Konsep Vektor Fisika [LENGKAP] - Part 1 : Vektor Fisika Kelas 10
Summary
TLDRIn this video, we explore the fundamentals of vectors in physics for grade 10 students. The video covers key concepts such as the definition of vectors, their representation, and equality. It also dives into vector operations like addition and subtraction using methods such as the polygon method, triangle method, parallelogram method, and component breakdown. The video demonstrates these operations through various examples and problems, offering a clear understanding of vector magnitudes, directions, and calculations using trigonometry and Pythagoras' theorem. A series of practice problems at the end helps reinforce the learning.
Takeaways
- 😀 Vectors are physical quantities that have both magnitude and direction, such as velocity, acceleration, and force.
- 😀 Vectors are represented by an arrow where the tail is the starting point and the head is the endpoint.
- 😀 Two vectors are considered equal if they have the same magnitude and direction.
- 😀 There are five methods to perform vector addition and subtraction: Simple addition, Polygon method, Triangle method, Parallelogram method, and Component breakdown.
- 😀 Simple addition method applies to vectors that are in the same direction, where their magnitudes are simply added.
- 😀 The Polygon method involves connecting the vectors head-to-tail to find the resultant vector.
- 😀 The Triangle method calculates the resultant vector by connecting the tail of one vector to the head of the other, using trigonometric relations.
- 😀 The Parallelogram method uses a diagonal from the intersection of two vectors to find the resultant.
- 😀 The Component method breaks down vectors into their horizontal (x) and vertical (y) components, making it easier to compute the resultant.
- 😀 The magnitude of the resultant vector can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem, and its direction using trigonometric ratios like sine and cosine.
Q & A
What is a vector in physics?
-A vector is a physical quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Examples include velocity, acceleration, and force.
What is the difference between a vector and a scalar?
-A scalar is a quantity that only has magnitude, such as temperature or time, while a vector has both magnitude and direction.
How is a vector represented mathematically?
-A vector is typically represented by an arrow with a starting point (tail) and an endpoint (head). In a mathematical context, a vector can be written as a component along the x, y, and z axes, such as 'a = ai + bj'.
What does it mean for two vectors to be equal?
-Two vectors are considered equal if they have the same magnitude and direction, regardless of their position or starting point.
What is the concept of vector addition?
-Vector addition involves combining two or more vectors to find a resultant vector. The methods for addition include simple addition for collinear vectors, the polygon method, and the triangle method.
What is the polygon method of vector addition?
-The polygon method involves connecting the tip of one vector to the tail of the next, forming a closed shape or polygon. The resultant vector is drawn from the tail of the first vector to the tip of the last vector.
How is vector subtraction different from addition?
-Vector subtraction involves reversing the direction of the second vector (making it negative) and then applying vector addition. This method effectively 'subtracts' one vector from another.
What is the triangle method of vector addition?
-The triangle method involves placing the tail of the second vector at the tip of the first. The resultant vector is the vector drawn from the tail of the first vector to the tip of the second vector.
What is the jajar genjang (parallelogram) method for vector addition?
-In the parallelogram method, two vectors are placed tail to tail, and a parallelogram is drawn where the vectors form adjacent sides. The diagonal of the parallelogram represents the resultant vector.
How do we find the magnitude and direction of a resultant vector in the jajar genjang method?
-The magnitude of the resultant vector is calculated using the cosine law, and the direction can be found using the sine rule, depending on the angles formed by the vectors.
What is the formula for finding the magnitude of the resultant vector from two vectors?
-The magnitude of the resultant vector R from two vectors A and B, with an angle θ between them, is given by the formula: R = √(A² + B² + 2AB cos(θ)).
How is vector decomposition used in solving vector problems?
-Vector decomposition involves breaking a vector into its components along the x and y axes. For example, a vector A can be decomposed into Ax = A cos(θ) and Ay = A sin(θ), which can help in finding the resultant vector in a specific direction.
How do you calculate the resultant vector for multiple vectors?
-To calculate the resultant vector for multiple vectors, each vector is decomposed into its x and y components. The sum of the x components gives the total x component of the resultant, and similarly for the y components. The resultant vector is then calculated using Pythagoras' theorem.
What is the significance of the angle between vectors when calculating the resultant?
-The angle between vectors is crucial in determining the magnitude and direction of the resultant. The angle affects the sum or difference between the vectors and is used in the cosine and sine laws to find the correct resultant.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
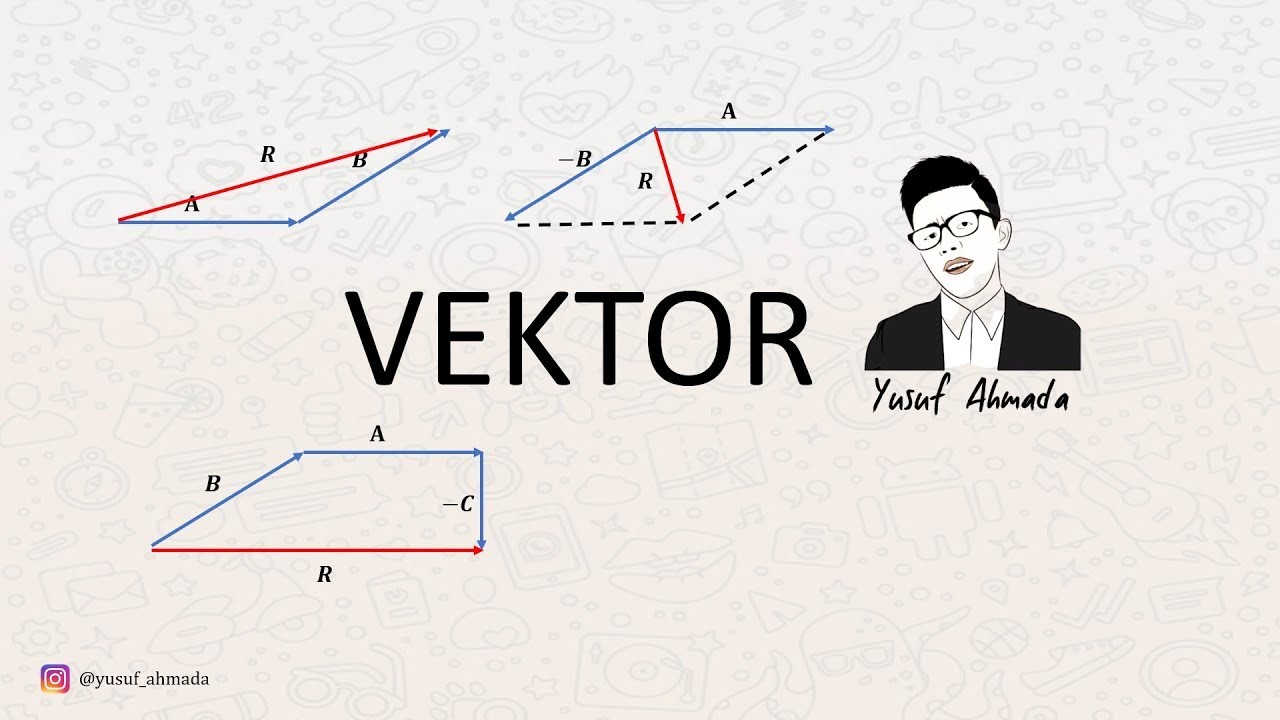
FISIKA KELAS X : VEKTOR (PART 1)

BESARAN BERDASARKAN ARAHNYA | Vektor #1 - Fisika Kelas 10
Besaran Vektor | Vektor | Part 1 | Fisika Dasar

(RINGKASAN) Materi Vektor | Fisika SMA Kelas 10
Vektor Matematika Kelas 10 : Konsep Dasar Vektor Matematika Peminatan Kelas 10 - Part 1

8.01x - Lect 3 - Vectors - Dot Products - Cross Products - 3D Kinematics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
