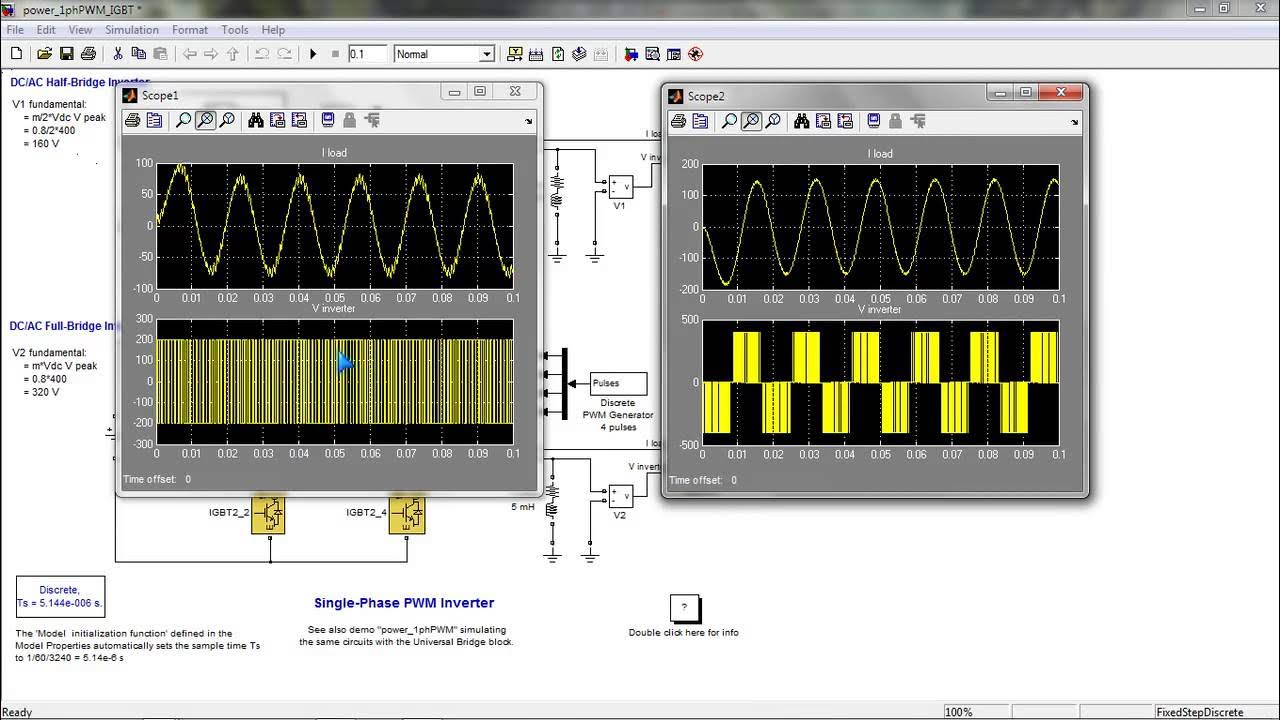
What is Pulse Width Modulation? How to generate PWM signal ? Pulse Width Modulation Explained
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the concept of Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is explained, showcasing its importance in controlling analog devices. PWM allows precise control of power delivered to devices like LEDs and motors by adjusting the pulse width. The video delves into how PWM works, using examples like LED dimming and motor speed control. Key parameters such as duty cycle and switching frequency are discussed, along with the advantages of using MOSFETs in PWM circuits. The video also explores PWM signal generation methods, including using comparators, 555 timers, and microcontrollers like Arduino.
Takeaways
- 😀 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is a technique used to control analog devices, offering high efficiency and low power loss.
- 😀 PWM allows precise control of power delivered to devices, making it ideal for applications like LED dimming and motor speed regulation.
- 😀 By adjusting the pulse width of a PWM signal, the average voltage applied to a device can be controlled, such as controlling LED brightness.
- 😀 PWM is used in modern electronics for more efficient power control, compared to traditional methods like variable resistors.
- 😀 The two main factors in PWM are the **switching frequency** (how fast the signal turns ON and OFF) and the **duty cycle** (the percentage of time the signal is ON).
- 😀 A higher switching frequency (e.g., 500 Hz) makes the ON/OFF switching imperceptible to the human eye, while a low frequency (e.g., 1 Hz) can cause visible flickering.
- 😀 Duty cycle changes the average voltage, thus controlling the power delivered to devices. A 50% duty cycle delivers half the voltage compared to a 100% duty cycle.
- 😀 MOSFETs are commonly used as switches in PWM circuits because they cause negligible power loss during switching, ensuring high efficiency.
- 😀 Compared to conventional methods like using resistors to control current, PWM ensures linear control of device performance, such as LED brightness.
- 😀 PWM signals can be generated using simple circuits like a comparator, 555 timer IC, or through microcontrollers like Arduino, making it versatile for different applications.
Q & A
What is Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)?
-Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is a technique used to control the power delivered to an analog device by adjusting the width of the pulse in a waveform, effectively controlling the voltage applied to the load.
Why is PWM preferred over conventional methods?
-PWM is preferred over conventional methods because of its high efficiency, low power loss, and ability to precisely control the power delivered to devices, making it ideal for applications like LED dimming and motor speed control.
How does PWM control the brightness of an LED?
-PWM controls the brightness of an LED by adjusting the width of the pulses in the control signal. A wider pulse means more voltage is applied, making the LED brighter, while a narrower pulse reduces the brightness.
What are the two main factors associated with PWM?
-The two main factors associated with PWM are switching frequency and duty cycle. The switching frequency determines how fast the pulse switches on and off, while the duty cycle represents the fraction of time the pulse remains on.
What is the role of the duty cycle in PWM?
-The duty cycle determines the fraction of time the pulse is on during each cycle. By adjusting the duty cycle, the average voltage delivered to the load can be controlled, affecting the brightness of LEDs or the speed of motors.
What happens if the switching frequency of PWM is too low?
-If the switching frequency is too low, such as 1Hz, the LED or motor may flicker, as the switching is not fast enough to appear continuous to the human eye or device.
How does a MOSFET benefit PWM applications?
-A MOSFET is commonly used in PWM applications because it dissipates negligible power during switching, making it highly efficient for controlling power without significant energy loss.
How does conventional LED brightness control differ from PWM?
-In conventional methods, LED brightness is controlled by adjusting the current through the LED using a resistor. However, this results in power dissipation across the resistor and non-linear brightness control, whereas PWM offers linear control of brightness by adjusting the pulse width.
What is a simple method to generate a PWM signal?
-A simple method to generate a PWM signal is using a comparator circuit, where a triangular waveform is compared with a control voltage to adjust the pulse width. Another method is using a 555 timer IC or a microcontroller like Arduino.
Why is PWM particularly useful in power electronics?
-PWM is particularly useful in power electronics due to its high efficiency, precise control of voltage and current, and minimal power loss during operation, making it ideal for applications like motor control and LED lighting.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)