, which can be either unicellular or multicellular, with examples like bacteria and plants/animals respectively.
- 🔬 Organisms are categorized into eukaryotes (e.g., animals, plants, fungi) and prokaryotes (e.g., bacteria), with the primary distinction being the storage of genetic material.
- 🧬 Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus for genetic material, while prokaryotic cells have their genetic material floating in the cytoplasm without a nucleus.
- 📏 Prokaryotic cells are approximately one micrometer in size, and eukaryotic cells are larger, ranging from 10 to 100 micrometers.
- 📏 A micrometer is a thousand times smaller than a millimeter, and 1000 micrometers equal one millimeter, highlighting the vast size difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- 🔢 The concept of orders of magnitude is introduced to compare sizes or quantities, where each tenfold increase represents an increase of one order of magnitude.
- 🏠 Animal cells have a cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, and ribosomes, with the nucleus controlling cell activities and mitochondria providing energy through aerobic respiration.
- 🌿 Plant cells share features with animal cells but also have a cell wall, permanent vacuole, and chloroplasts, which are crucial for photosynthesis and maintaining cell shape.
- 🦠 Bacterial cells possess cell membranes, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and cell walls, but lack a nucleus, having their genetic material in a single circular loop or plasmids within the cytoplasm.
- 🌱 The presence of chlorophyll in chloroplasts is responsible for the green color of plants and the process of photosynthesis.
- 📚 Understanding cell structure and the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is fundamental to grasping the basics of biology and the organization of life.
Q & A
What are the two main groups that all living organisms can be classified into?
-All living organisms can be classified into two main groups: eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
What is the key difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells concerning their genetic material?
-The key difference is that eukaryotic cells have their genetic material stored in a structure known as a nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus and their genetic material floats around in the cytoplasm.
How does the size of prokaryotic cells compare to eukaryotic cells?
-Prokaryotic cells are much smaller, with a size of around one micrometer, whereas eukaryotic cells are larger, ranging from 10 to 100 micrometers.
What is the significance of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells?
-The nucleus in eukaryotic cells is significant as it controls the cell's activities and contains all the genetic material of the cell.
What is the function of mitochondria in eukaryotic cells?
-Mitochondria are known as the 'powerhouse of the cell' because they release energy for the cell to carry out its activities through the process of aerobic respiration.
What is the purpose of the cell wall in plant cells?
-The cell wall in plant cells, made up of cellulose, strengthens the cell and allows it to keep its shape.
What is the role of chloroplasts in plant cells?
-Chloroplasts are where photosynthesis happens in plant cells. They contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs sunlight for photosynthesis and gives plants their green color.
How do bacteria cells differ in structure from eukaryotic cells?
-Bacteria cells lack a nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and a permanent vacuole. Their genetic material is found in a single circular loop or small rings of DNA known as plasmids, floating in the cytoplasm.
What is the unit of measurement used to describe the size of cells, and how does it relate to millimeters and meters?
-The unit of measurement used to describe the size of cells is the micrometer, which is a thousand times smaller than a millimeter. To convert from micrometers to millimeters, you divide by a thousand, and to convert from millimeters to meters, you also divide by a thousand.
What is the concept of 'orders of magnitude' and how is it used to compare the sizes of cells?
-Orders of magnitude is a concept used to make rough comparisons of sizes or quantities. For every 10 times an object is larger than another, the order of magnitude increases by one. For example, if a plant cell is 10 micrometers and a bacterial cell is 1 micrometer, the plant cell is one order of magnitude larger.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

NÚCLEO CELULAR - RESUMO PARA PROVA - Prof. Kennedy Ramos
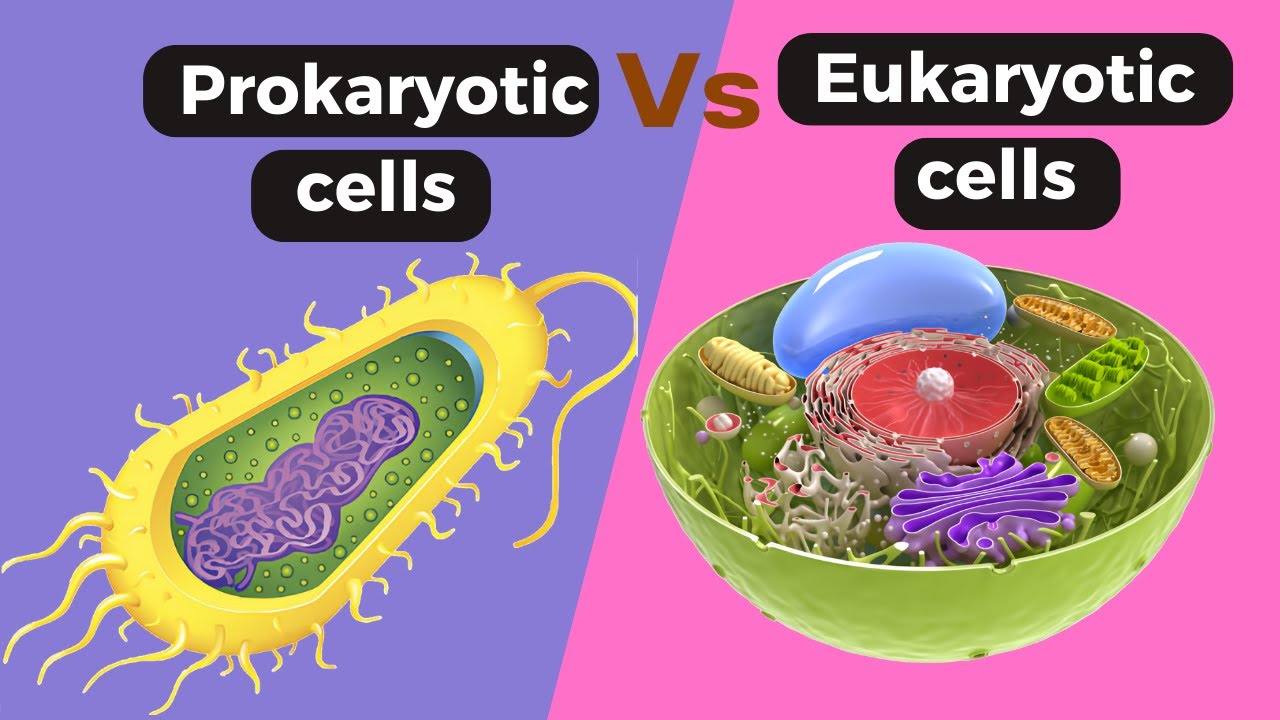
Prokaryotic cell Vs Eukaryotic cells|| Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell

Cell Theory and Organelles
BIOLOGIA - Lezione 3 - La Cellula Eucariota

Cell Biology: Introduction to Cell & Molecular Biology

Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells - High School Biology
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
